10-K: Annual report pursuant to Section 13 and 15(d)
Published on February 18, 2021
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED: December 31 , 2020
OR
FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM TO
COMMISSION FILE NUMBER: 1-33796
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation of organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) | |||||||
| (Address of Principal Executive Offices) | (Zip Code) | |||||||
(888 ) 895-6557
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered | ||||||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days:
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and files).
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definition of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Emerging growth company ☐
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act.
o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management's assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report.
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
Yes ☐ No þ
At June 30, 2020, the aggregate market value of the voting stock held by non-affiliates of the Registrant was 2,192,560,401 based on the closing sale price on the New York Stock Exchange on that date.
The number of shares of the Registrant’s Common Stock outstanding on January 31, 2021 was 230,559,010 .
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION
FORM 10-K
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ITEM 1. |
||||||||
ITEM 1A. |
||||||||
ITEM 1B. |
||||||||
ITEM 2. |
||||||||
ITEM 3. |
||||||||
ITEM 4. |
||||||||
PART II |
||||||||
ITEM 5. |
||||||||
ITEM 6. |
||||||||
ITEM 7. |
||||||||
ITEM 7A. |
||||||||
ITEM 8. |
||||||||
ITEM 9. |
||||||||
ITEM 9A. |
||||||||
ITEM 9B. |
||||||||
PART III |
||||||||
ITEM 10. |
||||||||
ITEM 11. |
||||||||
ITEM 12. |
||||||||
ITEM 13. |
||||||||
ITEM 14. |
||||||||
PART IV |
||||||||
ITEM 15. |
||||||||
SIGNATURES |
||||||||
1
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
We make forward-looking statements in this report that are subject to risks and uncertainties. These forward-looking statements include information about, among other things, possible or assumed future results of our business, financial condition, liquidity, results of operations, plans and objectives. When we use the words ‘‘believe,’’ ‘‘expect,’’ ‘‘anticipate,’’ ‘‘estimate,’’ ‘‘plan,’’ ‘‘continue,’’ ‘‘intend,’’ ‘‘should,’’ ‘‘may,’’ ‘‘would,’’ ‘‘will’’ or similar expressions, we intend to identify forward-looking statements. Statements regarding the following subjects, among others, are forward-looking by their nature:
•our business and investment strategy;
•our ability to accurately forecast the payment of future dividends on our common and preferred stock, and the amount of such dividends;
•our ability to determine accurately the fair market value of our assets;
•availability of investment opportunities in real estate-related and other securities, including our valuation of potential opportunities that may arise as a result of current and future market dislocations;
•effect of the novel coronavirus (or COVID-19) pandemic on real estate market, financial markets and our Company, including the impact on the value, availability, financing and liquidity of mortgage assets;
•how COVID-19 may affect us, our operations and our personnel;
•our expected investments;
•changes in the value of our investments, including negative changes resulting in margin calls related to the financing of our assets;
•changes in interest rates and mortgage prepayment rates;
•prepayments of the mortgage and other loans underlying our mortgage-backed securities, or RMBS, or other asset-backed securities, or ABS;
•rates of default, delinquencies, forbearance, deferred payments or decreased recovery rates on our investments;
•general volatility of the securities markets in which we invest;
•our ability to maintain existing financing arrangements and our ability to obtain future financing arrangements;
•our ability to effect our strategy to securitize residential mortgage loans;
•interest rate mismatches between our investments and our borrowings used to finance such purchases;
•effects of interest rate caps on our adjustable-rate investments;
•the degree to which our hedging strategies may or may not protect us from interest rate volatility;
•the impact of and changes to various government programs, including in response to COVID-19;
•impact of and changes in governmental regulations, tax law and rates, accounting guidance, and similar matters;
•market trends in our industry, interest rates, the debt securities markets or the general economy;
•estimates relating to our ability to make distributions to our stockholders in the future;
•our understanding of our competition;
•our ability to find and retain qualified personnel;
•our ability to maintain our classification as a real estate investment trust, or, REIT, for U.S. federal income tax purposes;
•our ability to maintain our exemption from registration under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, or 1940 Act;
•our expectations regarding materiality or significance; and
•the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures.
Special Note Regarding COVID-19 pandemic
Because there have been no comparable recent global pandemics that resulted in similar impact, we do not yet know the full extent of COVID-19’s effects on our business, operations, personnel, or the U.S. economy as a whole. Any future developments in this regard will be highly uncertain and cannot be predicted with any certainty, including the scope and duration of the pandemic, the effectiveness of our work from home or remote work arrangements, third-party providers’ ability to support our operation, and any actions taken by governmental authorities and other third parties in response to the pandemic, and the other factors discussed above and throughout this Annual report on Form 10-K. The uncertain future development of this crisis could materially and adversely affect our business, operations, operating results, financial condition, liquidity or capital levels.
2
These forward-looking statements are based on our beliefs, assumptions and expectations of our future performance, taking into account all information currently available to us. You should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. These beliefs, assumptions and expectations can change as a result of many possible events or factors, not all of which are known to us. Some of these factors are described under the caption ‘‘Risk Factors’’ in this Form 10-K for our fiscal year ended December 31, 2020. If a change occurs, our business, financial condition, liquidity, results of operations and prospects may vary materially from those expressed in our forward-looking statements. Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it is made. New risks and uncertainties arise from time to time, and it is impossible for us to predict those events or how they may affect us. Except as required by law, we are not obligated to, and do not intend to, update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
3
In this Annual Report on Form 10-K, references to “we,” “us,” “our” or “the Company” refer to Chimera Investment Corporation and its subsidiaries unless specifically stated otherwise or the context otherwise indicates. The following defines certain of the commonly used terms in this Annual Report on Form 10-K: Agency refers to a federally chartered corporation, such as Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, or an agency of the U.S. Government, such as Ginnie Mae; MBS refers to mortgage-backed securities secured by pools of residential or commercial mortgage loans; RMBS refers to mortgage-backed securities secured by pools of residential mortgage loans; CMBS refers to mortgage-backed securities secured by pools of commercial mortgage loans; Agency RMBS and Agency CMBS refer to MBS that are secured by pools of residential and commercial mortgage loans, respectively, and are issued or guaranteed by an Agency; Agency MBS refers to MBS that are issued or guaranteed by an Agency and includes Agency RMBS and Agency CMBS collectively; Non-Agency RMBS refers to residential MBS that are not guaranteed by any agency of the U.S. Government or any Agency.
PART I
Item 1. Business
The Company
We are an internally managed real estate investment trust, or REIT, that is primarily engaged, through our subsidiaries, in the business of investing in a diversified portfolio of mortgage assets, including residential mortgage loans, Agency RMBS, Non-Agency RMBS, Agency CMBS, and other real estate-related assets. We were incorporated in Maryland on June 1, 2007 and commenced operations on November 21, 2007.
Our Investment Strategy
Our objective is to provide attractive risk-adjusted returns to our investors over the long-term, primarily through dividends. We intend to achieve this objective by investing in a diversified investment portfolio of residential mortgage loans, Agency RMBS, Non-Agency RMBS, Agency CMBS, real estate-related securities and various other real estate-related asset classes. The MBS, and other real estate-related securities we purchase may include investment-grade, non-investment grade, and non-rated classes. Subject to maintaining our REIT status and exemption from registration under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, or the 1940 Act, we do not have any limitations on the amounts we may invest in any of our targeted asset classes.
We make investment decisions based on various factors, including expected cash yield, relative value, risk-adjusted returns, credit fundamentals, macroeconomic considerations, supply and demand, credit and market risk concentration limits, liquidity, cost of financing and financing availability, as well as maintaining our REIT qualification and our exemption from registration under the 1940 Act. Our primary source of income is net interest income from our investment portfolio. Net interest income is the interest income we earn on investments less the interest expense we incur on borrowed funds.
Our investment strategy is intended to take advantage of opportunities in the current interest rate and credit environment. We expect to adjust our strategy to changing market conditions by shifting our asset allocations across these various asset classes as interest rate and credit cycles change over time. We believe that our strategy will enable us to pay dividends throughout changing market cycles.
We use leverage to seek to increase our potential returns and to finance the acquisition of our assets. Our income is generated primarily by the difference, or net spread, between the income we earn on our assets and the cost of our borrowings. We expect to finance our investments using a variety of financing sources, including securitizations, warehouse facilities and repurchase agreements. We seek to manage our debt and interest rate risk by utilizing interest rate hedges, such as interest rate swaps, caps, options and futures to reduce the effect of interest rate fluctuations related to our financing sources.
Currently, we focus our investment activities primarily on acquiring and securitizing pools of residential mortgage loans and, when we believe market or other conditions are favorable, exercising call options on existing securitizations to acquire the underlying mortgage loans and use additional securitization to re-finance those called mortgage loans at lower rates and/or more
4
efficient leverage. When we securitize mortgage loans, we typically retain the most subordinate classes of securities, which means we are the first-loss security holder. Losses on any residential mortgage loan securing our RMBS will be borne first by the owner of the property (i.e., the owner will first lose any equity invested in the property) and, thereafter, by us as the first-loss security holder, and then by holders of more senior securities. In addition, most of these subordinate securities are subject to the Dodd-Frank Act and related laws and regulations relating to credit risk retention for securitizations, or the Risk Retention Rules, which significantly limits the liquidity of these securities. See “ Risk Factors - Risks Associated with Our Investments - A significant portion of the RMBS we acquire through securitization is subject to the U.S. credit risk retention rules which materially limit our ability to sell or hedge such investments as needed” discussion in Item 1A “Risk Factors” section for more details. We generally finance these subordinate securities with secured financing agreements. The securities we do not retain are typically sold through securities underwriters. Other than the Risk Retention Rules, there is no limit on the amount we may retain of these below-investment-grade subordinate certificates. As discussed below, our use of leverage with respect to the retained securities from the securitizations we sponsored declined during 2020 and we entered into several non-mark-to-market facilities to finance these retained securities.
In addition, we have purchased residential transition loans, also referred to as fix and flip loans. We believe these residential transition loans have strengthened our portfolio in 2020 because they are short duration assets and have a high average coupon, which are good asset traits in times of rate volatility. Currently, we do not use term securitization to finance residential transition loans because of their short duration. We currently finance these loans using repurchase facilities, but we may look to finance these loans with revolving securitization structures in the future.
Our Securitization Programs
We currently have the following four securitization programs: Our “J” program securitizes jumbo prime residential mortgage loans; Our “INV” program securitizes Agency-eligible investor mortgage loans; Our “NR” program securitizes seasoned residential mortgage loans that are not eligible to be securitized in REMIC transactions; and Our “R” program, our most active program, securitizes seasoned reperforming mortgage loans, whether newly acquired from a third party or upon the exercise of a call option, in a REMIC transaction.
“J” and “INV” Rated Programs. The securities issued in our “J” and “INV” securitizations are rated by one or more nationally recognized statistical ratings organizations (“NRSRO”). The loans for our “J” program are “qualified mortgage loans” and therefore the related securitizations are not subject to the Risk Retention Rules, and we typically do not retain any securities related to this program. Our “INV” securitizations are subject to the Risk Retention Rules and we retain subordinate securities to meet our risk retention obligations. Under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”) we do not consolidate the assets and liabilities of the securitization entities related to our “J” and “INV” securitization programs. During 2020, we sponsored two “J” securitizations and one “INV” securitization. The table below sets forth certain information about our “J” and “INV” securitization that were outstanding at December 31, 2020, including two earlier jumbo prime securitizations that are consolidated for financial reporting purposes.
DEAL (1)
|
TOTAL ORIGINAL FACE |
ORIGINAL FACE OF TRANCHES SOLD (2)
|
ORIGINAL FACE OF TRANCHES RETAINED (2)
|
TOTAL REMAINING FACE | REMAINING FACE OF TRANCHES SOLD | REMAINING FACE OF TRANCHES RETAINED | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-J1 | $ | 361,766 | $ | 361,766 | $ | — | $ | 276,918 | $ | 276,918 | $ | — | |||||||||||
| CIM 2020-J2 | 327,362 | 327,362 | — | 327,362 | 327,362 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-INV1 | 335,065 | 311,107 | 23,958 | 298,796 | 274,943 | 23,853 | |||||||||||||||||
(1) For certain of the above securitization deals, we retained certain IO and/or excess servicing classes.
(2) At the time of issuance.
“R” and “NR” Non-Rated Programs. The securities issued in our “R” and “NR” securitizations are generally not rated and are subject to the Risk Retention Rules. In these programs, we typically sell the senior securities to an unrelated third party and retain the subordinate securities, which include the first-loss securities which are subject to the Risk Retention Rules, and the interest-only securities. During 2020, we sponsored seven “R” securitizations and one “NR” securitization. We are generally
5
required under GAAP to consolidate the assets and liabilities of the “NR” and “R” securitization entities for financial reporting purposes. Each of the consolidated entities is independent of Chimera and of each other, and the assets and liabilities of these entities are not owned by us or legal obligations of ours, respectively, although we are exposed to certain financial risks associated with any role we carry out for these entities (e.g., as sponsor or depositor) and, to the extent we hold securities issued by, or other investments in, these entities, we are exposed to the performance of these entities and the assets they hold.
DEAL (1)
|
TOTAL ORIGINAL FACE |
ORIGINAL FACE OF TRANCHES SOLD (2)
|
ORIGINAL FACE OF TRANCHES RETAINED (2)
|
TOTAL REMAINING FACE | REMAINING FACE OF TRANCHES SOLD | REMAINING FACE OF TRANCHES RETAINED | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-NR1 | $ | 131,860 | $ | 84,165 | $ | 47,695 | $ | 130,664 | $ | 83,097 | $ | 47,567 | |||||||||||
| CIM 2020-R7 | 653,192 | 562,023 | 91,169 | 642,978 | 551,805 | 91,173 | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-R6 | 418,390 | 334,151 | 84,239 | 408,175 | 323,886 | 84,289 | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-R5 | 338,416 | 257,027 | 81,389 | 305,646 | 224,025 | 81,621 | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-R4 | 276,316 | 207,237 | 69,079 | 264,556 | 195,372 | 69,184 | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-R3 | 438,228 | 328,670 | 109,558 | 404,607 | 294,967 | 109,640 | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-R2 | 492,347 | 351,926 | 140,421 | 450,379 | 375,590 | 74,789 | |||||||||||||||||
| CIM 2020-R1 | 390,761 | 317,608 | 73,153 | 366,552 | 293,766 | 72,786 | |||||||||||||||||
(1) For certain of the above securitization deals, we retained certain IO and/or excess servicing classes.
(2) At the time of issuance.
Our Investment Portfolio
At December 31, 2020, based on the amortized cost balance of our interest earning assets, approximately 79% of our investment portfolio was residential mortgage loans, 10% of our investment portfolio was Agency CMBS, 10% of our investment portfolio was Non-Agency RMBS and 1% of our investment portfolio was Agency IOs. At December 31, 2019, based on the amortized cost balance of our interest earning assets, approximately 55% of our investment portfolio was residential mortgage loans, 26% of our investment portfolio was Agency RMBS, 11% of our investment portfolio was Agency CMBS, and 8% of our investment portfolio was Non-Agency RMBS.
As discussed in “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” the significant change in the composition of our assets during 2020 relates primarily to the sale of our Agency RMBS portfolio during the first quarter of 2020, as we sought to raise liquidity and reduce our exposure to mark-to-market financing during the severe market conditions created by the novel coronavirus (“COVID-19”) pandemic. Subject to market conditions, we expect our primary investment focus to continue to be on residential mortgage loans in the near term.
The following briefly discusses the principal types of investments that we have made and may in the future make:
Residential Mortgage Loans
We invest in residential mortgage loans (mortgage loans secured by residential real property) through secondary market purchases from banks, non-bank financial institutions, and the Agencies. These mortgage loans are secured primarily by residential properties in the United States.
We acquire residential mortgage loans primarily to securitize them, as discussed above, or to retain them in our portfolio as loans held for investment. Until we securitize our residential mortgage loans, we finance our residential mortgage loan portfolio through warehouse facilities and repurchase agreement, as discussed under “Our Financing Strategy” below.
We currently do not intend to establish a loan origination or loan servicing platform. Currently, we acquire mortgage loans in the secondary market that are originated by third parties and are not underwritten to our specifications. Third-party servicers service the mortgage loans in our portfolio. We conduct a due diligence review of each servicer before the servicer is retained and periodically thereafter. Servicing procedures typically follow Fannie Mae guidelines but are specified in each servicing
6
agreement. In addition, we have purchased residential mortgage loans on a servicing-retained basis, which means a third-party servicer (which may or may not be the seller of the mortgage loans) retained the right to service the loans. In the future, however, we may decide to originate mortgage loans or other types of financing, and we may elect to service mortgage loans and other types of assets.
We engage a third party to perform an independent review of the mortgage files to assess the origination and servicing of the mortgage loans as well as our ability to enforce the mortgages. We may not review all the loans in a pool, but rather select loans for diligence review utilizing random sampling based criteria such as property location, loan size, effective loan-to-value ratio, borrower’s credit score, delinquency status and other criteria we believe to be important indicators of credit risk. Additionally, we typically obtain representations and warranties with respect to the mortgage loans from each seller, including the origination and servicing of the mortgage loans as well as the enforceability of the lien on the related mortgaged properties. If any of the representations and warranties with respect to a mortgage loan we acquire are breached, the related seller may be obligated to repurchase the loan from us.
Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities
We invest in mortgage pass-through certificates issued or guaranteed by Ginnie Mae, Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac which are securities representing interests in “pools” of mortgage loans secured by residential real properties where payments of both interest and principal, plus pre-paid principal, on the securities are made monthly to holders of the security, in effect passing through monthly payments made by the individual borrowers on the mortgage loans that underlie the securities, net of fees paid to the issuer/guarantor and servicers of the securities. We may also invest in collateralized mortgage obligations, or CMOs, issued by the Agencies. CMOs consist of multiple classes of securities, with each class bearing different stated maturity dates. Monthly payments of principal, including prepayments, are first returned to investors holding the shortest maturity class; investors holding the longer maturity classes receive principal only after the first class has been retired. We refer to residential mortgage-backed securities issued or guaranteed by Ginnie Mae, Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac as Agency RMBS.
We also invest in investment grade, non-investment grade and non-rated Non-Agency RMBS. We evaluate certain credit characteristics of these types of securities and the underlying mortgage loans, including, but not limited to, loan balance distribution, geographic concentration, property type, occupancy, periodic and lifetime caps, weighted-average loan-to-value and weighted-average Fair Isaac Corporation, or FICO, score. Qualifying securities are then analyzed using base line expectations of expected prepayments and loss severities, the current state of the fixed-income market and the broader economy in general. Losses and prepayments are stressed simultaneously based on a credit risk-based model. Securities in this portfolio are monitored for variance from expected prepayments, severities, losses and cash flow. The due diligence process is particularly important and costly with respect to newly formed originators or issuers because there may be little or no information publicly available about these entities and investments. We may also invest in interest-only, or IO, Agency and Non-Agency RMBS. These IO RMBS represent the right to receive a specified proportion of the contractual interest flows of the collateral.
We have invested in and intend to continue to invest in Non-Agency RMBS which are typically certificates created by the securitization of a pool of mortgage loans that are collateralized by residential real estate properties. The respective bond class sizes are determined based on the review of the underlying collateral. The payments received from the underlying loans are used to make the payments on the RMBS. Based on the sequential payment priority, the risk of nonpayment for the investment grade RMBS is lower than the risk of nonpayment for the non-investment grade bonds. Accordingly, the investment grade class is typically sold at a lower yield compared to the non-investment grade or unrated classes which are sold at higher yields.
Agency CMBS
The Agency CMBS we acquire are Ginnie Mae Construction Loan Certificates, or CLCs, and the resulting project loan certificates, or PLCs, when the construction project is complete. Each CLC is backed by a single multifamily property or health care facility. The investor in the CLC is committed to fund the full amount of the project; however, actual funding occurs as construction progresses on the property. Before each construction advance is funded it is insured by the Federal Housing Administration, or the FHA, and issued by Ginnie Mae. The principal balance of the CLC increases as payments by the investor
7
fund each construction advance. Each Ginnie Mae approved mortgage originator must provide the agency with supporting documentation regarding advances and disbursements before each construction advance is issued by Ginnie Mae. We also review this documentation prior to funding each Ginnie Mae guaranteed advance. Upon completion of the construction project, the CLC is replaced with a PLC. Ginnie Mae guarantees the timely payment of principal and interest on each CLC and PLC. This obligation is backed by the full faith and credit of the United States.
As the holder of a CLC, we generally receive monthly payments of interest equal to a pro rata share of the interest payments on the underlying mortgage loan, less applicable servicing and guaranty fees. Ginnie Mae CLCs pay interest only during construction, and so there are no payments of principal. As a holder of a PLC, we generally receive monthly payments of principal and interest equal to the aggregate amount of the scheduled monthly principal and interest payments on the mortgage loans underlying that PLC, less applicable servicing and guaranty fees. In addition, such payments will include any prepayments and other unscheduled recoveries of principal of, and any prepayment penalties on, an underlying mortgage loan to the extent received by the Ginnie Mae Issuer during the month preceding the month of the payment. The mortgage loans underlying the PLCs generally contain a lock-out and prepayment penalty period of 10 years during which the related borrower must pay a prepayment penalty equal to a specified percentage of the principal amount of the mortgage loan in connection with voluntary and certain involuntary prepayments. Ginnie Mae does not guaranty the payment of prepayment penalties.
Other Real Estate-Related Assets
We may invest in commercial mortgage loans consisting of first or second lien loans secured by multifamily properties, which are residential rental properties consisting of five or more dwelling units, or by mixed residential or other commercial properties, retail properties, office properties or industrial properties. These loans may or may not conform to the Agency guidelines.
We may invest in non-Agency CMBS, which are secured by, or evidence ownership interests in, a single commercial mortgage loan or a pool of mortgage loans secured by commercial properties. These securities may be senior, subordinated, investment grade or non-investment grade.
We may invest in securities issued in various collateralized debt obligation, or CDO, offerings to gain exposure to bank loans, corporate bonds, asset-backed securities, or ABS, mortgages, RMBS, CMBS, and other instruments.
Investment Guidelines
We have adopted a set of investment guidelines that set out the asset classes, risk tolerance levels, diversification requirements and other criteria used to evaluate the merits of specific investments as well as the overall portfolio composition. Our investment committee periodically reviews our compliance with the investment guidelines. Our risk and audit committees of the Board of Directors also review our investment portfolio and related compliance with our investment policies and procedures and investment guidelines at regularly scheduled risk and audit committee meetings.
Our Board of Directors and our investment committee have adopted the following guidelines for our investments and borrowings:
•No investment shall be made that would cause us to fail to qualify as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes;
•No investment shall be made that would cause us to be regulated as an investment company under the 1940 Act;
•With the exception of real estate and housing, no single industry shall represent greater than 20% of the securities or aggregate risk exposure in our portfolio; and
•Investments in non-rated or deeply subordinated ABS or other securities that are non-qualifying assets for purposes of the 75% REIT asset test will be limited to an amount not to exceed 50% of our stockholders’ equity.
These investment guidelines may be changed from time to time by a majority of our Board of Directors without the approval of our stockholders.
8
Our Financing Strategy
We use leverage to increase potential returns to our stockholders. We are not required to maintain any specific debt-to-equity ratio as we believe the appropriate leverage for the particular assets we are financing depends on the credit quality and risk of those assets. At December 31, 2020 and 2019, our ratio of debt-to-equity was 3.6:1 and 5.5:1, respectively. For purposes of calculating this ratio, our equity is equal to the Total stockholders’ equity on our Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition, and our debt consists of securitized debt, warehouse facilities and repurchase agreements.
Subject to maintaining our qualification as a REIT, we may use a variety of sources to finance our investments, including the following primary sources:
•Securitization. A significant element of our financing strategy is to acquire residential mortgage loans for our portfolio with the intention of securitizing them. In our securitizations, we generally create subordinate certificates, providing a specified amount of credit enhancement, which we intend or are required under the Risk Retention Rules to retain in our portfolio. We have acquired and may in the future acquire Non-Agency RMBS for our portfolio with the intention of exercising the call rights and re-securitizing the underlying mortgage loans and retaining a portion of the re-securitized Non-Agency RMBS in our portfolio, typically the subordinate certificates.
•Warehouse Facilities. We have utilized and may in the future utilize credit facilities for capital needed to fund our assets. We seek to maintain formal relationships with multiple counterparties to maintain warehouse lines on favorable terms.
•Repurchase Agreements. We have financed certain of our assets through repurchase agreements. We anticipate that repurchase agreements will be one of the sources we will use to achieve our desired amount of leverage for our real estate assets. We seek to maintain formal relationships with many counterparties with the intent to obtain financing on the most favorable terms available while diversifying counterparty credit risk.
As a result of the negative impact COVID-19 had on the financial markets and thus the liquidity and market value of our assets beginning in March 2020, we significantly changed our financing strategy. In particular, in connection with the sale of our Agency RMBS portfolio at the onset of the COVID-19 related volatility, we reduced our Agency repurchase financing by $6 billion in the first quarter of 2020 and terminated all derivatives used for hedging interest rate risk across the entire portfolio (which had the effect of reducing our leverage and reliance on mark-to-market financing). Also, through loan securitizations we reduced our loan warehouse facilities to one non-mark-to-market facility for residential mortgage loans and one mark-to-market facility for residential fix-and-flip loans. We also entered into two non-mark-to-market facilities and one mark-to-market holiday facility (market value of the collateral must drop below a threshold before lender can issue a margin call) to finance a portion of our non-Agency RMBS, including risk retention securities. Finally, we took back a portion of securities held as collateral under repurchase facilities and did not finance the retained securities from some of our 2020 securitizations to further reduce our exposure to mark-to-market financing. We expect that as terms for repurchase facility financing improves, we will seek such financing, but we believe that non-mark-to-market facilities will continue to be a material portion of our financing strategy.
Our Interest Rate Hedging and Risk Management Strategy
From time to time, we use derivative financial instruments to hedge all or a portion of the interest rate risk associated with our borrowings. Under the U.S. federal income tax laws applicable to REITs, we generally enter certain transactions to hedge indebtedness that we incur, or plan to incur, to acquire or carry real estate assets.
We may engage in a variety of interest rate management techniques that seek to mitigate changes in interest rates or other potential influences on the values of our assets. Our interest rate management techniques may include:
•puts and calls on securities or indices of securities;
•Eurodollar futures contracts and options on such contracts;
•interest rate caps, swaps and swaptions;
•U.S. Treasury futures, forward contracts, other derivative contracts and options on U.S. Treasury securities; and
9
•other similar transactions.
We may attempt to reduce interest rate risks and to minimize exposure to interest rate fluctuations through match funded financing structures, when appropriate, whereby we seek (i) to match the maturities of our debt obligations with the maturities of our assets and (ii) to match the interest rates on our investments with similar debt directly or through interest rate swaps, caps or other financial instruments, or through a combination of these strategies. This helps us to minimize the risk that we have to refinance our liabilities before the maturities of our assets and to reduce the impact of changing interest rates on our earnings.
In connection with the sale of our Agency RMBS portfolio and termination of the related financing, we removed $4.7 billion notional amount of interest rate hedge positions related to such financing and reducing our hedge positions to zero. These changes were the result of changes in our portfolio composition rather than of a change to our hedging strategy.
Operational and Regulatory Structure
REIT Qualification
We have elected to be treated as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. In order to maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must comply with the requirements under federal tax law, including that we must distribute at least 90% of our annual REIT taxable income (subject to certain adjustments) to our stockholders. As a REIT, we generally are not subject to U.S. federal income tax on our taxable income that is distributed to our stockholders. To ensure we qualify as a REIT, no person may own more than 9.8%, in value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our capital stock, which includes our common stock and preferred stock, unless our Board of Directors waives this limitation. As of December 31, 2020, we have granted waivers to two mutual funds to own a certain class of our preferred stock above the 9.8% limitation. Also, we have elected to treat certain of our subsidiaries as taxable REIT subsidiaries (or TRS). In general, a TRS may hold assets and engage in activities that a REIT or qualified REIT subsidiary (or QRS) cannot hold or engage in directly and generally may engage in any real estate or non-real estate related business. A TRS is subject to U.S. federal income tax.
1940 Act Exclusion
We continued to conduct our operations so that neither we nor any of our subsidiaries are required to register as an investment company under the 1940 Act. Section 3(a)(1)(A) of the 1940 Act defines an investment company as any issuer that is or holds itself out as being engaged primarily in the business of investing, reinvesting or trading in securities. Section 3(a)(1)(C) of the 1940 Act defines an investment company as any issuer that is engaged or proposes to engage in the business of investing, reinvesting, owning, holding or trading in securities and owns or proposes to acquire investment securities having a value exceeding 40% of the value of the issuer’s total assets (exclusive of U.S. Government securities and cash items) on an unconsolidated basis (the “40% test”). Excluded from the term “investment securities,” among other things, are U.S. Government securities and securities issued by majority owned subsidiaries that are not themselves investment companies and are not relying on the exclusion from the definition of investment company for private funds set forth in Section 3(c)(1) or Section 3(c)(7) of the 1940 Act.
If the value of securities issued by our subsidiaries that are excluded from the definition of “investment company” by Section 3(c)(1) or 3(c)(7) of the 1940 Act, together with any other investment securities we own, exceeds the 40% test under Section 3(a)(1)(C) of the 1940 Act, or if one or more of such subsidiaries fail to maintain an exclusion or exception from the 1940 Act, we could, among other things, be required either (a) to substantially change the manner in which we conduct our operations to avoid being required to register as an investment company or (b) to register as an investment company under the 1940 Act, either of which could have an adverse effect on us and the market price of our securities. If we were required to register as an investment company under the 1940 Act, we could, among other things, be required either to (a) change the manner in which we conduct our operations to avoid being required to register as an investment company, (b) effect sales of our assets in a manner that, or at a time when, we would not otherwise choose to do so, or (c) register as an investment company, any of which could negatively affect the value of our common stock, the sustainability of our business model, and our ability to make
10
distributions. See “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business—Maintenance of our 1940 Act exclusion imposes limits on our operations.”
Licenses
While we are not required to obtain licenses to purchase mortgage-backed securities, the purchase and sale of residential mortgage loans in the secondary market may, in some circumstances, require us to maintain various state licenses. Acquiring the right to service residential mortgage loans may also, in some circumstances, require us to maintain various state licenses even though we currently do not directly engage in loan servicing ourselves and do not expect to do so. Currently, we hold licenses or exemption status, through two of our wholly owned subsidiaries in 23 states. We are required to comply with various information reporting and other regulatory requirements to maintain those licenses and exemption status. Our failure to obtain or maintain required licenses or exemption status or our failure to comply with regulatory requirements that are applicable to our business of acquiring residential mortgage loans may restrict our business and investment options and could harm our business and expose us to penalties or other claims.
Human Capital
The human capital objectives we focus on in managing our business include attracting, developing, and retaining key personnel. Our employees are critical to the success of our organization and the Company is committed to supporting our employees’ professional development. We believe our management team has the experience necessary to effectively implement our growth strategy and continue to drive shareholder value. We provide competitive compensation and benefits to attract and retain key personnel, while also providing a safe, inclusive and respectful workplace. We continue to have a focus on diversity initiatives. The Company offers internal training programs on financial markets, business ethics, government regulatory rules and other topics. The Company encourages personnel to attend industry sponsored or other conferences, and has a tuition reimbursement program to help personnel to further develop their skills and to stay current on evolving trends impacting our industry.
We focus on attracting and retaining employees by providing compensation and benefits packages that are competitive within the applicable market, taking into account the job position’s location and responsibilities. We provide competitive financial benefits such as a 401(k) retirement plan with a company match and offer a comprehensive healthcare benefit plan and other tools to support our employees’ health and well-being. We also generally grant awards of restricted stock units on an annual basis to a meaningful portion of our employee. The Company has a matching gift program to encourage personnel to be charitable and to support 501(c)3 organizations.
At December 31, 2020, we had 41 employees, all of whom were full-time. We believe that our relationship with our employees is good. None of our employees are unionized or represented under a collective bargaining agreement.
Competition
Our net income depends, in large part, on our ability to acquire assets at favorable spreads over our borrowing costs. In acquiring real estate-related assets, we compete with other mortgage REITs, specialty finance companies, savings and loan associations, banks, mortgage bankers, insurance companies, mutual funds, institutional investors, investment banking firms, financial institutions, hedge funds, governmental bodies (including the U.S. Federal Reserve) and other entities. Many of our competitors are significantly larger than we are, have access to greater capital and other resources and may have other advantages over us. In addition, some of our competitors may have higher risk tolerances or different risk assessments, which could allow them to consider a wider variety of investments and establish more favorable relationships than we can. The existence of these entities, as well as the possibility of additional entities forming in the future, may increase the competition for the acquisition of residential mortgage assets, resulting in higher prices and lower yields on such assets.
Available Information
Our investor relations website is www.chimerareit.com. We make available on the website under “Filings & Reports,” free of charge, our annual report on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, our current reports on Form 8-K and any other reports that we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, (including any amendments to such reports) as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file or furnish such materials to the SEC. Information on our website, however,
11
is not part of or incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In addition, all our filed reports can be obtained at the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
You should carefully consider the following factors, together with all the other information included in this 2020 Form 10-K, in evaluating our company and our business. If any of the following risks actually occur, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected, and the value of our stock could decline. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial also may impair our business operations. As such, you should not consider this list to be a complete statement of all potential risks or uncertainties.
Summary Risk Factors
Risks Associated with Our Investments
•The recent outbreak of the novel coronavirus has adversely affected, and will likely continue to adversely affect, our business, financial condition, liquidity and results of operations.
•We cannot predict the effect that government policies, laws and plans adopted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and the global recessionary economic conditions will have on us.
•The nature of the mortgage loans we acquire and that underlie the MBS we acquire, exposes us to credit risk that could negatively affect the value of those assets and investments.
•A significant portion of our investments are in Non-Agency RMBS that are the most subordinate securities in securitizations, making us the first-loss security holder, which means these securities are subject to significant credit risk, are illiquid, and are difficult to value.
•A significant portion of the RMBS we acquire through securitization is subject to the U.S. credit risk retention rules which materially limit our ability to sell or hedge such investments as needed, which may require us to hold investments that we may otherwise desire to sell during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
•We have a significant amount of investments in Non-Agency MBS collateralized by mortgage loans that do not meet the prime loan underwriting standards and are subject to increased risk of losses (particularly during periods of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic).
•We have, and may continue to, experience significant changes in our portfolio during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those being experienced now as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
•COVID-19 has created an uncertain and volatile interest rate environment, which could adversely affect our business.
•Changes in prepayment rates could negatively affect the value of our investment portfolio, which could result in reduced earnings or losses and negatively affect the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
•New assets we acquire may not generate yields as attractive as yields on our current assets, which could result in a decline in our earnings per share over time.
•We may change our investment strategy, asset allocation, or financing plans without stockholder consent, which may result in riskier investments.
•Changes in the fair values of our assets, liabilities, and derivatives can have various negative effects on us, including reduced earnings, increased earnings volatility, and volatility in our book value.
•Our calculations of the fair value of the assets we own or consolidate are based upon assumptions that are inherently subjective and involve a high degree of management judgment, and such assumptions may be more difficult to calculate during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Risks Related to Financing and Hedging
•Our business strategy involves the use of leverage, and we may not achieve what we believe to be optimal levels of leverage or we may become overleveraged, which may materially adversely affect our liquidity, results of operations or financial condition.
12
•Our inability to access funding or the terms on which such funding is available could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, particularly during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Risks Associated with Our Operations
•Through certain of our wholly-owned subsidiaries we have engaged in the past, and expect to continue to engage in, securitization transactions relating to residential mortgage loans. These types of transactions and investments expose us to potentially material risks.
•We rely on third parties to perform certain services particularly as it relates to servicing, comply with applicable laws and regulations, and carry out contractual covenants and terms, the failure of which by any of these third parties may adversely impact our business and financial results.
•We utilize third party analytical models and data to value our investments, and any incorrect, misleading or incomplete information used in connection therewith would subject us to potential risks.
•The third party analytical models and data we use to value our investments may be more prone to inaccuracies in light of the unprecedented conditions created by COVID-19.
•We are dependent on information systems and their failure could significantly disrupt our business.
Risks Related to Regulatory Matters, Accounting, and Our 1940 Act Exemption
•Our business is subject to extensive regulation.
•We are required to obtain various state licenses to purchase mortgage loans in the secondary market and there is no assurance we will be able to obtain or maintain those licenses.
•Our GAAP financial results may not be an accurate indicator of taxable income and dividend distributions.
•Loss of our 1940 Act exemption would adversely affect us and negatively affect the market price of shares of our capital stock and our ability to distribute dividends.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Risks
•Your investment has various U.S. federal income tax risks.
•Complying with REIT requirements may cause us to forego otherwise attractive opportunities.
•Complying with REIT requirements may force us to liquidate otherwise attractive investments.
•Complying with REIT requirements may limit our ability to hedge effectively.
•Failure to qualify as a REIT would subject us to U.S. federal income tax, which would reduce the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
Risks Related to Our Capital Stock
•Capital stock eligible for future sale may have adverse consequences for investors and adverse effects on our share price.
•Future offerings of debt securities, which would rank senior to our capital stock upon liquidation, and future offerings of equity securities (including upon the exercise of warrants we have issued to certain lenders), which would dilute our existing stockholders and may be senior to our capital stock for the purposes of dividend and liquidating distributions, may adversely affect the market price of our capital stock.
•There is a risk that you may not receive dividend distributions, or those dividend distributions may decrease over time. Changes in the amount of dividend distributions we pay or in the tax characterization of dividend distributions we pay may adversely affect the market price of our common stock or may result in holders of our common stock being taxed on dividend distributions at a higher rate than initially expected.
13
Risks Associated with Our Investments
The recent outbreak of the novel coronavirus (“COVID-19”) has adversely affected, and could continue to adversely affect, our business, financial condition, liquidity and results of operations.
We believe the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic has negatively affected our business and could continue to do so. The outbreak has caused significant volatility and disruption in the financial markets both globally and in the United States. If COVID-19, or another highly infectious or contagious disease, continues to spread or the response (including any vaccines) to contain it is unsuccessful, we could experience material adverse effects on our business, financial condition, liquidity, and results of operations. The extent of such effects will depend on future developments which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted, including the geographic spread of the virus, the overall severity of the disease, the duration of the outbreak, the effectiveness of any vaccine, the measures that may be taken by various governmental authorities in response to the outbreak (such as quarantines and travel restrictions) and the possible further impacts on the global economy. The continued spread of COVID-19 and related health concerns could also negatively impact the availability of key personnel necessary to conduct our business.
Any significant decrease in economic activity or resulting decline in the housing market could have an adverse effect on our investments in mortgage loans, Non-Agency RMBS, Agency RMBS, Agency CMBS, and other real estate assets. In particular, COVID-19 and related economic impacts has adversely impacted the housing and related markets, including as related to availability of mortgage financing, the ability of buyers and sellers and others industry participants to conducts sales, and the overall decline in home values if economic conditions do not improve. In addition, as interest rates continue to decline as result of demand for U.S. Treasury securities and the activities of the Federal Reserve, prepayments on our assets are likely to increase due to refinancing activity, which could have a materially adverse effect on our result of operations.
Further, in light of the current environment related to the COVID-19 outbreak on the overall economy, such as rising unemployment levels or changes in consumer behavior related to loans as well as government policies and pronouncements, borrowers may experience difficulties meeting their obligations or seek to forebear payment on or refinance their loans for lower rates, which may adversely affect our result of operations (particularly as related to assets we own that expose us to credit risk, as discussed below). Thus, the credit risk profile of our assets may be more pronounced during severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those being experienced now as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
We cannot predict the effect that government policies, laws and plans adopted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and the global recessionary economic conditions will have on us.
Governments have adopted, and we expect will continue to adopt, policies, laws and plans intended to address the COVID-19 pandemic and adverse developments in the credit, financial and mortgage markets. While the U.S. Federal Reserve, the U.S. government and other governments have implemented unprecedented financial support or relief measures in response to concerns surrounding the economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, the likelihood of such measures calming the volatility in the financial markets or addressing a long-term national or global economic downturn cannot be predicted and we cannot assure you that these programs will be effective, sufficient or otherwise have a positive impact on our business.
On March 27, 2020, the CARES Act was signed into law. Among the provisions in this wide-ranging law are protections
for homeowners experiencing financial difficulties due to the COVID-19 pandemic, including forbearance provisions
and procedures. Borrowers with federally backed mortgage loans, regardless of delinquency status, may request loan
forbearance for a six-month period, which could be extended for another six-month period if necessary. Federally
backed mortgage loans are loans secured by first- or subordinate-liens on 1-4 family residential real property,
including individual units of condominiums and cooperatives, which are insured or guaranteed pursuant to certain
government housing programs, such as by the FHA or U.S. Department of Agriculture, or are purchased or securitized
by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac. The CARES Act also includes a temporary 60 day foreclosure moratorium that applies
to federally backed mortgage loans, which lasted until July 24, 2020 and was extended to December 31, 2020 by Fannie
Mae, FHA and the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Some states and local jurisdictions have also implemented
moratoriums on foreclosures.
14
Moreover, certain actions taken by U.S. or other governmental authorities, including the Federal Reserve, that are intended to ameliorate the social and macroeconomic effects of COVID-19 may harm our business. For example, decreases in short-term interest rates, such as those announced by the Federal Reserve during 2020, including in response to COVID-19, may have a negative impact on our results, as we have certain assets and liabilities which are sensitive to changes in interest rates. We expect interest rates to remain low for the foreseeable future. These market interest rate declines may negatively affect our results of operations.
A significant portion of our investments are in Non-Agency RMBS that are the most subordinate securities in securitizations, making us the first-loss security holder, which means these securities are subject to significant credit risk, are illiquid, and are difficult to value.
A significant portion of our Non-Agency RMBS are subordinate classes we have acquired through securitization of mortgage loans. The mortgage loans we have securitized are generally recorded on our balance sheet as “securitized mortgage loans” for GAAP purposes, but in effect we own these assets in the form of securities. A substantial portion of the mortgage loans that we securitize and the subordinate securities that we retain are not newly originated “prime mortgage loans” but rather seasoned reperforming mortgage loans and Non-QM loans that have less strict underwriting standards and are therefore subject to greater risk of loss, as discussed below.
When we securitize mortgage loans, we sell the most senior securities backed by those loans and retain the most subordinate classes of securities, which means we are the first-loss security holder and the securities we own represent a portion of the “securitized mortgage loans” on our balance sheet. Losses on any residential mortgage loan securing our RMBS will be borne first by the owner of the property (i.e., the owner will first lose any equity invested in the property) and, thereafter, by us as the first-loss security holder, and then by holders of more senior securities. If the losses incurred upon loan default exceed any reserve fund, letter of credit, and classes of securities junior to those we own (if any), we may not be able to recover our investment in such securities. Also, if the underlying properties have been overvalued by the originating appraiser or if the values subsequently decline resulting in less collateral available to satisfy interest and principal payments due on the related security, as the first-loss security holder, we may suffer a total loss of principal, followed by losses on the more senior securities (or other RMBS that we may own). Losses with respect to these investments, which are subject to significant credit risk, could increase or otherwise be higher than anticipated. For a description of the credit risk we are exposed to, see the Risk Factor below captioned “The nature of the mortgage loans we acquire and that underlie the MBS we acquire, exposes us to credit risk that could negatively affect the value of those assets and investments.” As discussed in the Risk Factors above, credit risks associated with our investments are heightened during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those being experienced now as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In addition, many of our Non-Agency RMBS securities are first loss and subject to the Risk Retention Rules (see the Risk Factor directly below regarding the Risk Retention Rules) and are therefore illiquid for a period of time. The fair value of securities, especially our first loss credit risk retention securities, reperforming mortgage loans (loans that typically were significantly delinquent and subsequently modified), and other investments we make that are not frequently traded may not be readily determinable and it may be difficult to obtain third party pricing on such investments, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic which saw a significant increase in liquidation sales and few secondary market trades. Also, validating third party pricing for illiquid investments may be more subjective than more liquid investments and may not be reliable. Illiquid investments may also experience greater price volatility because an active market does not exist. We value our investments quarterly based on our judgment and in accordance with our valuation policy. Because such valuations are inherently uncertain, our fair value determination may differ materially from the values obtained from third parties or the values that would have been used, if an active trading market existed for these investments. Our results of operations, financial condition and business could be materially adversely affected if our fair value determinations of the investments were materially higher than the values that would exist if a ready market existed for these assets.
The illiquidity of our investments may make it difficult, or impossible for certain assets subject to the Risk Retention Rules, for us to sell and these assets may be more difficult to finance. Also, if we quickly liquidate all or a portion of our portfolio (for example, to meet a margin call, as we did with the sale of our entire Agency RMBS portfolio at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic), we may realize significantly less than the value at which we have previously recorded our investments. Thus, our ability to adjust our portfolio in response to changes in economic, and other conditions may be relatively limited, which could adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition and the value of our capital stock. This risk may be more
15
pronounced during any severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A significant portion of the RMBS we acquire through securitization is subject to the U.S. credit risk retention rules which materially limit our ability to sell or hedge such investments as needed, which may require us to hold investments that we may otherwise desire to sell during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A significant part of our business and growth strategy is to engage in securitization transactions to finance the acquisition of residential mortgage loans. Pursuant to the Risk Retention Rules, when we sponsor a residential mortgage loan securitization, we are required to retain at least 5% of the fair value of the mortgage-backed securities issued in the securitization. We can retain either an “eligible vertical interest” (which consists of at least 5% of each class of securities issued in the securitization), an “eligible horizontal residual interest” (which is the most subordinate class of securities with a fair market value of at least 5% of the aggregate credit risk) or a combination of both totaling 5%, or the Required Credit Risk. We typically own the eligible horizontal residual interest. We are required to hold the Required Credit Risk until the later of (i) the fifth anniversary of the securitization closing date and (ii) the date on which the aggregate unpaid principal balance of the mortgage loans in such securitization has been reduced to 25% of the aggregate unpaid principal balance of the mortgage loans as of the securitization closing date, but no longer than the seventh anniversary of the closing date (such date, the Sunset Date). In addition, before the Sunset Date, we may not engage in any hedging transactions if payments on the hedge instrument are materially related to the Required Credit Risk and the hedge position would limit our financial exposure to the Required Credit Risk. Also, we may not pledge our interest in any Required Credit Risk as collateral for any financing unless such financing is full recourse to us. We have financed our Required Credit Risk in full recourse transactions. Our Required Credit Risk subjects us to the first losses on our securitizations and is illiquid which may make it more difficult to meet our liquidity needs, each of which may materially and adversely affect our business and financing condition. Thus, the Risk Retention Rules materially limit our ability to sell and hedge a portion of our RMBS that we acquire through our securitizations and subjects us to the credit risk related to the retained RMBS that we otherwise may have sold. This risk may be more pronounced during any severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
We have a significant amount of investments in Non-Agency MBS collateralized by mortgage loans that do not meet the prime loan underwriting standards and are subject to increased risk of losses (particularly during periods of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic).
A significant portion of the Non-Agency MBS we have acquired on the secondary market or retained in our securitizations are backed by collateral pools containing mortgage loans that were originated using underwriting standards that were less strict than those used in underwriting “prime mortgage loans.” These lower standards permitted mortgage loans, often with LTV ratios exceeding 80%, to be made to borrowers having impaired credit histories, lower credit scores, higher debt-to-income ratios or unverified income. Such mortgage loans are likely to experience delinquency, foreclosure, bankruptcy, and other losses at rates that are higher, may be substantially higher, than those experienced by prime mortgage loans. Thus, the performance of our Non-Agency MBS that are backed by these types of loans could be correspondingly lower than those backed by prime mortgage loans especially during times of economic stress, which could materially adversely impact our results of operations, financial condition, and business. This risk is more pronounced during periods of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The nature of the mortgage loans we acquire and that underlie the MBS we acquire, exposes us to credit risk that could negatively affect the value of those assets and investments.
We assume credit risk primarily through the ownership of securities backed by residential, multi-family, and commercial real estate loans and through direct investments in residential real estate loans. The substantial majority of our investment assets are subject to various credit risks, as discussed below.
16
No U.S. Government Guarantee. We acquire residential loans including reperforming loans, nonperforming loans (the borrower is severely delinquent), and Non-QMs, which are subject to increased risk of loss. Unlike Agency RMBS, residential mortgage loans generally are not guaranteed by the U.S. Government or any government-sponsored enterprise such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Additionally, by directly acquiring residential loans, we do not receive the structural credit enhancements that benefit senior tranches of RMBS. A residential loan is directly exposed to losses resulting from the default. Therefore, the value of the underlying property, the creditworthiness and financial position of the borrower, and the priority and enforceability of the lien will significantly impact the value of such mortgage loan. In the event of a foreclosure, we may assume direct ownership of the underlying real estate. The liquidation proceeds upon sale of such real estate may not be sufficient to recover our cost basis in the loan, and any costs or delays involved in the foreclosure or liquidation process may increase losses. The value of residential loans is also subject to property damage caused by hazards, such as earthquakes or environmental hazards, not covered by standard property insurance policies and to a reduction in a borrower's mortgage debt by a bankruptcy court. In addition, claims may be assessed against us because of our position as a mortgage holder or property owner, including assignee liability, environmental hazards, and other liabilities. We could also be responsible for property taxes. In some cases, these claims may lead to losses exceeding the purchase price of the related mortgage or property. The occurrence of any of these risks could materially adversely impact our results of operations, financial condition, and business.
Enhanced Non-QM Loan Risks. In addition, we may from time to time acquire Non-QMs that will not have the benefit of enhanced legal protections otherwise available to residential mortgage loans originated to a more restrictive credit standard than just determining a borrower’s ability to repay. The ownership of Non-QMs will subject us to legal, regulatory and other risks, including those arising under federal consumer protection laws and regulations designed to regulate residential mortgage loan underwriting and originators’ lending processes, standards, and disclosures to borrowers. Failure of residential mortgage loan originators or servicers to comply with the ability-to-repay laws and regulations could subject us, as an assignee or purchaser of these loans (or as an investor in securities backed by these loans), to monetary penalties assessed by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, or CFPB, through its administrative enforcement authority and by mortgagors through a private right of action against lenders or as a defense to foreclosure, including by recoupment or setoff of finance charges and fees collected, and could result in rescission of the affected residential mortgage loans, which could adversely impact our business and financial results.
Greater General Credit Risks. In addition, credit losses on residential real estate loans can occur for many reasons (many of which are beyond our control), including: fraud; poor underwriting; poor servicing practices; weak economic conditions; increases in payments required to be made by borrowers; declines in the value of homes; earthquakes, the effects of climate change (including flooding, drought, wildfire and severe weather), and other natural disaster events; uninsured property loss; borrower over-leveraging; costs of remediation of environmental conditions, such as indoor mold; changes in zoning or building codes and the related costs of compliance; acts of war or terrorism; pandemics; changes in legal protections for borrowers and other changes in law or regulation; and personal events affecting borrowers, such as reduction in income and job loss. These and other credit-related risks have increased by the conditions created by the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, the amount and timing of credit losses could be affected by loan modifications, delays in the liquidation process, documentation errors, and other action by servicers. Weakness in the U.S. economy or the housing market could cause our credit losses to increase beyond levels that we currently anticipate.
Changes in prepayment rates could negatively affect the value of our investment portfolio, which could result in reduced earnings or losses and negatively affect the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
There are seldom any restrictions on borrowers’ abilities to prepay their residential mortgage loans. Homeowners tend to prepay mortgage loans faster when interest rates decline. Consequently, owners of the loans have to reinvest the money received from the prepayments at the lower prevailing interest rates. Conversely, homeowners tend not to prepay mortgage loans when interest rates increase. Consequently, owners of the loans are unable to reinvest money that would have otherwise been received from prepayments at the higher prevailing interest rates. A significant portion of the loans underlying our RMBS was originated before the 2008 financial crisis and possess higher than current prevailing interest rates. Accordingly, we may experience higher prepayment rates even in a rising interest rate environment due to the strong economy and origination profiles of the loans underlying our RMBS.
17
Volatility in prepayment rates may affect our ability to maintain targeted amounts of leverage and return on our portfolio of residential mortgage loans and RMBS and may result in reduced earnings or losses for us and negatively affect the cash available for distribution to our stockholders. In addition, if we purchased an investment at a premium, faster than expected prepayments will result in a faster than expected amortization of the premium paid, which would adversely affect our earnings. Conversely, if these investments were purchased at a discount, faster than expected prepayments accelerate our recognition of income. Increased prepayments also increase our reinvestment risk as we look to replace those assets with new investments. See below “New assets we acquire may not generate yields as attractive as yields on our current assets, which could result in a decline in our earnings per share over time” for details.
New assets we acquire may not generate yields as attractive as yields on our current assets, which could result in a decline in our earnings per share over time.
We expect that the assets we acquire or invest in may not generate the economic returns and GAAP yields of our existing portfolio. A significant portion of our securitized residential mortgage loans was originated before the 2008 financial crisis and have mortgage interest rates exceeding mortgage interest rates currently available to newly originated residential mortgage loans. In addition, after the 2008 financial crisis, we acquired residential mortgage-backed securities at a significant discount and re-securitized them, retaining high-yielding subordinate securities.
To maintain our portfolio size and our earnings, we must reinvest in new assets a portion of the cash flows we receive from principal, interest, and loan sales. However, prepayments, defaults, and loan amortization have reduced the supply of these pre-crisis assets. Also, investors seeking higher-yielding assets have created a significant demand for the remaining assets which may make it difficult for us to acquire such assets and reducing the return on assets we do acquire. Accordingly, realized cash flow from new investments could be significantly lower than expected and returns from new investments and acquisitions could be negative. We may also sell assets from time to time as part of our portfolio and capital management strategies. Principal payments, calls, and sales reduce the size of our current portfolio and generate cash for us. If the assets we invest in or acquire in the future earn lower GAAP yields than do the assets we currently own, our reported earnings per share could decline over time as the older assets are paid down or are sold, assuming comparable expenses, credit costs, and market valuation adjustments.
A significant portion of our Non-Agency MBS and residential loans are secured by properties in a small number of geographic areas and may be disproportionately affected by economic or housing downturns, natural disasters, terrorist events, regulatory changes, or other adverse events specific to those markets.
A significant number of the mortgages underlying our Non-Agency MBS and Loans held for investments are concentrated in certain geographic areas. For example, we have significant exposure in California, New York and Florida. For further information on the geographic concentration of our investments see Note 3 and Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements within this 2020 Form 10-K. Certain markets within these states (particularly in California and Florida) have experienced significant decreases in residential home values from time to time. Any event that adversely affects the economy or real estate market in any of these states could have a disproportionately adverse effect on our Non-Agency MBS and Loans held for investments. In general, any material decline in the economy or significant problems in a particular real estate market would likely cause a decline in the value of residential properties securing the mortgages in that market, thereby increasing the risk of delinquency, default, and foreclosure of mortgage loans underlying our Non-Agency MBS and residential loan investments and the risk of loss upon liquidation of these assets. Investors should consider the impact that the recession resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic will have on the mortgage market and ability of mortgagors to make timely payments on their mortgage loans. Furthermore, the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic may result in a decline in real estate values (particularly in certain geographic areas). This could have a material adverse effect on our Non-Agency MBS credit loss experience and residential loan investments in the affected market if higher-than-expected rates of default or higher-than-expected loss severities on such loans were to occur.
In addition, the occurrence of a natural disaster or a terrorist attack may cause a sudden decrease in the value of real estate in the area or areas affected and would likely reduce the value of the properties securing the mortgages collateralizing our Non-Agency MBS or Loans held for investments. Because certain natural disasters such as hurricanes or certain flooding are not
18
typically covered by the standard hazard insurance policies maintained by borrowers, or the proceeds payable under any such policy are not sufficient to cover the related repairs, the affected borrowers may have to pay for any repairs themselves. Under these circumstances, borrowers may decide not to repair their property or may stop paying their mortgages. This would cause defaults and credit loss severities to increase.
Changes in local laws and regulations, fiscal policies, property taxes and zoning ordinances in such states can also have a negative impact on property values, which could result in borrowers’ deciding to stop paying their mortgages. This circumstance could cause defaults and loss severities to increase, thereby adversely impacting our results of operations.
We may change our investment strategy, asset allocation, or financing plans without stockholder consent, which may result in riskier investments.
We may change our investment strategy, asset allocation, or financing plans at any time without the consent of our stockholders, which could result in our making investments that are different from, and possibly riskier than, the investments described in this 2020 Form 10-K. For example, during 2020 and in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, we sold our entire Agency RMBS portfolio and became more concentrated in credit-risk assets, and have also balanced our repurchase agreement financing with more non-market-to-market facilities.
A change in our investment strategy or financing plans may increase our exposure to interest rate and default risk and real estate market fluctuations. Furthermore, a change in our asset allocation could result in our making investments in asset categories different from those described in this 2020 Form 10-K. Additionally, we may enter other operating businesses that may or may not be closely related to our current business. These new assets or business operations may have new, different or increased risks than what we are currently exposed to in our business and we may not be able to manage these risks successfully. Additionally, when investing in new assets or businesses we will be exposed to the risk that those assets, or income generated by those assets or businesses, will affect our ability to meet the requirements to maintain our qualification as a REIT or our exemption from registration under the 1940 Act. If we are not able to successfully manage the risks associated with new asset types or businesses, it could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Interest rate fluctuations may have various negative effects on us and may lead to reduced earnings and increased volatility in our earnings.
Changes in interest rates, the interrelationships between various interest rates, and interest rate volatility may have negative effects on our earnings, the fair value of our assets and liabilities, loan prepayment rates, and our access to liquidity. Changes in interest rates may harm the credit performance of our assets. We generally seek to hedge some but not all interest rate risks. Our hedging may not work effectively, and we may change our hedging strategies or the degree or type of interest rate risk we assume.
Some of the loans and securities we own or may acquire have adjustable-rate coupons (i.e., they may earn interest at a rate that adjusts periodically based on an interest rate index) and some of the subordinate securities we own are entitled to cash flow only after the more senior securities have been paid and those senior securities have adjustable-rate coupons. As such, the cash flows, and earnings, we receive from these assets may vary as a function of interest rates. For example, if interest rates increase, the cash flow we receive from securities with adjustable-rate coupons is expected to increase while the cash flow we receive on securities that are subordinate to adjustable-rate securities may decrease. We also acquire loans and securities for future sale, as assets we are accumulating for securitization, or as a longer-term investment. We expect to fund assets, loans, and securities with a combination of equity and debt. If we use adjustable rate debt to fund assets that have a fixed interest rate (or use fixed rate debt to fund assets that have an adjustable interest rate), an interest rate mismatch could exist and we could earn less (and fair values could decline) if interest rates rise, at least for a time. We may seek to mitigate interest rate mismatches for these assets with hedges such as swaps and other derivatives, which may not be successful.
Higher interest rates generally reduce the fair value of many of our assets and increase the cost of our financing. This may affect our earnings results, reduce our ability to securitize, re-securitize, or sell our assets, or reduce our liquidity. Higher interest rates could reduce borrowers’ ability to make interest payments or to refinance their loans. Higher interest rates could reduce
19
property values and increased credit losses could result. Higher interest rates could reduce mortgage originations, thus reducing our opportunities to acquire new assets. In addition, when short-term interest rates are high relative to long-term interest rates, an increase in adjustable-rate residential loan prepayments may occur, which would likely reduce our returns from owning interest-only securities backed by adjustable-rate residential loans.
Changes in the fair values of our assets, liabilities, and derivatives can have various negative effects on us, including reduced earnings, increased earnings volatility, and volatility in our book value.
Fair values for our assets and liabilities, including derivatives, can be volatile and our revenue and income can be impacted by changes in fair values. The fair values can change rapidly and significantly, and changes can result from changes in interest rates, perceived risk, supply, demand, and actual and projected cash flows, prepayments, and credit performance. A decrease in fair value may not necessarily be the result of deterioration in future cash flows. Fair values for illiquid assets can be difficult to estimate, which may lead to volatility and uncertainty of earnings and book value.
For GAAP purposes, we may mark to market most, but not all, of the assets and liabilities on our Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. In addition, valuation adjustments on certain consolidated assets and our derivatives are reflected in our Consolidated Statements of Operations. Assets that are funded with certain liabilities and hedges may have different mark-to-market treatment than the liability or hedge. If we sell an asset that has not been marked to market through our Consolidated Statements of Operations at a reduced market price relative to its cost basis, our reported earnings will be reduced.
Our loan sale profit margins are generally reflective of gains (or losses) over the period from when we identify a loan for purchase until we subsequently sell or securitize the loan. These profit margins may encompass elements of positive or negative market valuation adjustments on loans, hedging gains or losses associated with related risk management activities, and any other related transaction expenses; however, under GAAP, the different elements may be realized unevenly over the course of one or more quarters for financial reporting purposes, with the result that our financial results may be more volatile and less reflective of the underlying economics of our business activity.
Our calculations of the fair value of the assets we own or consolidate are based upon assumptions that are inherently subjective and involve a high degree of management judgment, and such assumptions may be more difficult to calculate during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
We report the fair values of securities, loans, derivatives, and certain other assets on our Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. In computing the fair values for these assets, we may make several market-based assumptions, including assumptions regarding future interest rates, prepayment rates, discount rates, credit loss rates, and the timing of credit losses. These assumptions are inherently subjective and involve a high degree of management judgment, particularly for illiquid securities and other assets for which market prices are not readily determinable. These assumptions may be more difficult to calculate during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. For further information regarding our assets recorded at fair value see Note 5 to the consolidated financial statements within this 2020 Form 10-K. Use of different assumptions could materially affect our fair value calculations and our financial results and our actual experience may cause us to substantially revise our assumptions. Further discussion of the risk of our ownership and valuation of illiquid securities is set forth in the Risk Factors above and in this 2020 Form 10-K.
The federal conservatorship of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac and related efforts, along with any changes in laws and regulations affecting the relationship between Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac and the U.S. Government, may materially adversely affect our business.
The future roles of the GSEs may be reduced (perhaps significantly) and the nature of their guarantee obligations could be limited relative to historical measurements. Alternatively, it is possible that the GSEs could be dissolved entirely or privatized, and, the U.S. Government could determine to stop providing liquidity support of any kind to the mortgage market. Any changes
20
to the nature of the GSEs or their guarantee obligations could redefine what constitutes an Agency MBS and could have broad adverse implications for the market and our business, operations and financial condition. If Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac were eliminated, or their structures were to change radically (limiting or removing the guarantee obligation), we could be unable to acquire additional Agency MBS and our existing Agency MBS could be materially and adversely impacted.
We could be negatively affected in several ways depending on how events unfold for the GSEs. We could be unable to acquire additional Agency MBS or negatively affect the spreads at which they trade, and the value of our existing Agency MBS could be materially adversely impacted. Also, we rely on our Agency MBS as collateral for a significant portion of our financings. Any decline in our Agency MBS value, or perceived market uncertainty about their value, would make it more difficult for us to obtain financing on our Agency MBS on acceptable terms or at all, or to maintain our compliance with the terms of any financing transactions.
The recent U.S. elections may result in changes in federal policy with significant impacts on the legal and regulatory framework affecting the mortgage industry. These changes, including personnel changes at the applicable regulatory agencies, may alter the nature and scope of oversight affecting the mortgage finance industry generally (particularly with respect to the future role of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac).
Risks Related to Financing and Hedging
Our inability to access funding or the terms on which such funding is available could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, particularly during times of severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Our ability to fund our operations, meet financial obligations and finance target asset acquisitions may be impacted by our ability to secure and maintain our master repurchase agreements, warehouse facilities and repurchase agreement facilities with our counterparties. Because repurchase agreements and warehouse facilities are short-term commitments of capital, lenders may respond to market conditions making it more difficult for us to renew or replace on a continuous basis our maturing short-term borrowings and have and may continue to impose more onerous conditions when rolling such financings. If we are not able to renew our existing facilities or arrange for new financing on terms acceptable to us, or if we default on our covenants or are otherwise unable to access funds under our financing facilities or if we are required to post more collateral or face larger haircuts, we may have to curtail our asset acquisition activities and/or dispose of assets at a loss.
Issues related to financing are exacerbated in times of significant dislocation in the financial markets, such as those experienced related to the COVID-19 pandemic. It is possible our lenders will become unwilling or unable to provide us with financing and we could be forced to sell our assets at an inopportune time when prices are depressed (all of which are conditions that we experienced in 2020). In addition, if the regulatory capital requirements imposed on our lenders change, they may be required to significantly increase the cost of the financing that they provide to us. Our lenders also have and may continue to revise their eligibility requirements for the types of assets they are willing to finance or the terms of such financings, including haircuts and requiring additional collateral in the form of cash, based on, among other factors, the regulatory environment and their management of actual and perceived risk, particularly with respect to assignee liability. Moreover, the amount of financing we receive under our repurchase agreements will be directly related to our lenders’ valuation of our target assets that cover the outstanding borrowings. Typically, repurchase agreements grant the lender the absolute right to reevaluate the fair market value of the assets that cover outstanding borrowings at any time. If a lender determines in its sole discretion that the value of the assets has decreased, it has the right to initiate a margin call. These valuations may be different than the values that we ascribe to these assets and may be influenced by recent asset sales and distressed levels by forced sellers. A margin call requires us to transfer additional assets to a lender without any advance of funds from the lender for such transfer or to repay a portion of the outstanding borrowings.
During the first two quarters of 2020, we observed a mark-down of a portion of our mortgage assets by the counterparties to our financing arrangements, resulting in us having to pay cash or securities to satisfy margin calls. We also sold our Agency RMBS portfolio to increase liquidity and reduce our exposure to margin calls. The margin calls had a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, business, liquidity and ability to make distributions to our stockholders. In addition,
21
we have also experienced an increase in haircuts on financings we have rolled. If haircuts are increased, we will be required to post additional collateral. As a result of these developments we have entered into longer term financing arrangements as well as non-mark-to-market and mark-to-market holiday facilities, which have increased our financing costs and had a negative impact on our profitability. These trends, if continued, will have a negative adverse impact on our liquidity.
Our business strategy involves the use of leverage. We may not achieve what we believe to be optimal levels of leverage or we may become overleveraged, which may materially adversely affect our liquidity, results of operations or financial condition.
Our business strategy involves the use of borrowing, or leverage. Pursuant to our leverage strategy, we borrow against a substantial portion of the market value of our assets and use the borrowed funds to finance our investment portfolio and the acquisition of additional investment assets. We are not required to maintain any particular debt-to-equity ratio. Future increases in the amount by which the collateral value is required to contractually exceed the amount borrowed in such leverage financing transactions, decreases in the market value of our residential mortgage investments, increases in interest rate volatility and changes in the availability of acceptable financing could cause us to be unable to achieve the amount of leverage we believe to be optimal. The return on our assets and cash available for distribution to our stockholders may be reduced to the extent that changes in market conditions prevent us from achieving the desired amount of leverage on our investments or cause the cost of our financing to increase relative to the income earned on our leveraged assets. For example, in response to the changes in rates and margins calls we received during the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic, we entered into several non-mark-to-market and mark-to-market holiday financing facilities. These facilities typically have higher interest rates and cash trapping provisions which reduce the net cash we receive from these levered assets. If the interest income on the investments that we have purchased with borrowed funds fails to cover the interest expense of the related borrowings, we will experience net interest losses and may experience net losses from operations. Such losses could be significant because of our leveraged structure. The risks associated with leverage are more acute during periods of economic slowdown or recession, which the U.S. economy has experienced in connection with the conditions created by the COVID-19 pandemic. The use of leverage to finance our investments involves many other risks, including, among other things, the following:
•Our profitability may be materially adversely affected by a reduction in our leverage. As long as we earn a positive spread between interest and other income we earn on our leveraged assets and our borrowing costs, we believe that we can generally increase our profitability by using greater amounts of leverage. There can be no assurance, however, that repurchase financing will remain an efficient source of long-term financing for our assets. The amount of leverage that we use may be limited because our lenders might not make funding available to us at acceptable rates or they may require that we provide additional collateral to secure our borrowings. If our financing strategy is not viable, we will have to find alternative forms of financing for our assets which may not be available to us on acceptable terms or at acceptable rates. In addition, in response to certain interest rate and investment environments or to changes in market liquidity, we could adopt a strategy of reducing our leverage by selling assets or not reinvesting principal payments as MBS amortize or prepay, thereby decreasing the outstanding amount of our related borrowings. Such an action could reduce interest income, interest expense and net income, the extent of which would depend on the level of reduction in assets and liabilities as well as the sale prices for which the assets were sold.
•An increase in our borrowing costs relative to the interest we receive on our assets may materially adversely affect our profitability. Our earnings are primarily generated from the difference between the interest income we earn on our investment portfolio, less net amortization of purchase premiums and discounts, and the interest expense we pay on our borrowings. Historically, we relied primarily on borrowings under repurchase agreements to finance our investments, which have short-term contractual maturities. However, as a result of the decrease in value of our assets and the subsequent margin calls we received during the early phases of the COVID-19 crises, we move some of our financing to longer-term mark-to-market financing and longer-term non-market-to-market and market holiday financing which is more expensive that traditional short-term mark-to-market financing. In general, if the interest expense on our borrowings increases relative to the interest income we earn on our investments, our profitability may be materially adversely affected. Interest rates are highly sensitive to many factors, including fiscal and monetary policies and domestic and international economic and political conditions, as well as other factors beyond our control. During a period of rising interest rates, our borrowing costs generally will increase at a faster pace than our interest
22
earnings on the leveraged portion of our investment portfolio, which could result in a decline in our net interest spread and net interest margin. The severity of any such decline would depend on our asset/liability composition, including the impact of hedging transactions, at the time as well as the magnitude and period over which interest rates increase. Further, an increase in short-term interest rates could also have a negative impact on the market value of our investments. If any of these events happen, we could experience a decrease in net income or incur a net loss during these periods.
•A decline in the market value of our assets may result in margin calls that may force us to sell assets under adverse market conditions, which may materially adversely affect our liquidity and profitability. In general, the market value of our residential mortgage investments is impacted by changes in interest rates, prevailing market yields and other market conditions, including general economic conditions, home prices, and the real estate market generally. A decline in the market value of our residential mortgage investments may limit our ability to borrow against such assets or result in lenders initiating margin calls, which require a pledge of additional collateral or cash to re-establish the required ratio of borrowing to collateral value, under our repurchase agreements. For example, during the initial stages of the COVID-19 pandemic and related market dislocations, we experienced significantly higher margin calls and haircuts with respect to our repurchase agreements. Posting additional collateral or cash to support our credit will reduce our liquidity and limit our ability to leverage our assets, which could materially adversely affect our business. Thus, we could be forced to sell a portion of our assets, including MBS in an unrealized loss position, to maintain liquidity.
•If a counterparty to our repurchase transactions defaults on its obligation to resell the underlying security back to us at the end of the transaction term or if we default on our obligations under the repurchase agreement, we could incur losses. When we engage in repurchase transactions, we generally sell assets to the counterparty to the agreement for cash. Because the cash we receive from the counterparty is less than the value of those securities (this difference is referred to as the “haircut”), if the lender defaults on its obligation to transfer the same securities back to us, we would incur a loss on the transaction equal to the amount of the haircut (assuming there was no change in the value of the securities). (See Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of this 2020 Form 10-K, for further discussion regarding risks related to exposure to financial institution counterparties in light of recent market conditions.) Our exposure to defaults by counterparties may be more pronounced during periods of significant volatility in the market conditions for mortgages and mortgage-related assets as well as the broader financial markets. At December 31, 2020 the Company had amounts at risk with Goldman Sachs and Nomura of 17% and 11%, respectively, of its equity related to the collateral posted on secured financing agreements. The weighted average maturities of the secured financing agreements with Goldman Sachs and Nomura were 938 and 106 days, respectively. The amounts at risk with Goldman Sachs and Nomura were $649 million and $421 million, respectively. There were no other amounts at risk with any other counterparties greater than 10% of the Company’s equity as of December 31, 2020. In addition, generally, if we default on a repurchase transaction the counterparty could liquidate the assets and use the proceeds to repay the amounts it is sold. If the amount received from the sale is equal to or less than the amount they are owed, we will incur a loss equal to the haircut and the counterparty has recourse to us to repay any remaining deficiency. In addition, if we default on a transaction under any one agreement and fail to honor the related guarantee, the counterparties on our other repurchase agreements could also declare a default under their respective repurchase agreements. Any losses we incur on our repurchase transactions could materially adversely affect our earnings and thus our cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
•Our financing facilities may contain covenants that restrict our operations. Certain financing facilities we may enter contain restrictions, covenants, and representations and warranties that, among other things, may require us to satisfy specified financial, asset quality, loan eligibility, and loan performance tests. If we fail to meet or satisfy any of these covenants or representations and warranties, we would be in default under these agreements and our lenders could elect to declare all amounts outstanding under the agreements to be immediately due and payable, enforce their respective rights against collateral pledged under such agreements, and restrict our ability to make additional borrowings. Certain financing agreements may contain cross-default provisions by a guarantor so that if a default occurs under any guaranty agreement, the lenders under our other agreements could also declare a default under their respective agreements. Further, under our mark-to-market agreements, we are typically required to pledge additional
23
assets to our lenders in the event the estimated fair value of the existing pledged collateral under such agreements declines and such lenders demand additional collateral, which may take the form of additional securities, loans or cash. These restrictions may interfere with our ability to obtain financing or to engage in other business activities, which may have a significant negative impact on our business, financial condition, liquidity and results of operations. A default and resulting repayment acceleration could significantly reduce our liquidity, which could require us to sell our assets to repay amounts due and outstanding. This could also significantly harm our business, financial condition, results of operations, and our ability to make distributions, which could cause the value of our capital stock to decline. A default will also significantly limit our financing alternatives such that we will be unable to pursue our leverage strategy, which could lower our investment returns.
•Adverse developments involving major financial institutions or involving one of our lenders could result in a rapid reduction in our ability to borrow and materially adversely affect our business, profitability, and liquidity. As of December 31, 2020, we had amounts outstanding under repurchase agreements with 16 separate lenders. A material adverse development involving one or more major financial institutions or the financial markets, in general, could result in our lenders reducing our access to funds available under our repurchase agreements or terminating such repurchase agreements altogether. Because substantially all our repurchase agreements are uncommitted and renewable at our lenders’ discretion, our lenders could determine to reduce or terminate our access to future borrowings at virtually any time, which could materially adversely affect our business and profitability. Furthermore, if a few of our lenders became unwilling or unable to continue to provide us with financing, we could be forced to sell assets, including assets in unrealized loss positions, to maintain liquidity. Forced sales, particularly under adverse market conditions, may result in lower sale prices than ordinary market sales made in the normal course of business. If our investments were liquidated at prices below our amortized cost of such assets, we would incur losses, which would adversely affect our earnings. We and many other mortgage REITs experienced these conditions in 2020 in connection with conditions created by the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, uncertainty in the global finance market and weak economic conditions in Europe, including the United Kingdom’s exit from the European Union (commonly referred to as “Brexit”), could cause the conditions described above to have a more pronounced effect on our European counterparties.
•Our use of repurchase agreements to borrow money may give our lenders greater rights in the event of bankruptcy. In the event of our insolvency or bankruptcy, certain repurchase agreements may qualify for special treatment under the Bankruptcy Code, the effect of which, among other things, would be to allow the creditor under the agreement to avoid the automatic stay provisions of the Bankruptcy Code and take possession of, and liquidate, the collateral under such repurchase agreements without delay.
•A re-characterization of the repurchase agreements as sales for tax purposes rather than as secured lending transactions would adversely affect our ability to maintain our qualification as a REIT and to maintain our 1940 Act exemption. When we enter a repurchase agreement, we generally sell assets to our counterparty to the agreement for cash. The counterparty is obligated to resell the assets back to us at the end of the transaction term. We believe that for U.S. federal income tax purposes we will be treated as the owner of the assets that are the subject of repurchase agreements and that the repurchase agreements will be treated as secured lending transactions notwithstanding that such agreement may transfer record ownership of the assets to the counterparty during the term of the agreement. It is possible, however, that the IRS or the SEC could successfully assert that we did not own these assets during the term of the repurchase agreements, in which case we could fail to qualify as a REIT or fail to maintain our 1940 Act exemption, respectively.
Changes in banks’ inter-bank lending rate reporting practices, the method pursuant to which LIBOR is determined or elimination of LIBOR may adversely affect the value of the financial obligations to be held or issued by us that are linked to LIBOR as well as adjustable-rate mortgage loans we hold.
The interest rates on our repurchase agreements, as well as adjustable-rate mortgage loans in our securitizations, are generally based on LIBOR, which is subject to recent national, international, and other regulatory guidance and proposals for reform. Some of these reforms are already effective while others are still to be implemented. These reforms may cause such
24
benchmarks to perform differently than in the past or have other consequences which cannot be predicted. In particular, regulators and law enforcement agencies in the U.K. and elsewhere are conducting criminal and civil investigations into whether the banks that contribute information to the British Bankers’ Association, or BBA, in connection with the daily calculation of LIBOR may have been under-reporting or otherwise manipulating or attempting to manipulate LIBOR. A number of BBA member banks have entered settlements with their regulators and law enforcement agencies with respect to this alleged manipulation of LIBOR. Actions by the regulators or law enforcement agencies, as well as ICE Benchmark Administration (the current administrator of LIBOR), may result in changes to the way LIBOR is determined or the establishment of alternative reference rates. For example, on July 27, 2017, the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority (“FCA”) announced that it intends to stop persuading or compelling banks to submit LIBOR rates after 2021.
Currently, it is not possible to predict the effect of any such changes, any establishment of alternative reference rates or any other reforms to LIBOR that may be implemented in the U.K. or elsewhere. Uncertainty as to the nature of such potential changes, alternative reference rates or other reforms may adversely affect the rates on our repurchase facilities, securitizations or residential loans held for longer-term investment. If LIBOR is discontinued or is no longer quoted, the applicable base rate used to calculate interest on our repurchase agreements will be determined using alternative methods. In the U.S., efforts to identify a set of U.S. dollar reference interest rates include proposals by the Alternative Reference Rates Committee of the Federal Reserve Board and the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. The U.S. Federal Reserve, in conjunction with the Alternative Reference Rates Committee, a steering committee comprised of large U.S. financial institutions, is considering replacing U.S. dollar LIBOR with the Secured Overnight Funding Rate, or SOFR. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York began publishing SOFR rates in April 2018. The market transition away from LIBOR and towards SOFR is expected to be gradual and complicated. There are significant differences between LIBOR and SOFR, such as LIBOR being an unsecured lending rate and SOFR a secured lending rate, another is SOFR is an overnight rate and LIBOR reflects term rates at different maturities. These and other differences create the potential for basis risk between the two rates. The impact of any basis risk difference between LIBOR and SOFR may negatively affect our net interest margin. Any of these alternative methods may result in interest rates that are higher than if the LIBOR Rate was available in its current form, which could have a material adverse effect on our net interest margin. In addition, the manner and timing of the shift is currently unknown. Market participants are still considering how various types of financial instruments and securitization vehicles should react to a discontinuation of LIBOR. It is possible that not all of our assets and liabilities will transition away from LIBOR at the same time, and it is possible that not all of our assets and liabilities will transition to the same alternative reference rate, in each case increasing the difficulty of hedging. We and other market participants have less experience understanding and modeling SOFR-based assets and liabilities than LIBOR-based assets and liabilities, increasing the difficulty of investing, hedging, and risk management. The process of transition involves operational risks. It is also possible that no transition will occur for many financial instruments.
Any additional changes announced by the FCA, other regulators or any other successor governance or oversight body, or future changes adopted by such body, in the method pursuant to which reference rates are determined may result in a sudden or prolonged increase or decrease in the reported reference rates. If that were to occur, the level of interest payments we incur may change. Although certain of our LIBOR based obligations provide for alternative methods of calculating the interest rate payable on certain of our obligations if LIBOR is not reported, which include requesting certain rates from major reference banks in London or New York, or alternatively using LIBOR for the immediately preceding interest period or using the initial interest rate, as applicable, uncertainty as to the extent and manner of future changes may result.
Hedging against interest rate exposure may not be successful in mitigating the risks associated with interest rates and may adversely affect our earnings, which could reduce our cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
Subject to maintaining our qualification as a REIT, we pursue various hedging strategies to seek to reduce our exposure to losses from adverse changes in interest rates. Our hedging activity varies in scope based on the level and volatility of interest rates, the type of assets held, financing used, and other changing market conditions. There are no perfect hedging strategies, and interest rate hedging may fail to protect us from loss. Alternatively, we may fail to properly assess a risk to our investment portfolio or may fail to recognize a risk entirely, leaving us exposed to losses without the benefit of any offsetting hedging activities. The derivative financial instruments we select may not have the effect of reducing our interest rate risk. The nature and timing of hedging transactions may influence the effectiveness of these strategies. Poorly designed strategies or improperly
25
executed transactions could increase our risk and losses. In addition, hedging activities could result in losses if the event against which we hedge does not occur. For example, interest rate hedging could fail to protect us or adversely affect us because among other things:
•interest rate hedging can be expensive, particularly during periods of rising and volatile interest rates;
•available interest rate hedges may not correlate directly with the interest rate risk for which protection is sought;
•the duration of the hedge may not match the duration of the related liability;
•the amount of income that a REIT may earn from hedging transactions to offset interest rate losses may be limited by U.S. federal tax provisions governing REITs;
•the credit quality of the party owing money on the hedge may be downgraded to such an extent that it impairs our ability to sell or assign our side of the hedging transaction;
•the party owing money in the hedging transaction may default on its obligation to pay; and
•the value of derivatives used for hedging may be adjusted from time to time in accordance with accounting rules to reflect changes in fair value. Downward adjustments, or “mark-to-market losses,” would reduce our stockholders’ equity.
Our hedging transactions, which are intended to limit losses, may limit gains and increase our exposure to losses. Thus, our hedging activity may adversely affect our earnings, which could reduce our cash available for distribution to our stockholders. In addition, some hedging instruments involve risk since they are not currently traded on regulated exchanges, guaranteed by an exchange or its clearing house, or regulated by any U.S. or foreign governmental authorities.
Clearing facilities or exchanges upon which some of our hedging instruments are traded may increase margin requirements on our hedging instruments in the event of uncertainty or adverse developments in financial markets.
In response to events having or expected to have adverse economic consequences or which create market uncertainty, clearing facilities or exchanges upon which some of our hedging instruments, such as interest rate swaps, are traded may require us to post additional collateral against our hedging instruments. Generally, the initial margin goes up in times of interest rate volatility. If future adverse economic developments or market uncertainty result in increased margin requirements for our hedging instruments, it could materially adversely affect our liquidity position, business, financial condition and results of operations.
We have elected not to qualify for hedge accounting treatment for GAAP reporting.
We record derivative and hedge transactions in accordance with GAAP. Our interest rate swaps have not been designated as hedging instruments for accounting purposes. Consequently, all changes in the fair value of swaps are reported as a component of net income in the Consolidated Statements of Operations rather than Accumulated other comprehensive income, (or AOCI), a component of stockholders' equity, which can make our GAAP net income volatile.
Risks Associated with Our Operations
Through certain of our wholly-owned subsidiaries we have engaged in the past, and expect to continue to engage in, securitization transactions relating to residential mortgage loans. These types of transactions and investments expose us to potentially material risks.
A significant part of our business and growth strategy is to engage in various securitization transactions related to mortgage assets, and such transactions expose us to potentially material risks, including without limitation:
Financing Risk: Engaging in securitization transactions and other similar transactions generally require us to incur short-term debt on a recourse basis to finance the accumulation of residential mortgage loans. If investor demand for securitization transactions weakens, we may be unable to complete the securitization of loans accumulated for that purpose, which may hurt our business or financial results.
26
Diligence Risk: We engage in due diligence with respect to the loans or other assets we are securitizing and make representations and warranties relating to those loans and assets. When conducting due diligence, we rely on resources and data available to us and on a review of the collateral by third parties, each of which may be limited. We may also only conduct due diligence on a sample of a pool of loans or assets we are acquiring and assume that the sample is representative of the entire pool. Our due diligence efforts may not reveal matters which could lead to losses. If our due diligence process is not robust enough, or the scope of our due diligence is limited, we may incur losses. Losses could occur because a counterparty that sold us a loan or other asset refuses or is unable (e.g., due to its financial condition) to repurchase that loan or asset or pay damages to us if we determine after purchase that one or more of the representations or warranties made to us was inaccurate or because we don’t get a representation or warranty that covers a discovered defect or violation. In addition, losses with respect to such loans will generally be borne by us as the holder of the “first-loss” securities in our securitizations.
Disclosure and Indemnity Risk: When engaging in securitization transactions, we also prepare marketing and disclosure documentation, including term sheets and prospectuses, that include disclosures regarding the securitization transactions, the securitization transaction agreements and the assets being securitized. If our marketing and disclosure documentation are alleged or found to contain inaccuracies or omissions, we may be liable under federal and state securities laws (or under other laws) for damages to third parties that invest in these securitization transactions, including in circumstances where we relied on a third party in preparing accurate disclosures, or we may incur other expenses and costs disputing these allegations or settling claims. Additionally, we typically retain various third party service providers when we engage in securitization transactions, including underwriters, trustees, administrative and paying agents, servicers and custodians, among others. We frequently contractually agree to indemnify these service providers against various claims and losses they may suffer from providing these services to us or the securitization trust. If any of these service providers are liable for damages to third parties that have invested in these securitization transactions, we may incur costs and expenses because of these indemnities.
Documentation Defects: In recent years, there has also been debate as to whether there are defects in the legal process and legal documents governing transactions in which securitization trusts and other secondary purchasers take legal ownership of residential mortgage loans and establish their rights as priority lien holders on underlying mortgaged property. If there are problems with the establishment of title and lien priority rights are transferred, securitization transactions that we sponsored and third party sponsored securitizations that we hold investments in may experience losses, which could expose us to losses and could damage our ability to engage in future securitization transactions.
Our ability to profitably execute or participate in future securitization transactions has been, and is expected to continue to be, negatively impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
A significant part of our business and growth strategy is to engage in various securitization transactions related to residential mortgage loans. There are many factors that can have a significant impact on our ability to profitably effectuate securitization transaction. One of these factors is the price we pay for the mortgage loans that we securitize, which, in the case of residential mortgage loans, is impacted by the level of competition in the marketplace for acquiring residential mortgage loans and the relative desirability to originators or other financial institutions of retaining residential mortgage loans as investments or selling them to third parties such as us. The cost and availability of the short-term debt we use to finance our mortgage loan before securitization impacts the profitability of our securitization transactions. This short-term debt cost is affected by several factors including its availability to us, its interest rate, its duration, and the percentage of our mortgage loans that third parties are willing to provide short-term financing, all of which have been negatively impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
After we acquire mortgage loans that we intend to securitize, we can also suffer losses if the value of those loans declines before securitization. Declines in the value of a residential mortgage loan, for example, can be due to, among other things, changes in interest rates, changes in the credit quality of the loan, changes in the projected yields required by investors to invest in securitization transactions, and increased delinquencies which we expect to occur as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Hedging against a decline in loan value due to changes in interest rates may impact the profitability of a securitization.
The price that investors in mortgage-backed securities will pay for securities issued in our securitization transactions also has a significant impact on the profitability of the transactions to us, and these prices are impacted by numerous market forces and factors including the uncertainty, potential delinquencies, and lack of liquidity we are experiencing during the COVID-19
27
pandemic. In addition, the underwriter(s) or placement agent(s) we select for securitization transactions, the terms of their engagement and the transaction costs incurred in such securitizations can also impact the profitability of our securitizations. Also, any liability that we may incur, or may be required to reserve for when executing a transaction can cause a loss to us. To the extent that we are not able to profitably execute future securitizations of residential mortgage loans or other assets, including for the reasons described above or for other reasons, it could have a material adverse impact on our business and financial results.
We rely on third parties to perform certain services particularly as it relates to servicing, comply with applicable laws and regulations, and carry out contractual covenants and terms, the failure of which by any of these third parties may adversely impact our business and financial results.
To conduct our business of acquiring loans, engaging in securitization transactions, and investing in third party issued securities and other assets, we rely on third party service providers to perform certain services, comply with applicable laws and regulations, and carry out contractual covenants and terms. Thus, we are subject to the risks associated with a third party’s failure to perform, including failure to perform due to reasons such as fraud, negligence, errors, miscalculations, or insolvency. The COVID-19 pandemic and the resulting economic disruption it has caused may result in liquidity pressures on servicers and other third party vendors that we rely upon. For instance, as a result of an increase in mortgagors requesting relief in the form of forbearance plans and/or other loss mitigation, servicers and other parties responsible in capital markets securitization transactions for funding advances with respect to delinquent mortgagor payments of principal and interest may begin to experience financial difficulties if mortgagors do not make monthly payments as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The negative impact on the business and operations of such servicers or other parties responsible for funding such advances could be significant. Sources of liquidity typically available to servicers and other relevant parties for the purpose of funding advances of monthly mortgage payments, especially entities that are not depository institutions, may not be sufficient to meet the increased need that could result from significantly higher delinquency and/or forbearance rates. The extent of such liquidity pressures in the future is not known at this time and is subject to continual change.
We rely on third party servicers to service and manage the mortgage loans we own and that underlie our MBS. The ultimate returns generated by these investments may depend on the quality of the servicer. If a servicer is not vigilant in seeing that borrowers make their required monthly payments, borrowers may be less likely to make these payments, resulting in higher default rates. If a servicer takes longer than expected to liquidate non-performing loans, our losses related to those loans may be higher than originally anticipated. Any failure by servicers to service these mortgages or to competently manage and dispose of the related real properties could negatively impact the value of these investments and our financial performance. In addition, while we have contracted with third party servicers to carry out the actual servicing of the loans we own, other than our securitized loans (including all direct interface with the borrowers) we are nevertheless ultimately responsible, vis-à-vis the borrowers and state and federal regulators, for ensuring that the loans are serviced in accordance with the terms of the related notes and mortgages and applicable law and regulation (See “Risks Related to Regulatory Matters and Our 1940 Act Exemption” for further discussion). Considering the current regulatory environment, such exposure could be significant even though we might have contractual claims against our servicers for any failure to service the loans to the required standard.
For a majority of the loans that we hold and securitize, we hold the right to service those loans and we retain a sub-servicer to service those loans. In these circumstances, we are exposed to certain risks, including, without limitation, that we may not be able to enter sub-servicing agreements on favorable terms to us or at all, or that the sub-servicer may not properly service the loan in compliance with applicable laws and regulations or the contractual provisions governing their sub-servicing role, and that we would be held liable for the sub-servicer’s improper acts or omissions. Additionally, in its capacity as a servicer of residential mortgage loans, a sub-servicer will have access to borrowers’ non-public personal information, and we could incur liability for a data breach relating to a sub-servicer or misuse or mismanagement of data by a sub-servicer. We also rely on technology infrastructure and systems of third parties who provide services to us and with whom we transact business. To the extent any one sub-servicer counterparty services a significant percentage of the loans with respect to which we own the servicing rights, the risks associated with our use of that sub-servicer are concentrated around this single sub-servicer counterparty. To the extent that there are significant amounts of advances that need to be funded in respect of loans where we own the servicing right, it could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial results.
28
We also rely on corporate trustees to act on behalf of us in enforcing our rights as security holders. Under the terms of most RMBS we hold, we do not have the right to directly enforce remedies against the issuer of the security but instead must rely on a trustee to act on behalf of us and other security holders. Should a trustee not be required to act under the terms of the securities, or fail to act, we could experience losses.
The expanding body of federal, state and local regulations and the investigations of servicers may increase their cost of compliance and the risks of noncompliance and may adversely affect their ability to perform their servicing obligations.
We rely on third party servicers to service the residential mortgage loans that we acquire through consolidated trusts and that underlie the MBS that we acquire. The mortgage servicing business is subject to extensive regulation by federal, state and local governmental authorities and is subject to various laws and judicial and administrative decisions imposing requirements and restrictions and increased compliance costs on a substantial portion of their operations. The volume of new or modified laws and regulations has increased in recent years. Some jurisdictions and municipalities have enacted laws that restrict loan servicing activities, including delaying or preventing foreclosures or forcing the modification of certain mortgages.
Federal laws and regulations have also been proposed or adopted which, among other things, could hinder the ability of a servicer to foreclose promptly on defaulted residential loans, and which could result in assignees being held responsible for violations in the residential loan origination process. Certain mortgage lenders and third party servicers have voluntarily, or as part of settlements with law enforcement authorities, established loan modification programs relating to loans they hold or service. These federal, state and local legislative or regulatory actions that result in modifications of our outstanding mortgages, or interests in mortgages acquired by us either directly through consolidated trusts or through our investments in residential MBS, may adversely affect the value of, and returns on, such investments. Mortgage servicers may be incented by the federal government to pursue such loan modifications, as well as forbearance plans and other actions intended to prevent foreclosure, even if such loan modifications and other actions are not in the best interests of the beneficial owners of the mortgages. The foregoing matters may cause our business, financial condition, results of operations and ability to pay dividends to be adversely affected.
We utilize third party analytical models and data to value our investments, and any incorrect, misleading or incomplete information used in connection therewith would subject us to potential risks.
Given the complexity of our investments and strategies, we rely heavily on analytical models and information and data supplied by third parties, or Third Party Data. Third Party Data is used to value investments or potential investments and to hedge our investments. When we rely on Third Party Data that proves to be incorrect, misleading or incomplete, our decisions expose us to potential risks. For example, by relying on Third Party Data, especially valuation models, we may be induced to buy certain investments at prices that are too high, to sell certain other investments at prices that are too low, or to miss favorable opportunities altogether. Similarly, any hedging based on faulty Third Party Data may prove to be unsuccessful. Furthermore, any valuations of our investments that are based on valuation models may prove to be incorrect.
These risks include the following: (i) collateral cash flows and/or liability structures may be incorrectly modeled in all or only certain scenarios, or may be modeled based on simplifying assumptions that lead to errors; (ii) information about collateral may be incorrect, incomplete, or misleading; (iii) collateral or bond historical performance (such as historical prepayments, defaults, cash flows, etc.) may be incorrectly reported, or subject to interpretation (e.g., different issuers may report delinquency statistics based on different definitions of what constitutes a delinquent loan); or (iv) collateral or bond information may be outdated, in which case the models may contain incorrect assumptions as to what has occurred since the date information was last updated.
Some of the Third Party Data we use, such as mortgage prepayment models or mortgage default models, are predictive in nature. The use of predictive models has inherent risks. For example, such models may incorrectly forecast future behavior, leading to potential losses on a cash flow and/or a mark-to-market basis. In addition, the predictive models we use may differ substantially from those models used by other market participants, with the result that valuations based on these predictive models may be substantially higher or lower for certain investments than actual market prices. Furthermore, since predictive models are usually constructed based on historical data supplied by third parties, the success of relying on such models may
29
depend heavily on the accuracy and reliability of the supplied historical data and the ability of these historical models to accurately reflect future periods.
All valuation models rely on correct market data inputs. Certain assumptions used as inputs to the models may be based on historical trends and these trends may not be indicative of future results. If incorrect market data is used, even a well-designed valuation model may result in incorrect valuations. Even if market data is appropriately captured in the model, the resulting “model prices” will often differ substantially from market prices, especially for securities with complex characteristics, such as derivative securities.
For example, the economic, financial and related impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic are and will be very difficult to model (including as related to the housing and mortgage markets), as the catalyst for these conditions (i.e., a global pandemic) is an event that is unparalleled in modern history and therefore is subject to wide variables, assumptions and inputs. Therefore, historical data used in Third Party Data may be less reliable in predicting future conditions. Further, the conditions created by the COVID-19 pandemic have increased volatility across asset classes. Extreme volatility in any asset class, including real estate and mortgage-related assets, increases the likelihood of Third Party Data being inaccurate as market participants attempt to value assets that have frequent, significant swings in pricing.
We are dependent on information systems and their failure could significantly disrupt our business.
Our business is highly dependent on our information and communications systems. Any failure or interruption of our systems or cyber-attacks or security breaches of our networks or systems could cause delays or other problems in our investment activities as well as subject us to penalties, fines and other regulatory actions, which could have a material adverse effect on operating results, the market price of our common stock and other securities and our ability to pay dividends. We have a suite of controls including technology hardware and software solutions as well as regular training sessions on cybersecurity risks and mitigation strategies. We have established an incident response team to take steps it determines are appropriate to contain, mitigate and remediate a cybersecurity incident and to respond to the associated business, legal and reputational risks. However, due to the transition to remote working environments as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, there is an elevated risk of such events occurring.
Additionally, there is no assurance that these efforts will fully mitigate cybersecurity risk and mitigation efforts are not an assurance that no cybersecurity incidents will occur.
We also face the risk of operational failure, termination, or capacity constraints of any of the third parties with which we do business or that facilitate our business activities, including clearing agents, mortgage servicers, trustees, business counterparties, technology service providers including hardware, software and cloud based solutions or other financial intermediaries we use to facilitate our business.
Risks Related to Regulatory Matters, Accounting, and Our 1940 Act Exemption
Our business is subject to extensive regulation.
Our business is subject to extensive regulation by federal and state governmental authorities, self-regulatory organizations, and securities exchanges. We are required to comply with numerous federal and state laws. The laws, rules and regulations comprising this regulatory framework change frequently, as can the interpretation and enforcement of existing laws, rules, and regulations. Some of the laws, rules and regulations to which we are subject are intended primarily to safeguard and protect consumers, rather than stockholders or creditors. From time to time, we may receive requests from federal and state agencies for records, documents, and information regarding our policies, procedures, and practices regarding our business activities. We incur significant ongoing costs to comply with these government regulations.
Although we do not originate or directly service residential mortgage loans, we must comply with various federal and state laws, rules, and regulations because we purchase residential mortgage loans. These rules generally focus on consumer protection and include, among others, rules promulgated under the Dodd-Frank Act and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Financial
30
Modernization Act of 1999. These requirements can and do change as statutes and regulations are enacted, promulgated, amended, and interpreted, and the recent trends among federal and state lawmakers and regulators have been toward increasing laws, regulations, and investigative proceedings concerning the mortgage industry generally. For example, on December 10, 2020, the CFPB issued a final rule that adopts a set of “bright-line” loan pricing thresholds to replace the previous General Qualified Mortgage 43% debt-to-income threshold calculated in accordance with “Appendix Q” and removes Appendix Q (the “General QM Final Rule”). The effective date of the General QM Final Rule is March 1, 2021, but the mandatory compliance date is July 1, 2021. On December 10, 2020, the CFPB also issued a final rule that creates a new category of a qualified mortgage, referred to as a “Seasoned QM” (the “Seasoned QM Final Rule”). A loan is eligible to become a Seasoned QM if it is a first-lien, fixed rate loan that meets certain performance requirements over a seasoning period of 36 months, is held in portfolio until the end of the seasoning period by the originating creditor or first purchaser, complies with general restrictions on product features and points and fees, and meets certain underwriting requirements. The effective date for the Seasoned QM Final Rule is March 1, 2021. At this time, however, there can be no assurance what impact these final rules will have on the mortgage market and the “ability-to-repay” rules. Furthermore, the temporary qualified mortgage provision applicable to certain mortgage loans eligible for purchase or guarantee by the GSEs, commonly referred to as the “GSE Patch,” will expire on the earlier of: (i) July 1, 2021 or (ii) the date that the GSEs exit conservatorship. We cannot predict the impact of its expiration on the mortgage market.
Although we believe that we have structured our operations and investments to comply with existing legal and regulatory requirements and interpretations, changes in regulatory and legal requirements, including changes in their interpretation and enforcement by lawmakers and regulators, could materially and adversely affect our business and our financial condition, liquidity, and results of operations.
We are required to obtain various state licenses to purchase mortgage loans in the secondary market and there is no assurance we will be able to obtain or maintain those licenses.
While we are not required to obtain licenses to purchase mortgage-backed securities, the purchase of residential mortgage loans in the secondary market may, in some circumstances, require us to maintain various state licenses. Acquiring the right to service residential mortgage loans may also, in some circumstances, require us to maintain various state licenses even though we currently do not expect to directly engage in loan servicing ourselves. Thus, we could be delayed in conducting certain business if we were first required to obtain a state license. We cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain all the licenses we need or that we would not experience significant delays in obtaining these licenses. Furthermore, once licenses are issued, we are required to comply with various information reporting and other regulatory requirements to maintain those licenses, and there is no assurance that we will be able to satisfy those requirements or other regulatory requirements applicable to our business of acquiring residential mortgage loans on an ongoing basis. Our failure to obtain or maintain required licenses or our failure to comply with regulatory requirements that are applicable to our business of acquiring residential mortgage loans may restrict our business and investment options and could harm our business and expose us to penalties or other claims.
Our GAAP financial results may not be an accurate indicator of taxable income and dividend distributions.
Generally, the cumulative net income we report over the life of an asset will be the same for GAAP and tax purposes, although the timing of this income recognition over the life of the asset could be materially different. Differences exist in the accounting for GAAP net income and REIT taxable income, which can lead to significant variances in the amount and timing of when income and losses are recognized under these two measures. Due to these differences, our reported GAAP financial results could materially differ from our determination of taxable income, which impacts our dividend distribution requirements, and, therefore, our GAAP results may not be an accurate indicator of future taxable income and dividend distributions.
Changes in accounting rules could occur at any time and could impact us in significantly negative ways that we are unable to predict or protect against.
The Financial Accounting Standards Board, or the FASB, and other regulatory bodies that establish the accounting rules applicable to us have recently proposed or enacted a wide array of changes to accounting rules. Moreover, in the future, these regulators may propose additional changes that we do not currently anticipate. Changes to accounting rules that apply to us
31
could significantly impact our business or our reported financial performance in ways that we cannot predict or protect against. We cannot predict whether any changes to current accounting rules will occur or what impact any codified changes will have on our business, results of operations, liquidity or financial condition, directly or through their impact on our business partners or counterparties.
Loss of our 1940 Act exemption would adversely affect us and negatively affect the market price of shares of our capital stock and our ability to distribute dividends.
We conduct our operations so that neither we nor any of our subsidiaries are required to register as an investment company under the 1940 Act. Section 3(a)(1)(A) of the 1940 Act defines an investment company as any issuer that is or holds itself out as being engaged primarily in the business of investing, reinvesting, or trading in securities. Section 3(a)(1)(C) of the 1940 Act defines an investment company as any issuer that is engaged or proposes to engage in the business of investing, reinvesting, owning, holding, or trading in securities and owns or proposes to acquire investment securities having a value exceeding 40% of the value of the issuer’s total assets (exclusive of U.S. Government securities and cash items) on an unconsolidated basis, which we refer to as the 40% test. Excluded from the term “investment securities,” among other things, are U.S. government securities and securities issued by majority-owned subsidiaries that are not themselves investment companies and are not relying on the exclusion from the definition of investment company set forth in Section 3(c)(1) or Section 3(c)(7) of the 1940 Act.
Because we are a holding company that conducts its businesses primarily through wholly-owned subsidiaries and majority-owned subsidiaries, the securities issued by these subsidiaries that are excepted from the definition of “investment company” under Section 3(c)(1) or Section 3(c)(7) of the 1940 Act, together with any other investment securities we may own, may not have a combined value in excess of 40% of the value of our adjusted total assets on an unconsolidated basis. This requirement limits the types of businesses in which we may engage through our subsidiaries. In addition, the assets we and our subsidiaries may acquire are limited by the provisions of the 1940 Act, the rules and regulations promulgated under the 1940 Act and SEC staff interpretative guidance, which may adversely affect our performance.
If the value of securities issued by our subsidiaries that are excepted from the definition of “investment company” by Section 3(c)(1) or 3(c)(7) of the 1940 Act, together with any other investment securities we own, exceeds 40% of our adjusted total assets on an unconsolidated basis, or if one or more of such subsidiaries fail to maintain an exception or exemption from the 1940 Act, we could, among other things, be required either (a) to substantially change the manner in which we conduct our operations to avoid being required to register as an investment company or (b) to register as an investment company under the 1940 Act, either of which could have an adverse effect on us and the market price of our securities. If we were required to register as an investment company under the 1940 Act, we would become subject to substantial regulation with respect to our capital structure (including our ability to use leverage), management, operations, transactions with affiliated persons (as defined in the 1940 Act), portfolio composition, including restrictions with respect to diversification and industry concentration, and other matters.
Certain of our subsidiaries rely on the exemption from registration provided by Section 3(c)(5)(C) of the 1940 Act. Section 3(c)(5)(C) as interpreted by the staff of the SEC, requires us to invest at least 55% of our assets in “mortgages and other liens on and interest in real estate”, or Qualifying Real Estate Assets, and at least 80% of our assets in Qualifying Real Estate Assets plus real estate-related assets. The assets that we acquire, therefore, are limited by the provisions of the 1940 Act and the rules and regulations promulgated under the 1940 Act. If the SEC determines that any of a subsidiary’s securities are not Qualifying Real Estate Assets or real estate-related assets or otherwise believes such subsidiary does not satisfy the exemption under Section 3(c)(5)(C), we could be required to restructure our activities or sell certain of our assets. The net effect of these factors will be to lower our net interest income. If we fail to qualify for exemption from registration as an investment company, our ability to use leverage would be substantially reduced, and we would not be able to conduct our business as described.
Certain of our subsidiaries may rely on the exemption provided by Section 3(c)(6) which excludes from the definition of “investment company” any company primarily engaged, directly or through majority-owned subsidiaries, in a business, among others, described in Section 3(c)(5)(C) of the 1940 Act (from which not less than 25% of such company’s gross income during its last fiscal year was derived) together with an additional business or additional businesses other than investing, reinvesting,
32
owning, holding or trading in securities. The SEC staff has issued little interpretive guidance with respect to Section 3(c)(6) and any guidance published by the staff could require us to adjust our strategy accordingly.
Certain of our subsidiaries may rely on Section 3(c)(7) for their 1940 Act exemption and, therefore, our interest in each of these subsidiaries would constitute an “investment security” for purposes of determining whether we pass the 40% test.
Certain of our subsidiaries may rely on Rule 3a-7 which exempts certain securitization vehicles. There are numerous requirements that must be met to exclude such subsidiaries from the definition of an investment company. Our ability to manage assets held in a special purpose subsidiary that complies with Rule 3a-7 will be limited and we may not be able to purchase or sell assets owned by that subsidiary when we would otherwise desire to do so, which could lead to losses.
The determination of whether an entity is a majority-owned subsidiary of our company is made by us. The 1940 Act defines a majority-owned subsidiary of a person as a company of which 50% or more of the outstanding voting securities are owned by such person, or by another company which is a majority-owned subsidiary of such person. The 1940 Act further defines voting securities as any security presently entitling the owner or holder thereof to vote for the election of directors of a company. We treat companies in which we own at least a majority of the outstanding voting securities as majority-owned subsidiaries for purposes of the 40% test. We have not requested the SEC to approve our treatment of any company as a majority-owned subsidiary and the SEC has not done so. If the SEC were to disagree with our treatment of one or more companies as majority-owned subsidiaries, we may need to adjust our strategy and our assets to continue to pass the 40% test. Any such adjustment in our strategy could have a material adverse effect on us.
There can be no assurance that the laws and regulations governing the 1940 Act status of REITs, including guidance from the Division of Investment Management of the SEC regarding these exemptions, will not change in a manner that adversely affects our operations. If we or our subsidiaries fail to maintain an exception or exemption from the 1940 Act, we could, among other things, be required either to (a) change the manner in which we conduct our operations to avoid being required to register as an investment company, (b) effect sales of our assets in a manner that, or at a time when, we would not otherwise choose to do so, or (c) register as an investment company, any of which could negatively affect the value of our capital stock, the sustainability of our business model, and our ability to make distributions which could have an adverse effect on our business and the market price for our shares of capital stock.
We Have an Ownership Interest in a Registered Investment Adviser
We own 24.9% of a registered investment adviser and we are the sole investor in a fund managed by that adviser. While we believe we have structured our investment so that we are not deemed a “control person” with respect to that adviser such as our equity interest is non-voting; we do not have consent rights to the budget or other significant control rights; none of our employees is an officer of the adviser, or have any consent rights or other control of the adviser’s personnel; and we do not have a board seat or similar role in the oversight of the adviser, we cannot assure you that the SEC or a court will not determine that we are a “control person”. Control Persons may be held liable for violations committed by persons under their control. Sanctions the SEC may impose on control persons include industry bars and suspensions, financial penalties, disgorgement of financial proceeds obtained through the violation, and cease and desist orders. Civil litigants may recover financial compensation from control persons for damages suffered because of misconduct by controlled persons. Control persons are not automatically liable for violations committed by the persons under their control. It is a defense to regulatory and private civil liability if the control person acted in good faith and did not induce the act or acts constituting the violation or cause of action. This defense can be established by showing that the control person exercised due care in his supervision of the violator’s activities by maintaining and enforcing a reasonable and proper system of supervision and internal control.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Risks
Your investment has various U.S. federal income tax risks.
This summary of certain tax risks is limited to the U.S. federal tax risks addressed below. Additional risks or issues may exist that are not addressed in this Form 10-K and that could affect the U.S. federal tax treatment of us or our stockholders. This is
33
not intended to be used and cannot be used by any stockholder to avoid penalties that may be imposed on stockholders under the Code. We strongly urge you to seek advice based on your particular circumstances from an independent tax advisor concerning the effects of U.S. federal, state and local income tax law on an investment in common stock or preferred stock and on your individual tax situation.
Complying with REIT requirements may cause us to forego otherwise attractive opportunities.
To maintain our qualification as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we must continually satisfy various tests regarding the sources of our income, the nature and diversification of our assets, the amounts we distribute to our stockholders and the ownership of our stock. To meet these tests, we may be required to forego investments we might otherwise make. We may be required to make distributions to stockholders at disadvantageous times or when we do not have funds readily available for distribution. Thus, compliance with the REIT requirements may hinder our investment performance.
Complying with REIT requirements may force us to liquidate otherwise attractive investments.
To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we generally must ensure that at the end of each calendar quarter at least 75% of the value of our total assets consists of cash, cash items, government securities and qualifying real estate assets, including certain mortgage loans and mortgage-backed securities. The remainder of our investments in securities (other than government securities and qualifying real estate assets) generally cannot include more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of any one issuer or more than 10% of the total value of the outstanding securities of any one issuer. In addition, in general, no more than 5% of the value of our assets (other than government securities, qualifying real estate assets, and stock in one or more TRSs) can consist of the securities of any one issuer, and no more than 20% of the value of our total assets can be represented by securities of one or more TRSs. If we fail to comply with these requirements at the end of any quarter, we must correct the failure within 30 days after the end of such calendar quarter or qualify for certain statutory relief provisions to avoid losing our REIT status and suffering adverse tax consequences. Thus, we may be required to liquidate from our portfolio otherwise attractive investments. These actions could have the effect of reducing our income and amounts available for distribution to our stockholders.
Complying with REIT requirements may limit our ability to hedge effectively.
The REIT provisions of the Code substantially limit our ability to hedge our assets and related borrowings. Under these provisions, our annual gross income from non-qualifying hedges, together with any other income not generated from qualifying real estate assets, cannot exceed 25% of our annual gross income. In addition, our aggregate gross income from non-qualifying hedges, fees, and certain other non-qualifying sources cannot exceed 5% of our annual gross income. As a result, we might have to limit our use of advantageous hedging techniques or implement certain hedges through a TRS. This could increase the cost of our hedging activities or expose us to greater risks associated with changes in interest rates than we would otherwise want to bear.
Failure to qualify as a REIT would subject us to U.S. federal income tax, which would reduce the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
We have elected to be treated as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes and intend to operate so that we will qualify as a REIT. However, the U.S. federal income tax laws governing REITs are extremely complex, and interpretations of the U.S. federal income tax laws governing qualification as a REIT are limited. Qualifying as a REIT requires us to meet various tests regarding the nature of our assets and our income, the ownership of our outstanding stock, and the amount of our distributions on an ongoing basis. While we intend to operate so as to maintain our qualification as a REIT, given the highly complex nature of the rules governing REITs, the ongoing importance of factual determinations, including the tax treatment of certain investments we may make, and the possibility of future changes in our circumstances, no assurance can be given that we will so qualify for any particular year.
We also indirectly own an entity that has elected to be taxed as a REIT under the U.S. federal income tax laws, or a "Subsidiary REIT." Our Subsidiary REIT is subject to the same REIT qualification requirements that are applicable to us. If our Subsidiary
34
REIT were to fail to qualify as a REIT, then (i) that Subsidiary REIT would become subject to regular U.S. federal, state and local corporate income tax, (ii) our interest in such Subsidiary REIT would cease to be a qualifying asset for purposes of the REIT asset tests, and (iii) it is possible that we would fail certain of the REIT asset tests, in which event we also would fail to qualify as a REIT unless we could avail ourselves of certain relief provisions. While we believe that the Subsidiary REIT has qualified as a REIT under the Code, we have joined the Subsidiary REIT in filing a "protective" TRS election under Section 856(l) of the Code for each taxable year in which we have owned an interest in the Subsidiary REIT. We cannot assure you that such "protective" TRS election would be effective to avoid adverse consequences to us. Moreover, even if the "protective" election were to be effective, the Subsidiary REIT would be subject to regular corporate income tax, and we cannot assure you that we would not fail to satisfy the requirement that not more than 20% of the value of our total assets may be represented by the securities of one or more TRSs. See "Our ownership of and relationship with our TRSs will be limited, and a failure to comply with the limits would jeopardize our REIT status and may result in the application of a 100% excise tax," below.
If we fail to qualify as a REIT in any calendar year and we do not qualify for certain statutory relief provisions, we would be required to pay U.S. federal income tax on our taxable income at regular corporate income tax rates. We might need to borrow money or sell assets to pay any such tax. Our payment of income tax would decrease the amount of our income available for distribution to our stockholders. Furthermore, if we fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT and we do not qualify for certain statutory relief provisions, we no longer would be required to distribute substantially all our REIT taxable income to our stockholders. Unless our failure to qualify as a REIT was excused under U.S. federal tax laws, we would be disqualified from taxation as a REIT for the four taxable years following the year during which qualification was lost.
The ability of our Board of Directors to revoke our REIT election without stockholder approval may cause adverse consequences to our stockholders.
Our charter provides that our Board of Directors may revoke or otherwise terminate our REIT election, without the approval of our stockholders, if our Board of Directors determines that it is no longer in our best interest to attempt to, or continue to, qualify as a REIT. If we cease to qualify as a REIT, we would become subject to U.S. federal income tax on our net taxable income and we generally would no longer be required to distribute any of our net taxable income to our stockholders, which may have adverse consequences on the total return to our stockholders.
Potential characterization of distributions or gain on sale may be treated as unrelated business taxable income to tax-exempt investors.
If (1) all or a portion of our assets are subject to the rules relating to taxable mortgage pools, (2) we are a ‘‘pension-held REIT,’’ or (3) a tax-exempt stockholder has incurred debt to purchase or hold our capital stock, then a portion of the distributions to and, in the case of a stockholder described in clause (3), gains realized on the sale of capital stock by such tax-exempt stockholder may be subject to U.S. federal income tax as unrelated business taxable income under the Code.
Classification of our securitizations or financing arrangements as a taxable mortgage pool could subject us or certain of our stockholders to increased taxation.
We intend to structure our securitization and financing arrangements so as to not allocate “excess inclusion income” to our stockholders. However, if we have borrowings with two or more maturities and, (1) those borrowings are secured by mortgages or mortgage-backed securities and (2) the payments made on the borrowings are related to the payments received on the underlying assets, then the borrowings and the pool of mortgages or mortgage-backed securities to which such borrowings relate may be classified as a taxable mortgage pool under the Code. If any part of our investments were to be treated as a taxable mortgage pool, then our REIT status would not be impaired, but a portion of the taxable income we recognize may, under regulations to be issued by the Treasury Department, be characterized as excess inclusion income and allocated among our stockholders to the extent of and generally in proportion to the distributions we make to each stockholder. Any excess inclusion income would:
•not be allowed to be offset by a stockholder’s net operating losses;
•be subject to a tax as unrelated business income if a stockholder were a tax-exempt stockholder;
35
•be subject to the application of U.S. federal withholding tax at the maximum rate (without reduction for any otherwise applicable income tax treaty) with respect to amounts allocable to foreign stockholders; and
•be taxable (at the highest corporate tax rate) to us, rather than to our stockholders, to the extent the excess inclusion income relates to stock held by disqualified organizations (generally, tax-exempt organizations not subject to tax on unrelated business income, including governmental organizations).
Failure to make required distributions would subject us to tax, which would reduce the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must distribute to our stockholders each calendar year at least 90% of our REIT taxable income (excluding certain items of non-cash income in excess of a specified threshold), determined without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and excluding net capital gain. To the extent that we satisfy the 90% distribution requirement, but distribute less than 100% of our taxable income, we will be subject to federal corporate income tax on our undistributed income. In addition, we will incur a 4% nondeductible excise tax on the amount, if any, by which our distributions in any calendar year are less than the sum of:
•85% of our REIT ordinary income for that year;
•95% of our REIT capital gain net income for that year; and
•any undistributed taxable income from prior years.
We intend to distribute our REIT taxable income to our stockholders in a manner intended to satisfy the 90% distribution requirement and to avoid both corporate income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax. REIT taxable income only includes after-tax TRS net income to the extent such TRS distributes a dividend to the REIT. Therefore, our REIT dividend distributions may or may not include after-tax net income from our TRSs.
Our taxable income may substantially exceed our net income as determined by GAAP. As an example, realized capital losses may be included in our GAAP net income, but may not be deductible in computing our taxable income. In addition, we may invest in assets that generate taxable income in excess of economic income or in advance of the corresponding cash flow from the assets. Also, our ability, or the ability of our subsidiaries, to deduct interest may be limited under Section 163(j) of the Code. To the extent that we generate such non-cash taxable income or have limitations on our deductions in a taxable year, we may incur corporate income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax on that income if we do not distribute such income to stockholders in that year. In that event, we may be required to use cash reserves, incur debt, or liquidate non-cash assets at rates or at times that we regard as unfavorable to satisfy the distribution requirement and to avoid corporate income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax in that year. Moreover, our ability to distribute cash may be limited by available financing facilities. Therefore, our dividend payment level may fluctuate significantly, and, under some circumstances, we may not pay dividends at all.
Our ownership of and relationship with our TRSs will be limited, and a failure to comply with the limits would jeopardize our REIT status and may result in the application of a 100% excise tax.
A REIT may own up to 100% of the equity of one or more TRSs. A TRS may earn income that would not be qualifying income if earned directly by the parent REIT. Both the subsidiary and the REIT must jointly elect to treat the subsidiary as a TRS. Overall, no more than 20% of the value of a REIT’s assets may consist of stock or securities of one or more TRSs. A TRS will pay U.S. federal, state and local income tax at regular corporate rates on any taxable income that it earns. In addition, the TRS rules impose a 100% excise tax on certain transactions between a TRS and its parent REIT that are not conducted on an arm’s-length basis. Our TRS after-tax net income would be available for distribution to us but would not be required to be distributed to us. We anticipate that the aggregate value of the TRS stock and securities owned by us will be less than 20% of the value of our total assets (including the TRS stock and securities). Furthermore, we will monitor the value of our investments in our TRSs to ensure compliance with the rule that no more than 20% of the value of our assets may consist of TRS stock and securities (which is applied at the end of each calendar quarter). In addition, we will scrutinize all our transactions with TRSs to ensure that they are entered on arm’s-length terms to avoid incurring the 100% excise tax described above. There can be no assurance,
36
however, that we will be able to comply with the 20% limitation discussed above or to avoid application of the 100% excise tax discussed above.
The tax on prohibited transactions will limit our ability to engage in transactions, including certain methods of securitizing mortgage loans, that would be treated as sales for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
A REIT’s net income from prohibited transactions is subject to a 100% tax. In general, prohibited transactions are sales or other dispositions of property, other than foreclosure property, but including mortgage loans, held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business. We might be subject to this tax if we sold or securitized our assets in a manner that was treated as a sale for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Therefore, to avoid the prohibited transactions tax, we may choose not to engage in certain sales of assets at the REIT level and may securitize assets in transactions that are treated as financing transactions and not as sales for tax purposes even though such transactions may not be the optimal execution on a pre-tax basis. We could avoid any prohibited transactions tax concerns by engaging in securitization transactions through a TRS, subject to certain limitations described above. To the extent that we engage in such activities through domestic TRSs, the income associated with such activities will be subject to U.S. federal (and applicable state and local) corporate income tax. There can be no assurance, however, that we will avoid the application of the 100% tax on net income from prohibited transactions described above.
The interest apportionment rules may affect our ability to comply with the REIT asset and gross income tests.
The mortgage loans we acquire may be subject to the interest apportionment rules under Treasury Regulations Section 1.856-5(c), or the Interest Apportionment Regulation, which generally provides that if a mortgage is secured by both real property and other property, a REIT is required to apportion its annual interest income for purposes of the REIT 75% gross income test. If a mortgage is secured by both real property and personal property and the value of the personal property does not exceed 15% of the aggregate value of the property securing the mortgage, the mortgage is treated as secured solely by real property for this purpose.
For purposes of the asset tests applicable to REITs, Revenue Procedure 2014-51 provides a safe harbor under which the IRS will generally not challenge a REIT’s treatment of a loan as being in part a real estate asset in an amount equal to the lesser of the fair market value of the loan or the fair market value of the real property securing the loan at certain relevant testing dates. We believe that all of the mortgage loans that we acquire are secured only by real property. Therefore, we believe that the Interest Apportionment Regulation does not apply to our portfolio.
Nevertheless, if the IRS were to assert successfully that our mortgage loans were secured by property other than real estate, that the Interest Apportionment Regulation applied for purposes of our REIT testing, and that the position taken in Revenue Procedure 2014-51 should be applied to our portfolio, then we might not be able to meet the REIT 75% gross income test, and possibly the asset tests applicable to REITs. If we did not meet these tests, we could lose our REIT status or be required to pay a tax penalty to the IRS.
Even if we remain qualified as a REIT, we may face other tax liabilities that reduce our cash flow.
Even if we remain qualified for taxation as a REIT, we may be subject to certain U.S. federal, state and local taxes on our income and assets, including taxes on any undistributed income, tax on income from some activities conducted because of a foreclosure, excise taxes, state or local income, property and transfer taxes, such as mortgage recording taxes, and other taxes. In addition, to meet the REIT qualification requirements, prevent the recognition of certain types of non-cash income, or to avert the imposition of a 100% tax that applies to certain gains derived by a REIT from dealer property or inventory, we may hold some of our assets through our TRSs or other subsidiary corporations that will be subject to corporate-level income tax at regular corporate rates. In certain circumstances, the ability of our TRSs to deduct net interest expense may be limited. Any of these taxes would decrease cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
We may be subject to adverse legislative or regulatory tax changes that could reduce the market price of our capital stock.
37
At any time, the U.S. federal income tax laws or regulations governing REITs or the administrative interpretations of those laws or regulations may be amended. We cannot predict when or if any new U.S. federal income tax law, regulation or administrative interpretation, or any amendment to any existing U.S. federal income tax law, regulation or administrative interpretation, will be adopted, promulgated or become effective and any such law, regulation or interpretation may take effect retroactively. We and our stockholders could be adversely affected by any such change in, or any new, U.S. federal income tax law, regulation or administrative interpretation.
Risks Related to Our Organization and Structure
Certain provisions of Maryland Law, of our charter, and of our bylaws contain provisions that may inhibit potential acquisition bids that stockholders may consider favorable, and the market price of our capital stock may be lower as a result.
•There are ownership limits and restrictions on transferability and ownership in our charter. To qualify as a REIT, not more than 50% of the value of our outstanding stock may be owned, directly or constructively, by five or fewer individuals during the second half of any calendar year. To assist us in satisfying this test, among other things, our charter generally prohibits any person or entity from beneficially or constructively owning more than 9.8% in value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of any class or series of our outstanding capital stock. This restriction may discourage a tender offer or other transactions or a change in the composition of our Board of Directors or control that might involve a premium price for our shares or otherwise be in the best interests of our stockholders and any shares issued or transferred in violation of such restrictions being automatically transferred to a trust for a charitable beneficiary, thereby resulting in a forfeiture of the additional shares.
•Our charter permits our Board of Directors to issue stock with terms that may discourage a third party from acquiring us. Our charter permits our Board of Directors to amend the charter without stockholder approval to increase the total number of authorized shares of stock or the number of shares of any class or series and to issue common or preferred stock, having preferences, conversion or other rights, voting powers, restrictions, limitations as to dividends or other distributions, qualifications, or terms or conditions of redemption as determined by our Board of Directors. Thus, our Board of Directors could authorize the issuance of stock with terms and conditions that could have the effect of discouraging a takeover or other transaction in which holders of some or a majority of our shares might receive a premium for their shares over the then-prevailing market price of our shares.
•Maryland Control Share Acquisition Act. Maryland law provides that holders of ‘‘control shares’’ of our company (defined as voting shares of stock which, when aggregated with all other shares controlled by the acquiring stockholder, entitle the stockholder to exercise one of three increasing ranges of voting power in electing directors) acquired in a “control share acquisition” (defined as the direct or indirect acquisition of ownership or control of “control shares”) have no voting rights except to the extent approved by our stockholders by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of all the votes entitled to be cast on the matter, excluding all interested shares. Our bylaws provide that we are not subject to the “control share” provisions of Maryland law. Our Board of Directors, however, may elect to make the “control share” statute applicable to us at any time and may do so without stockholder approval.
•Business Combinations. We are subject to the “business combination” provisions of Maryland law that, subject to limitations, prohibit certain business combinations (including a merger, consolidation, share exchange, or, in circumstances specified in the statute, an asset transfer or issuance or reclassification of equity securities) between us and an “interested stockholder” (defined generally as any person who beneficially owns 10% or more of our then outstanding voting capital stock or an affiliate or associate of ours who, at any time within the two‑year period before the date in question, was the beneficial owner of 10% or more of our then outstanding voting capital stock) or an affiliate thereof for five years after the most recent date on which the stockholder becomes an interested stockholder. After the five‑year prohibition, any business combination between us and an interested stockholder generally must be recommended by our Board of Directors and approved by the affirmative vote of at least (i) 80% of the votes entitled to be cast by holders of outstanding shares of our voting capital stock and (ii) two‑thirds of the votes entitled to be cast by holders of voting capital stock of the corporation other than shares held by the interested stockholder with whom or
38
with whose affiliate the business combination is to be effected or held by an affiliate or associate of the interested stockholder. These super‑majority voting requirements do not apply if our common stockholders receive a minimum price, as defined under Maryland law, for their shares in the form of cash or other consideration in the same form as previously paid by the interested stockholder for its shares. These provisions of Maryland law also do not apply to business combinations that are approved or exempted by a Board of Directors before the time that the interested stockholder becomes an interested stockholder. Pursuant to the statute, our Board of Directors has by resolution exempted business combinations between us and any other person, provided, that such business combination is first approved by our Board of Directors (including a majority of our directors who are not affiliates or associates of such person).
•Unsolicited Takeovers: The “unsolicited takeover” provisions of Maryland law, permit our Board of Directors, without stockholder approval and regardless of what is currently provided in our charter or bylaws, to elect to be subject to any or all of five provisions, including a classified board, a two-thirds vote requirement for removing a director, a requirement that the number of directors be fixed only by vote of the directors, a requirement that a vacancy on the board be filled only by the remaining directors and for the remainder of the full term of the class of directors in which the vacancy occurred, and majority requirement for the calling of a special meeting of stockholders. Through provisions in our charter and Bylaws unrelated to this statute, we already (a) require, unless called by the chairman of our Board of Directors, our chief executive officer, our president or our Board of Directors, the request of stockholders entitled to cast not less than a majority of all the votes entitled to be cast at the meeting to call a special meeting of stockholders, (b) require that the number of directors be fixed only by the Board of Directors, (c) have a classified board and (d) have a two-thirds vote requirement for the removal of a director. We have elected in our charter to be subject to the provision whereby any vacancy on the board is filled only by a vote of the remaining directors (whether or not they constitute a quorum) for the remainder of the full term of the directorship in which the vacancy occurred and until a successor is duly elected and qualifies. These provisions may have the effect of inhibiting a third party from making an acquisition proposal for us or of delaying, deferring, or preventing a change in control of us under the circumstances that otherwise could provide the holders of shares of common stock with the opportunity to realize a premium over the then current market price.
•Classified Board. Our Board of Directors is divided into three classes of directors. Directors of each class are chosen for terms expiring at the annual meeting of stockholders held in the third year following the year of their election, and each year one class of directors is elected by the stockholders. The staggered terms of our directors may reduce the possibility of a tender offer or an attempt at a change in control, even though a tender offer or change in control might be in the best interests of our stockholders.
Our rights and the rights of our stockholders to take action against our directors and officers are limited, which could limit stockholders’ recourse in the event of actions, not in their best interests.
Our charter limits the liability of our directors and officers to us and our stockholders for money damages, except for liability resulting from:
•actual receipt of an improper benefit or profit in money, property or services; or
•a final judgment based upon a finding of active and deliberate dishonesty by the director or officer that was material to the cause of action adjudicated for which Maryland law prohibits such exemption from liability.
In addition, our charter authorizes us to obligate our company to indemnify our present and former directors and officers for actions taken by them in those capacities to the maximum extent permitted by Maryland law. Our bylaws require us to indemnify each present or former director or officer, to the maximum extent permitted by Maryland law, in the defense of any proceeding to which he or she is made or threatened to be made, a party because of his or her service to us.
Risks Related to Our Capital Stock
The market price and trading volume of our shares of capital stock may be volatile.
39
The market price of shares of our capital stock, including our common and preferred stock, may be highly volatile and could be subject to wide fluctuations. During 2020, we experienced extremely volatile movements in the market price of our shares of stock. Also, the trading volume in our shares of capital stock may fluctuate and cause significant price variations to occur. We cannot assure you that the market price of our shares of capital stock will not fluctuate or decline significantly in the future. Some of the factors that could negatively affect our share price or result in fluctuations in the price or trading volume of our shares of common and preferred stock include those set forth under “Risk Factors” and “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and in the information incorporated and deemed to be incorporated by reference herein.
Capital stock eligible for future sale may have adverse consequences for investors and adverse effects on our share price.
We cannot predict the effect, if any, of future sales of capital stock, or the availability of shares for future sales, on the market price of the capital stock. Sales of substantial amounts of capital stock, or the perception that such sales could occur, may adversely affect prevailing market prices for the common stock. In addition, with certain limited exceptions related to some financing facilities, we are not required to offer any such shares to existing shareholders on a pre-emptive basis. Therefore, it may not be possible for existing shareholders to participate in such future share issues, which may dilute the existing shareholders’ interests in us.
Future offerings of debt securities, which would rank senior to our capital stock upon liquidation, and future offerings of equity securities (including upon the exercise of warrants we have issued to certain lenders), which would dilute our existing stockholders and may be senior to our capital stock for the purposes of dividend and liquidating distributions, may adversely affect the market price of our capital stock.
In the future, we may attempt to increase our capital resources by making offerings of debt or additional offerings of equity securities, including commercial paper, warrants, senior or subordinated notes and series or classes of preferred stock or common stock. Upon liquidation, holders of our debt securities and shares of preferred stock, if any, and lenders with respect to other borrowings will receive a distribution of our available assets before the holders of our common stock. Additional equity offerings (including upon the exercise of warrants or similar instruments issued to lenders or other parties) may dilute the holdings of our existing stockholders or reduce the market price of our capital stock, or both. Preferred stock, including our Series A, Series B, Series C, and Series D Preferred Stock, will have a preference on liquidating distributions or a preference on dividend payments or both that could limit our ability to make a dividend distribution to the holders of our capital stock, including our common stock. Because our decision to issue securities in any future offering will depend on market conditions and other factors beyond our control, we cannot predict or estimate the amount, timing or nature of our future offerings. Thus, holders of our capital stock bear the risk of our future offerings reducing the market price of our capital stock and diluting their stock holdings in us.
There is a risk that you may not receive dividend distributions, or those dividend distributions may decrease over time. Changes in the amount of dividend distributions we pay or in the tax characterization of dividend distributions we pay may adversely affect the market price of our common stock or may result in holders of our common stock being taxed on dividend distributions at a higher rate than initially expected.
Our dividend distributions are driven by a variety of factors, including our minimum dividend distribution requirements under the REIT tax laws and our REIT taxable income as calculated for tax purposes pursuant to the tax code. We generally intend to distribute to our common shareholders at least 90% of our REIT taxable income, although our reported financial results for GAAP purposes may differ materially from our REIT taxable income.
Our ability to pay a dividend per common share per quarter and the dividend on each series of our preferred stock at the stated dividend rate may be adversely affected by many factors, including the risk factors described herein. These same factors may affect our ability to pay other future dividends. In addition, to the extent we determine that future dividends would represent a return of capital to investors, rather than the distribution of income, we may determine to discontinue dividend payments until such time that dividends would again represent a distribution of income. Any reduction or elimination of our payment of
40
dividend distributions would not only reduce the number of dividends you would receive as a holder of our common stock but could also have the effect of reducing the market price of our common stock.
The declaration, amount and payment of future cash dividends on our common stock are subject to uncertainty due to disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as market conditions related to COVID-19.
The declaration, amount and payment of any future dividends on shares of common stock will be at the sole discretion of our Board of Directors. Consistent with our intention to enhance our liquidity and strengthen our cash position to take advantage of future opportunities, our Board of Directors may adjust our quarterly cash dividend on our shares of common stock from prior quarters. The payment of dividends may be more uncertain during severe market disruption in the mortgage, housing or related sectors, such as those experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
We may not be able to pay dividends or other distributions on our Capital Stock.
Under Maryland law, no distributions on stock may be made if, after giving effect to the distribution, (i) the corporation would not be able to pay the indebtedness of the corporation as such indebtedness becomes due in the usual course of business or (ii) except in certain limited circumstances when distributions are made from net earnings, the corporation’s total assets would be less than the sum of the corporation’s total liabilities plus, unless the charter provides otherwise (which our charter does, with respect to any outstanding series of preferred stock), the amount that would be needed, if the corporation were to be dissolved at the time of the distribution, to satisfy the preferential rights upon dissolution of stockholders whose preferential rights on dissolution are superior to those receiving the distribution. There can be no guarantee that we will have sufficient cash to pay dividends on any series of our capital stock. Our ability to pay dividends may be impaired if any of the risks described in this Item 1A Risk Factors were to occur. In addition, payment of our dividends depends upon our earnings, our financial condition, maintenance of our REIT qualification and other factors as our Board of Directors may deem relevant from time to time. We cannot assure you that our business will generate sufficient cash flow from operations or that future borrowings will be available to us in an amount sufficient to enable us to make distributions on our common stock or any series of our preferred stock.
Dividends payable by REITs generally do not qualify for the reduced tax rates available for some dividends.
The maximum U.S. federal income tax rate applicable to qualified dividend income payable to certain non-corporate U.S. holders is 20%. Dividends payable by REITs, however, generally are not eligible for the reduced qualified dividend rates. For taxable years beginning before January 1, 2026, non-corporate taxpayers may deduct up to 20% of certain pass-through business income, including “qualified REIT dividends” (generally, dividends received by a REIT shareholder that are not designated as capital gain dividends or qualified dividend income), subject to certain limitations, resulting in an effective maximum U.S. federal income tax rate of 29.6% on such income. Although the reduced U.S. federal income tax rate applicable to qualified dividend income does not adversely affect the taxation of REITs or dividends payable by REITs, the more favorable rates applicable to regular corporate qualified dividends and the reduced corporate tax rate (currently 21%) could cause certain non-corporate investors to perceive investments in REITs to be relatively less attractive than investments in the stocks of non-REIT corporations that pay dividends, which could adversely affect the value of the shares of REITs, including our stock.
Holders of our Preferred Stock have limited voting rights.
The voting rights of holders of any series of our outstanding preferred stock are limited. Our common stock is the only class of our securities that currently carries full voting rights. Holders of any series of our preferred stock may vote only (i) to elect, voting together as a single class, with holders of parity stock having similar voting rights two additional directors to our Board of Directors if six full quarterly dividends (whether or not consecutive) payable on any series of our preferred stock are in arrears, (ii) on amendments to our charter, including the articles supplementary designating any series of our outstanding preferred stock, that materially and adversely affect the rights of the holders of such series or (iii) to authorize or create, or increase the authorized or issued amount of, additional classes or series of Senior Stock.
41
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 2. Properties
As of December 31, 2020, we do not own any property. Our executive and administrative office is located in leased space at 520 Madison Avenue, 32nd Floor, New York, New York 10022, telephone (212) 626-2300. Our office lease expires on August 2021. We believe that this space is suitable and adequate for our current needs. In addition, we have leases through November 2021, for our off-site back-up facilities and data centers located in Wappingers Falls, New York and Norwalk, Connecticut.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
None.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
Part II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our common stock began trading publicly on the NYSE under the trading symbol “CIM” on November 16, 2007. As of January 31, 2021, we had 230,559,010 shares of common stock issued and outstanding which were held by 219 holders of record.
Dividends
We pay quarterly dividends and distribute to our stockholders all or substantially all of our taxable income in each year (subject to certain adjustments). This enables us to qualify for the tax benefits accorded to a REIT under the Code. We have not established a set minimum dividend payment level and our ability to pay dividends may be adversely affected for the reasons described under the caption “Risk Factors.” All distributions will be made at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on our taxable income, our financial condition, maintenance of our REIT status and such other factors as our Board of Directors may deem relevant from time to time.
The Board of Directors declared dividends of $1.40 and $2.00 per share during 2020 and 2019.
Purchases of Equity Securities
In March 2020, our Board of Directors reauthorized $150 million under our share repurchase program, or the Repurchase Program. Such authorization does not have an expiration date and, at present, there is no intention to modify or otherwise rescind such authorization. Shares of our common stock may be purchased in the open market, including through block purchases, through privately negotiated transactions, or pursuant to any trading plan that may be adopted in accordance with Rule 10b5-1 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The timing, manner, price and amount of any repurchases will be determined at our discretion and the program may be suspended, terminated or modified at any time for any reason. Among other factors, the Company intends to only consider repurchasing shares of our common stock when the purchase price is less than the last publicly reported book value per common share. In addition, the Company does not intend to repurchase any shares from directors, officers or other affiliates. The program does not obligate the Company to acquire any specific number of shares, and all repurchases will be made in accordance with Rule 10b-18, which sets certain restrictions on the method, timing, price and volume of stock repurchases.
Pursuant to our Repurchase Program, the Company repurchased approximately 1.4 million shares of its common stock at an average price of $15.34 per share for a total of $22 million during the first quarter of 2020. The approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the Repurchase Program is $128 million as of December 31, 2020. The Company did not repurchase any of its common stock during the year ended December 31, 2019.
42
| Total Number of Common Shares Repurchased | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased As Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Approximate Dollar Value of the Purchase | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares That May Yet be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs | |||||||||||||
| 3/1/2020 - 3/31/2020 | 1,437,996 | $ | 15.34 | 1,437,996 | $ | 22,065,953 | $ | 127,934,047 | |||||||||
| 1,437,996 | $ | 15.34 | 1,437,996 | $ | 22,065,953 | $ | 127,934,047 | ||||||||||
Share Performance Graph
The following graph and table set forth certain information comparing the yearly percentage change in cumulative total return on our common stock to the cumulative total return of the Standard & Poor’s Composite-500 Stock Index or S&P 500 Index, and the Bloomberg REIT Mortgage Index, or BBG REIT Index, an industry index of mortgage REITs. The comparison is for the period from December 31, 2015 to December 31, 2020 and assumes the reinvestment of dividends. The graph and table assume that $100 was invested in our common stock and each of the two other indices on December 31, 2015.
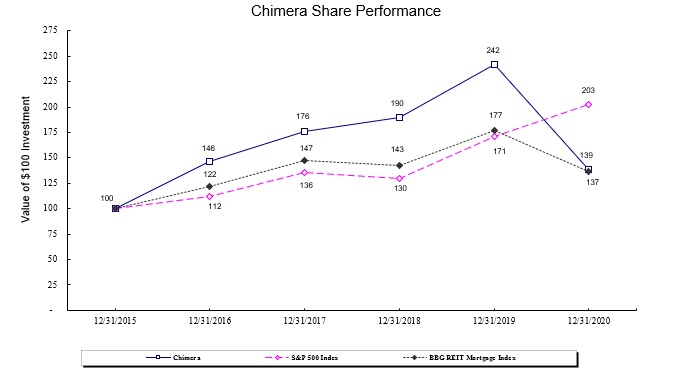
| 12/31/2015 | 12/31/2016 | 12/31/2017 | 12/31/2018 | 12/31/2019 | 12/31/2020 | |||||||||||||||
| Chimera | 100 | 146 | 176 | 190 | 242 | 139 | ||||||||||||||
| S&P 500 Index | 100 | 112 | 136 | 130 | 171 | 203 | ||||||||||||||
| BBG REIT Index | 100 | 122 | 147 | 143 | 177 | 137 | ||||||||||||||
The information in the share performance graph and table has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, but neither its accuracy nor its completeness can be guaranteed. The historical information set forth above is not necessarily indicative of future performance. Accordingly, we do not make or endorse any predictions as to future share performance.
The share performance graph and table shall not be deemed, under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, to be (i) “soliciting material” or “filed” or (ii) incorporated by reference by any general statement into any filing made by us with the SEC, except to the extent that we specifically incorporate such share performance graph and table by reference.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
43
The following selected financial data are as of and for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, 2018, 2017 and 2016. The selected financial data should be read in conjunction with the more detailed information contained in the Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes thereto contained in Part IV, Financial Statements, and “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Part II, Item 7, included elsewhere in this 2020 Form 10-K.
| Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition Highlights | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | |||||||||||||||||
| For the year ended | |||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||
| Non-Agency Mortgage-Backed Securities | $ | 2,150,714 | $ | 2,614,408 | $ | 2,486,130 | $ | 2,851,316 | $ | 3,330,063 | |||||||
| Agency RMBS | $ | 90,738 | $ | 6,490,293 | $ | 9,240,057 | $ | 2,329,059 | $ | 2,727,047 | |||||||
| Agency CMBS | $ | 1,740,368 | $ | 2,850,717 | $ | 2,948,893 | $ | 2,035,769 | $ | 1,440,706 | |||||||
| Loans held for investment, at fair value | $ | 13,112,129 | $ | 14,292,815 | $ | 12,572,581 | $ | 13,678,263 | $ | 8,753,653 | |||||||
| Total assets | $ | 17,523,019 | $ | 27,118,671 | $ | 27,708,639 | $ | 21,222,070 | $ | 16,684,908 | |||||||
| Secured financing agreements | $ | 4,636,847 | $ | 13,427,545 | $ | 14,030,465 | $ | 7,250,452 | $ | 5,600,903 | |||||||
| Securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS | $ | 113,433 | $ | 133,557 | $ | 159,955 | $ | 205,780 | $ | 334,124 | |||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, loans held for investment | $ | 8,711,677 | $ | 8,179,608 | $ | 8,455,376 | $ | 9,388,657 | $ | 6,941,097 | |||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 13,743,633 | $ | 23,165,378 | $ | 24,004,810 | $ | 17,587,093 | $ | 13,561,375 | |||||||
| Stockholders' equity | $ | 3,779,386 | $ | 3,953,293 | $ | 3,703,829 | $ | 3,634,977 | $ | 3,123,533 | |||||||
| Book value per common share | $ | 12.36 | $ | 16.15 | $ | 15.90 | $ | 16.85 | $ | 15.87 | |||||||
| Number of shares outstanding | 230,556,760 | 187,226,081 | 187,052,398 | 187,809,288 | 187,739,634 | ||||||||||||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations Highlights | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | |||||||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||
| Interest income | $ | 1,030,250 | $ | 1,361,110 | $ | 1,273,316 | $ | 1,138,758 | $ | 934,068 | |||||||
| Interest expense | $ | 516,181 | $ | 758,814 | $ | 679,108 | $ | 532,748 | $ | 347,857 | |||||||
| Net interest income | $ | 514,069 | $ | 602,296 | $ | 594,208 | $ | 606,010 | $ | 586,211 | |||||||
| Net income | $ | 88,854 | $ | 413,551 | $ | 411,637 | $ | 524,668 | $ | 551,943 | |||||||
| Income per share-basic | $ | 0.07 | $ | 1.82 | $ | 1.97 | $ | 2.62 | $ | 2.93 | |||||||
| Weighted average shares - basic | 212,995,533 | 187,156,990 | 187,146,170 | 187,780,355 | 187,728,634 | ||||||||||||
Core earnings per adjusted diluted common share (1)
|
$ | 1.46 | $ | 2.24 | $ | 2.39 | $ | 2.45 | $ | 2.51 | |||||||
| Weighted Average diluted shares - Core earnings | 229,282,125 | 188,406,444 | 187,748,862 | 188,287,320 | 188,024,838 | ||||||||||||
Dividends declared per share (2)
|
$ | 1.40 | $ | 2.00 | $ | 2.00 | $ | 2.00 | $ | 2.44 | |||||||
(1) Core Earnings is a non-GAAP measure. See discussion of Core Earnings per adjusted diluted common share in Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Core Earnings.
(2) For applicable period as reported in our earnings announcements.
44
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and notes to those statements included in Item 15 of this 2020 Form 10-K. The discussion may contain certain forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Forward-looking statements are those that are not historical in nature. As a result of many factors, such as those set forth under “Risk Factors” in this 2020 Form 10-K, our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in such forward-looking statements.
This section of this 2020 Form 10-K generally discusses 2020 and 2019 items and year-to year comparisons between 2020 and 2019. Discussions of 2018 items and year-to-year comparisons between 2019 and 2018 that are not included in this 2020 Form 10-K can be found in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Part II, Item 7 of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019.
Executive Summary
We are a publicly traded REIT that is primarily engaged in the business of investing in a diversified portfolio of mortgage assets, including residential mortgage loans, Agency RMBS, Non-Agency RMBS, Agency CMBS, and other real estate-related securities. We use leverage to increase returns while managing the difference or spread between longer duration assets and shorter duration financing. Our principal business objective is to deliver shareholder value through the generation of distributable income and through asset performance linked to residential mortgage credit fundamentals. We selectively invest in residential mortgage assets with a focus on credit analysis, projected prepayment rates, interest rate sensitivity and expected return.
We currently focus our investment activities primarily on acquiring residential mortgage loans and Non-Agency and Agency residential and commercial mortgage-backed securities, or MBS. At December 31, 2020, based on the amortized cost balance of our interest earning assets, approximately 79% of our investment portfolio was residential mortgage loans, 10% of our investment portfolio was Agency CMBS, 10% of our investment portfolio was Non-Agency RMBS and 1% of our investment portfolio was Agency IOs. At December 31, 2019, based on the amortized cost balance of our interest earning assets, approximately 55% of our investment portfolio was residential mortgage loans, 26% of our investment portfolio was Agency RMBS, 11% of our investment portfolio was Agency CMBS, and 8% of our investment portfolio was Non-Agency RMBS. The significant change in the composition of our portfolio at December 31, 2020 as compared to December 31, 2019 was driven by the sale of our Agency RMBS portfolio during the first quarter of 2020, as discussed below, as we sought to raise liquidity during the severe market conditions created by the COVID-19 pandemic.
We use leverage to increase returns and to finance the acquisition of our assets. We expect to finance our investments using a variety of financing sources including, when available, securitizations, warehouse facilities, repurchase agreements, structured asset financing and offerings of our securities. We may manage our debt and interest rate risk by utilizing interest rate hedges, such as interest rate swaps, caps, options, swaptions and futures to reduce the effect of interest rate fluctuations related to our financing sources. As of December 31, 2020, we did not own any interest rate hedges.
Our investment strategy is intended to take advantage of opportunities in the current interest rate and credit environment. We expect to adjust our strategy to changing market conditions by shifting our asset allocations across these various asset classes as interest rate and credit cycles change over time. We expect to take a long-term view of assets and liabilities.
Market Conditions and our Strategy
Conditions Related to COVID-19 Pandemic
2020 was a very volatile year driven by the global COVID-19 pandemic and its effects on the broader economy. Through March and April as businesses closed and more people worked from home, normal daily patterns of work, school and daily life changed dramatically. As a result, unemployment skyrocketed, equity markets experienced large declines and interest rates fell. Liquidity and lending from banks to businesses was significantly reduced. These conditions put significant pressure on the mortgage REIT industry due to its reliance on financing operations and repurchase lending from banks. The Federal Reserve assisted with asset purchase programs, government stimulus and monetary policy in the form of low interest rates, and signaled its intent to keep interest rates low. These measures were intended to promote price stability and the smooth functioning of markets.
In the residential loan sector servicers have worked with borrowers to provide different options to keep borrowers in their homes, including modification, deferral and forbearance programs. The residential housing market has shown resilience this year as housing saw strong home price appreciation supported by low mortgage rates and increasing demand as some
45
individuals left cities to buy homes in the suburbs. In addition, as the year progressed, the number of homeowners relying on forbearance programs trended down.
In the second half of 2020, unemployment started to trend down as some businesses reopened. Equities rebounded quickly and fixed income prices improved. The end of the presidential election cycle as well as the news about COVID vaccines provided some stability for financial markets.
Despite improving conditions, there is still significant uncertainty and risks related to COVID-19 and economic conditions. See “Part I. Item 1A Risk Factors” for additional details on COVID pandemic's impact on our business. In particular, our residential mortgage loans and Non-Agency MBS are subject to significant credit risk, and it is unclear how the conditions created by the COVID-19 pandemic may impact the credit quality of these assets over time.
We have been working remotely since March 2020 and expect that to continue. We have the technology in place for all employees to work remotely with limited change in normal working patterns. We have exercised our business continuity plans effectively to date, with limited operational impact.
Portfolio and Financing
Consistent with current market conditions and our intention to enhance our liquidity and strengthen our cash position, we de-levered during the first quarter of 2020 and took steps to manage our portfolio through the unprecedented market volatility and preserve long-term stockholder value, including completing various transactions to reposition our portfolio. Consistent with our business strategy of using our Agency MBS portfolio as a source of liquidity, we sold our Agency RMBS portfolio during the first quarter. The proceeds from the sale were used to pay off debt, reduce leverage and to otherwise strengthen our balance sheet.
While market conditions are challenging, we have continued our business strategy of buying residential mortgage loans and securitizing them. During the year ended December 31, 2020, we purchased $1.9 billion of residential mortgage loans. We sponsored two securitizations of $883 million during the first quarter, two securitizations of $715 million during the second quarter, three securitizations of $1.0 billion during the third quarter, and four securitizations of $1.5 billion during the fourth quarter. These securitizations reduced our warehouse financing risk and resulted in longer term financing by selling senior securities from the securitization trusts.
We have also taken action to limit our exposure to repurchase agreement financing to reduce margin call risk. As of December 31, 2020, our outstanding secured financing agreements which includes repurchase agreements were approximately $4.6 billion, compared to $13.4 billion at December 31, 2019, representing a reduction of approximately 65%. In addition, during 2020 we have obtained $1.2 billion of Non-Agency and loan financing on a non-mark-to-market basis and an additional $251 million on longer term credit financing facilities that mature in 2023 or later. We believe these actions provide more stability to our credit financing strategy. Non-mark-to-market and longer term Non-Agency and loan financing represents approximately 46% of our credit repurchase facilities as of December 31, 2020. Financing for our Agency CMBS portfolio continues to be available at relatively attractive terms, given the current rate environment.
In April 2020, we completed the issuance of $374 million aggregate principal amount of 7.00% convertible senior notes due 2023. After deducting the underwriting discount and offering costs, we received $362 million. At completion of the offering, these notes were convertible at the option of the holder at a conversion rate of 153.8461 common shares per $1,000 principal amount of convertible senior notes (equivalent to a conversion price of $6.50 per common share). Upon conversion of these notes by a holder, the holder receives shares of our common stock. As of December 31, 2020, approximately $321 million of senior notes have been converted into approximately 49 million shares of our common stock. In April 2020, concurrently with the pricing of the Notes, we entered into call option transactions at an initial strike price of approximately $6.50 per share and covered approximately $250 million of the offering. We exercised our capped call options during the fourth quarter of 2020 and received a settlement of 4.7 million shares, which were retired and removed from issued and outstanding shares.
On June 8, 2020, we entered into a $400 million senior secured, non-mark-to-market credit agreement with certain lenders. Pursuant to the credit agreement, we pledged approximately $550 million of existing assets, including approximately $482 million of securities from our sponsored mortgage loan securitizations, related risk retention securities, and resecuritizations. In connection with the credit agreement, we issued warrants to each of the lenders, which provides the lenders the right to purchase up to an aggregate of 20,300,000 shares of our common stock, at a price of $0.01 per share, which represented approximately 7.7% of our common stock after giving effect to the issuance of the warrant shares. We are permitted to settle any exercise of the warrants in cash at a price of 90% of the fair market value of our common stock at the time of exercise.
46
We continue to seek attractive financing terms for the portfolio; however, no assurance can be given as to whether, when or what may be the terms of any such financing.
The steps we discussed above, including selling Agency RMBS and negotiating new financing arrangements, added liquidity to our balance sheet which allowed us to retain investments we deem valuable and difficult to replace. This strategy helped us to participate in the recovery of asset prices from the depressed levels experienced in March to much improved prices and valuations during the second half of 2020. We also have taken advantage of selling certain ACMBS bonds at attractive prices as the market has rallied given recent market stability, Federal Reserve buying programs and stronger financing terms. These actions have led an improvement in book value during the second half of 2020. Our book value per common share was $12.36 as of December 31, 2020, down from $16.15 as of December 31, 2019, but up from $11.91 as of September 30, 2020. Our book value is based on December 31, 2020 issued and outstanding common shares and excludes the warrant shares discussed above.
Common Stock Buyback
On March 13, 2020, we announced a reauthorization of $150 million common stock buyback program. As of December 31, 2020, we had repurchased approximately $22 million of common stock under the program.
2020 Common Stock Dividends
During the year ended December 31, 2020, we declared dividends to common shareholders of $301 million, or $1.40, per share.
We will continue to monitor market conditions and the potential impact the ongoing volatility and uncertainty may have on our business. Our Board of Directors will continue to evaluate the payment of dividends as market conditions evolve, and no definitive determination has been made at this time. While the terms and timing of the approval and declaration of cash dividends, if any, on shares of our capital stock is at the sole discretion of our Board of Directors and we cannot predict how market conditions may evolve, we intend to distribute to our stockholders an amount equal to at least 90% of our REIT taxable income determined before applying the deduction for dividends paid and by excluding net capital gains consistent with our intention to maintain our qualification as a REIT under the Code.
Business Operations
Net Income Summary
The table below presents our net income on a GAAP basis for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
47
| Net Income | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | |||||||||||
| (unaudited) | |||||||||||
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| Net interest income: | |||||||||||
Interest income (1)
|
$ | 1,030,250 | $ | 1,361,110 | $ | 1,273,316 | |||||
Interest expense (2)
|
516,181 | 758,814 | 679,108 | ||||||||
| Net interest income | 514,069 | 602,296 | 594,208 | ||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in provision for credit losses | 180 | — | — | ||||||||
| Net other-than-temporary credit impairment losses | — | (4,853) | (21,791) | ||||||||
| Other investment gains (losses): | |||||||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives | 201,000 | (106,209) | (141,162) | ||||||||
| Realized gains (losses) on terminations of interest rate swaps | (463,966) | (359,726) | — | ||||||||
| Net realized gains (losses) on derivatives | (41,086) | (34,423) | 18,369 | ||||||||
| Net gains (losses) on derivatives | (304,052) | (500,358) | (122,793) | ||||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value | (110,664) | 409,634 | 46,632 | ||||||||
| Net realized gains (losses) on sales of investments | 166,946 | 20,360 | (2,743) | ||||||||
| Gains (losses) on extinguishment of debt | (54,418) | 9,318 | 26,376 | ||||||||
| Total other gains (losses) | (302,188) | (61,046) | (52,528) | ||||||||
| Other expenses: | |||||||||||
| Compensation and benefits | 44,811 | 48,880 | 35,114 | ||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 25,346 | 26,555 | 22,664 | ||||||||
| Servicing fees | 37,464 | 36,290 | 40,773 | ||||||||
| Transaction expenses | 15,068 | 10,928 | 9,610 | ||||||||
| Total other expenses | 122,689 | 122,653 | 108,161 | ||||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 89,012 | 413,744 | 411,728 | ||||||||
| Income taxes | 158 | 193 | 91 | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | 88,854 | $ | 413,551 | $ | 411,637 | |||||
| Dividends on preferred stock | 73,750 | 72,704 | 43,197 | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common shareholders | $ | 15,104 | $ | 340,847 | $ | 368,440 | |||||
| Net income (loss) per share available to common shareholders: | |||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 0.07 | $ | 1.82 | $ | 1.97 | |||||
| Diluted | $ | 0.07 | $ | 1.81 | $ | 1.96 | |||||
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding: | |||||||||||
| Basic | 212,995,533 | 187,156,990 | 187,146,170 | ||||||||
| Diluted | 226,438,341 | 188,406,444 | 187,748,862 | ||||||||
| Dividends declared per share of common stock | $ | 1.40 | $ | 2.00 | $ | 2.00 | |||||
(1) Includes interest income of consolidated VIEs of $683,456, $780,746 and $904,830 for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. See Note 9 to consolidated financial statements for further discussion.
(2) Includes interest expense of consolidated VIEs of $285,142, $337,387 and $395,255 for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. See Note 9 to consolidated financial statements for further discussion.
48
Results of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
Beginning in March 2020, the global COVID-19 pandemic began to impact the U.S. and global economies including the mortgage REIT industry and impacted our business and our results of operations. Because of the size and breadth of the COVID-19 pandemic, all of the direct and indirect consequences of COVID-19 are not yet known and may not emerge for some time. As discussed above, the significant dislocation in the financial markets due to the COVID-19 pandemic has caused a sharp decrease in interest rates, credit spread widening and an unprecedented illiquidity in secured financing agreements and MBS markets which in turn has negatively affected asset pricing on our portfolio.
We have taken steps to respond to current market conditions, enhance our liquidity and strengthen our cash position by, among other things, selling our Agency RMBS portfolio and using the proceeds to pay off debt and terminate hedging, closing eight securitizations and reducing short term repurchase agreement financing risk and establishing longer term financing. However, the COVID-19 pandemic and related disruptions in the real estate and financial markets have negatively affected and is expected to continue to negatively affect our business. We have also adopted current expected credit losses (or CECL) accounting guidance beginning January 1, 2020. The factors described above and throughout this Annual Report on Form 10-K (particularly as related to COVID-19) have driven the majority of our results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2020 and are expected to continue to impact our results of operations in future periods. Thus, our results of operations should be read and viewed in the context of these unprecedented conditions and related future uncertainty.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, our net income available to common shareholders was $15 million, or $0.07 per average basic common share, compared to $341 million, or $1.82 per average basic common share, for the same period in 2019. The lower net income available to common shareholders for the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to December 31, 2019 was primarily due to portfolio repositioning efforts and decreasing asset prices in our portfolio because of the COVID-19 pandemic and related illiquidity and volatility experienced in financial markets. We had net losses on derivatives of $304 million, net unrealized losses on financial instruments at fair value of $111 million and losses on extinguishment of debt of $54 million, partially offset by net interest income of $514 million and gains on sales of investments of $167 million during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Interest Income
The changes in our interest income for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period in 2019, are primarily driven by the selling of our Agency RMBS portfolio and adoption of CECL guidance.
Interest income decreased by $331 million, or 24%, to $1.0 billion for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to $1.4 billion for the same period in 2019. The decline in interest income for the year ended December 31, 2020 is primarily due to the sale of the Agency RMBS portfolio to respond to current market conditions driven by COVID-19 disruptions. The sale of the Agency RMBS portfolio reduced our interest income earned on Agency RMBS by $246 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period in 2019. Additionally, interest income on our Non-Agency RMBS investments decreased by approximately $67 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period in 2019, driven mostly by lower yields due in part to the adoption of CECL guidance and a decrease in Non-Agency RMBS asset balances from paydowns and some losses.
Interest Expense
Interest expense decreased by $243 million, or 32%, to $516 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to $759 million for the same period in 2019. The decline in interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period in 2019, was primarily driven by Federal Funds rate cuts, a reduction on secured financing agreements collateralized by Agency MBS and lower borrowing rates on our Securitized Debt collateralized by Loans held for investments. While balances declined as leverage was reduced and secured financing rates on borrowings collateralized by Agency securities fell, rates on borrowings collateralized by non-agency securities increased due to limited liquidity and implied risk, as many of the non-agency securities we own are in the first loss tranche and the future value for these securities is uncertain given COVID -19 impacts, modification, deferral and forbearance programs.
Interest expense for GAAP reporting does not include the periodic costs of our derivatives, which are reported separately in our GAAP financial statements.
Economic Net Interest Income
Our “Economic net interest income” is a non-GAAP financial measure that equals GAAP net interest income excluding net realized gains or losses on interest rate swaps, interest expense on long term debt and any interest earned on cash. Realized
49
gains or losses on our interest rate swaps are the periodic net settlement payments made or received. For the purpose of computing Economic net interest income and ratios relating to cost of funds measures throughout this section, interest expense includes net payments on our interest rate swaps, which is presented as a part of Net realized gains (losses) on derivatives in our Consolidated Statements of Operations. Interest rate swaps are used to manage the increase in interest paid on secured financing agreements in a rising rate environment. Presenting the net contractual interest payments on interest rate swaps with the interest paid on interest-bearing liabilities reflects our total contractual interest payments. We believe this presentation is useful to investors because it depicts the economic value of our investment strategy by showing all components of interest expense and net interest income. However, Economic net interest income should not be viewed in isolation and is not a substitute for net interest income computed in accordance with GAAP. Where indicated, interest expense, including interest payments on interest rate swaps, is referred to as Economic interest expense. Where indicated, net interest income reflecting interest payments on interest rate swaps, is referred to as Economic net interest income.
The following table reconciles the Economic net interest income to GAAP Net interest income for the periods presented.
| GAAP Interest Income |
GAAP Interest Expense |
Net Realized (Gains) Losses on Interest Rate Swaps |
Interest Expense on Long Term Debt | Economic Interest Expense |
GAAP Net Interest Income |
Net Realized Gains (Losses) on Interest Rate Swaps |
Other (1)
|
Economic Net Interest Income |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2020 | $ | 1,030,250 | $ | 516,181 | $ | 6,385 | $ | (7,082) | $ | 515,484 | $ | 514,069 | $ | (6,385) | $ | 5,755 | $ | 513,439 | |||||||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2019 | $ | 1,361,110 | $ | 758,814 | $ | (3,012) | $ | — | $ | 755,802 | $ | 602,296 | $ | 3,012 | $ | (7,938) | $ | 597,370 | |||||||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | $ | 1,273,316 | $ | 679,108 | $ | 1,488 | $ | — | $ | 680,596 | $ | 594,208 | $ | (1,488) | $ | 760 | $ | 593,480 | |||||||||||||||||
| For the Quarter Ended December 31, 2020 | $ | 236,156 | $ | 120,285 | $ | — | $ | (1,197) | $ | 119,088 | $ | 115,871 | $ | — | $ | 1,177 | $ | 117,048 | |||||||||||||||||
| For the Quarter Ended September 30, 2020 | $ | 247,905 | $ | 124,557 | $ | — | $ | (1,495) | $ | 123,062 | $ | 123,348 | $ | — | $ | 1,487 | $ | 124,835 | |||||||||||||||||
| For the Quarter Ended June 30, 2020 | $ | 245,922 | $ | 129,256 | $ | — | $ | (4,391) | $ | 124,865 | $ | 116,666 | $ | — | $ | 4,358 | $ | 121,024 | |||||||||||||||||
| For the Quarter Ended March 31, 2020 | $ | 300,266 | $ | 142,083 | $ | 6,385 | $ | — | $ | 148,468 | $ | 158,183 | $ | (6,385) | $ | (1,266) | $ | 150,532 | |||||||||||||||||
(1) Primarily interest expense on Long term debt and interest income on cash and cash equivalents.
Net Interest Rate Spread
The following table shows our average earning assets held, interest earned on assets, yield on average interest earning assets, average debt balance, economic interest expense, economic average cost of funds, economic net interest income and net interest rate spread for the periods presented.
50
| For the Quarter Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Balance |
Interest | Average Yield/Cost |
Average Balance |
Interest | Average Yield/Cost |
||||||||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-earning assets (1):
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | $ | 121,440 | $ | 479 | 1.6 | % | $ | 7,417,646 | $ | 63,108 | 3.4 | % | |||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | 1,455,855 | 15,400 | 4.2 | % | 2,298,601 | 24,856 | 4.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | 1,650,268 | 56,259 | 13.6 | % | 1,976,632 | 81,429 | 16.5 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment | 12,770,508 | 163,998 | 5.1 | % | 12,851,351 | 169,605 | 5.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 15,998,071 | $ | 236,136 | 5.9 | % | $ | 24,544,230 | $ | 338,998 | 5.5 | % | |||||||||||
| Liabilities and stockholders' equity: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secured financing agreements collateralized by: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | $ | 71,689 | $ | 173 | 1.0 | % | $ | 7,015,513 | $ | 37,949 | 2.2 | % | |||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | 1,323,972 | 738 | 0.2 | % | 2,272,069 | 14,819 | 2.6 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | 1,069,348 | 13,797 | 5.2 | % | 1,404,981 | 11,466 | 3.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment | 2,200,314 | 26,627 | 4.8 | % | 3,786,840 | 33,781 | 3.6 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Securitized debt | 8,630,854 | 77,753 | 3.6 | % | 7,758,406 | 76,597 | 3.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 13,296,177 | $ | 119,088 | 3.6 | % | $ | 22,237,809 | $ | 174,612 | 3.1 | % | |||||||||||
| Economic net interest income/net interest rate spread | $ | 117,048 | 2.3 | % | $ | 164,386 | 2.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Net interest-earning assets/net interest margin | $ | 2,701,894 | 2.9 | % | $ | 2,306,421 | 2.7 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Ratio of interest-earning assets to interest bearing liabilities | 1.20 | 1.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) Interest-earning assets at amortized cost | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (2) Interest includes net cash paid/received on swaps | |||||||||||||||||||||||
51
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Balance |
Interest | Average Yield/Cost |
Average Balance |
Interest | Average Yield/Cost |
||||||||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-earning assets (1):
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | $ | 1,519,071 | $ | 44,319 | 2.9 | % | $ | 8,544,127 | $ | 290,389 | 3.4 | % | |||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | 1,909,846 | 81,831 | 4.3 | % | 2,167,044 | 83,558 | 3.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | 1,745,703 | 231,099 | 13.2 | % | 1,913,792 | 297,948 | 15.6 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment | 13,140,311 | 671,674 | 5.1 | % | 12,255,009 | 681,277 | 5.6 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 18,314,931 | $ | 1,028,923 | 5.6 | % | $ | 24,879,972 | $ | 1,353,172 | 5.4 | % | |||||||||||
| Liabilities and stockholders' equity: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secured financing agreements collateralized by: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | $ | 1,407,713 | $ | 27,723 | 2.0 | % | $ | 8,062,881 | $ | 197,624 | 2.5 | % | |||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | 1,818,721 | 16,585 | 0.9 | % | 1,993,372 | 55,793 | 2.8 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | 1,220,248 | 63,366 | 5.2 | % | 1,308,615 | 49,726 | 3.8 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment | 2,869,663 | 114,669 | 4.0 | % | 3,127,518 | 115,272 | 3.7 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Securitized debt | 8,449,048 | 293,141 | 3.5 | % | 7,977,011 | 337,387 | 4.2 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 15,765,393 | $ | 515,484 | 3.3 | % | $ | 22,469,397 | $ | 755,802 | 3.4 | % | |||||||||||
| Economic net interest income/net interest rate spread | $ | 513,439 | 2.3 | % | $ | 597,370 | 2.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Net interest-earning assets/net interest margin | $ | 2,549,538 | 2.8 | % | $ | 2,410,575 | 2.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Ratio of interest-earning assets to interest bearing liabilities | 1.16 | 1.11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) Interest-earning assets at amortized cost | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (2) Interest includes net cash paid/received on swaps | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Economic Net Interest Income and the Average Earning Assets
Our Economic net interest income (which is a non-GAAP measure, see “Economic net interest income” discussion earlier for details) decreased by $84 million to $513 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $597 million for the same period of 2019. Our net interest rate spread, which equals the yield on our average interest-earning assets less the economic average cost of funds, increased by 30 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period of 2019. The net interest margin, which equals the Economic net interest income as a percentage of the net average balance of our interest-earning assets less our interest-bearing liabilities, increased by 40 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period of 2019. Our Average net interest-earning assets increased by $139 million to $2.5 billion for the year ended December 31, 2020, compared to $2.4 billion for the same period of 2019. The increase in our net interest rate spread and net interest margin is primarily due to the change in our portfolio composition. We sold lower yielding Agency assets and retained higher yielding Non-Agency RMBS and Loans. Following the sale of our Agency RMBS portfolio in the first quarter of 2020, we expect that our total Economic net interest income will decline over the near term as our interest earnings asset balances will be lower and financing expenses are expected to be higher.
Economic Interest Expense and the Cost of Funds
The borrowing rate at which we are able to finance our assets using secured financing agreements and securitized debt is typically correlated to LIBOR and the term of the financing. The table below shows our average borrowed funds, Economic interest expense, average cost of funds (inclusive of realized losses on interest rate swaps), average one-month LIBOR, average three-month LIBOR and average one-month LIBOR relative to average three-month LIBOR.
52
| Average Debt Balance |
Economic Interest Expense (1)
|
Average Cost of Funds | Average One-Month LIBOR | Average Three-Month LIBOR | Average One-Month LIBOR Relative to Average Three-Month LIBOR | |||||||||||||||
| (Ratios have been annualized, dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| For The Year Ended December 31, 2020 | $ | 15,765,393 | $ | 515,484 | 3.27 | % | 0.52 | % | 0.65 | % | (0.13) | % | ||||||||
| For The Year Ended December 31, 2019 | $ | 22,469,397 | $ | 755,802 | 3.36 | % | 2.22 | % | 2.33 | % | (0.11) | % | ||||||||
| For The Year Ended December 31, 2018 | $ | 18,901,451 | $ | 680,596 | 3.60 | % | 2.02 | % | 2.30 | % | (0.28) | % | ||||||||
| For The Quarter Ended December 31, 2020 | $ | 13,296,177 | $ | 119,088 | 3.58 | % | 0.15 | % | 0.22 | % | (0.07) | % | ||||||||
| For The Quarter Ended September 30, 2020 | $ | 13,981,065 | $ | 123,062 | 3.52 | % | 0.16 | % | 0.25 | % | (0.09) | % | ||||||||
| For The Quarter Ended June 30, 2020 | $ | 14,995,904 | $ | 124,865 | 3.33 | % | 0.35 | % | 0.60 | % | (0.25) | % | ||||||||
| For The Quarter Ended March 31, 2020 | $ | 19,834,389 | $ | 148,468 | 2.99 | % | 1.40 | % | 1.53 | % | (0.13) | % | ||||||||
(1) Includes effect of realized losses on interest rate swaps.
Average interest-bearing liabilities decreased by $6.7 billion for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period of 2019. Economic interest expense decreased by $240 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period of 2019. The decrease in average interest-bearing liabilities and Economic interest expense is a result of the decrease in the amount of our secured financing agreements collateralized by Agency MBS, the decrease in average one-month and three-month LIBOR, and the sale of our Agency RMBS portfolio during first quarter of 2020. While we may use interest rate hedges to mitigate changes in interest rate risks, the hedges may not fully offset interest expense movements.
Provision for Credit Losses
On January 1, 2020 we adopted accounting standards update (or ASU) No. 2016-13, Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, which replaced incurred credit loss model to a current expected credit loss (or CECL) model for financial instruments measured at amortized cost and required us to record reserves for available-for-sale (or AFS) debt securities for all expected (rather than incurred) credit losses of the asset rather than reduce the carrying amount, as we did under the old other than temporary impairment (or OTTI) model. This update also revised the accounting model for purchased credit-impaired debt securities. The changes in the loss reserves created in accordance with this update have been recorded in earnings. Expected credit losses were limited to the amount of the unrealized loss on the debt securities impacted by the update. We did not record expected credit losses where the debt security was in an unrealized gain position.
The update did not have any impact on financial instruments which were carried at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings. The update required us to record a cumulative-effect adjustment related to the financial instruments under the scope of this update to the statement of financial position at the effective date. As all financial instruments impacted by the update were in an unrealized gain position as of the transition date, there was no impact on the financial statements on transition date and no cumulative-effect adjustment was required. For the year ended December 31, 2020, we recorded an increase in provision for credit losses of $180 thousand. The increase in provision for credit losses was primarily driven by changes in expected losses and delinquencies during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Net Gains (losses) on derivatives
As discussed earlier, we removed all of our derivative positions during the first quarter of 2020 in response to market disruptions driven by COVID-19. Our interest rate swaps are primarily used to economically hedge the effects of changes in interest rates on our portfolio, specifically our secured financing agreements. Therefore, we included the periodic interest costs of the interest rate swaps for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 on these economic hedges in our presentation of economic net interest income and our net interest spreads. As we do not account for these as hedges for GAAP presentation, we present these gains and losses separately in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The increase in the net periodic interest cost of the interest rate swaps during the year ended December 31, 2020 are primarily due to lower floating receive rates driven by lower LIBOR rates, compared to fixed higher pay rates on our swap portfolio as compared to the same period of 2019.
The table below shows a summary of our net gains (losses) on derivative instruments, for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
53
| For the Years Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Periodic interest income (expense) on interest rate swaps, net | $ | (6,386) | $ | 3,013 | $ | (1,488) | |||||
| Realized gains (losses) on derivative instruments, net: | |||||||||||
| Swaps Terminations | (463,966) | (359,726) | — | ||||||||
| Treasury Futures | (34,700) | (37,032) | 21,333 | ||||||||
| Swaptions | — | (404) | (1,476) | ||||||||
| Total realized gains (losses) on derivative instruments, net | (498,666) | (397,162) | 19,857 | ||||||||
| Unrealized gains (losses) on derivative instruments, net: | |||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps | 204,611 | (122,272) | (125,595) | ||||||||
| Treasury Futures | (3,611) | 16,986 | (16,928) | ||||||||
| Swaptions | — | (923) | 1,361 | ||||||||
| Total unrealized gains (losses) on derivative instruments, net: | 201,000 | (106,209) | (141,162) | ||||||||
| Total gains (losses) on derivative instruments, net | $ | (304,052) | $ | (500,358) | $ | (122,793) | |||||
The net gains and losses on our derivatives include both unrealized and realized gains and losses. Realized gains and losses include the net cash paid and received on our interest rate swaps during the period as well as sales and settlements of our Treasury Futures and swaptions. All of our interest rate swaps pay a fixed rate of interest and receive a floating rate of interest. Therefore, as the floating rate leg of the swap declines, the fair value of the interest rate swaps also declines.
Unrealized gains and losses include the change in market value, period over period, on our derivatives portfolio, including reversals of any mark-to-market losses taken on derivatives in prior periods upon settlement. During the year ended December 31, 2020, we recognized total net losses on derivatives of $304 million, compared to net losses on derivatives of $500 million during the same period of 2019. This was primarily driven by realized losses on swap terminations and changes to the yield curve which resulted in realized and unrealized losses on interest rate swaps in 2020 and 2019.
We paid $464 million to terminate interest rate swaps with a notional value of $4.1 billion during the year ended December 31, 2020. The terminated swaps had original maturities of 2023 to 2048. During the year ended December 31, 2019, we terminated interest rate swap agreements with a notional value of $6.4 billion.
We closed our short Treasury futures positions during the first quarter of 2020. We had net realized losses of $37 million on our short Treasury futures positions for the year ended December 31, 2019. The realized loss on Treasury futures was driven by the declines in interest rates which reduces the value of our short Treasury futures. Treasury futures are not included in our economic interest expense and economic net interest income. We closed our swaption position during the year ended December 31, 2019.
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) on Financial Instruments at Fair Value
The disruptions of the financial markets due to the COVID-19 pandemic caused credit spread widening, a sharp decrease in interest rates and unprecedented illiquidity in secured financing agreements and MBS markets during the first half of 2020. These conditions have moderately stabilized during the second half of 2020 and help recover some of the mark to market losses we experienced during the first half of 2020. We recorded Net unrealized losses on financial instruments at fair value of $111 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. For the year ended December 31, 2019 we recorded Net unrealized gains on financial instruments at fair value of $410 million.
Gains and Losses on Sales of Assets and Extinguishment of Securitized Debt
We do not forecast sales of investments as we generally expect to invest for long term gains. However, from time to time, we may sell assets to create liquidity necessary to pursue new opportunities, achieve targeted leverage ratios as well as for gains when prices indicate a sale is most beneficial to us, or is the most prudent course of action to maintain a targeted risk adjusted yield for our investors.
54
In response to the current disruptions in the financial market and to strengthen our liquidity position, we sold all of our Agency RMBS portfolio during the first quarter of 2020. Additionally, we sold some of our Agency CMBS and Non-Agency RMBS investments during the second and third quarter of 2020. We had net realized gains on sales of investments of $167 million and $20 million during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
When we acquire our outstanding securitized debt, we extinguish the outstanding debt and recognize a gain or loss based on the difference between the carrying value of the debt and the cost to acquire the debt which is reflected in the Consolidated Statements of Operations as a gain or loss on extinguishment of debt. During the year ended December 31, 2020, we did not acquire any securitized debt collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS. During the year ended December 31, 2019, we acquired securitized debt collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS with an amortized cost balance of $2.9 million for $3.5 million. This transaction resulted in net loss on extinguishment of debt of $608 thousand.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, we acquired securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investment with an amortized cost balance of $785 million for $784 million. This transaction resulted in net gain on extinguishment of debt of $1 million. We did not acquire any securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investments during the year ended December 31, 2019.
During the first quarter of 2020, we transferred Non-Agency RMBS investments with a market value of $135 million to a third party. As part of the transfer, we purchased an option to re-acquire these assets for a fixed price at a future date. This transfer was accounted for as a secured borrowing within the Secured financing agreements on the Statement of Financial Condition. During the third quarter of 2020, we exercised our option and repurchased the transferred investments with an amortized cost of $196 million for $251 million, which extinguished the secured borrowing. This transaction resulted in a loss on extinguishment of debt of $55 million.
Long Term Debt Expense
During second quarter of 2020, we issued $374 million aggregate principal amount of 7.00% convertible senior notes due 2023 that pays semi-annual interest. As of December 31, 2020, approximately $321 million of senior notes were converted into approximately 49 million shares of our common stock. At December 31, 2020, the outstanding principal amount of these notes was $53 million and the accrued interest payable on the debt was $1 million. At December 31, 2020, the unamortized deferred debt issuance cost was $1 million and the net interest expense was $7 million.
Compensation, General and Administrative Expenses and Transaction Expenses
The table below shows our total compensation and benefit expense, general and administrative, or G&A expenses, and transaction expenses as compared to average total assets and average equity for the periods presented.
| Total Compensation, G&A and Transaction Expenses | Total Compensation, G&A and Transaction Expenses/Average Assets | Total Compensation, G&A and Transaction Expenses/Average Equity | |||||||||
| (Ratios have been annualized, dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| For The Year Ended December 31, 2020 | $ | 85,225 | 0.42 | % | 2.36 | % | |||||
| For The Year Ended December 31, 2019 | $ | 86,362 | 0.31 | % | 2.21 | % | |||||
| For The Year Ended December 31, 2018 | $ | 67,388 | 0.28 | % | 1.81 | % | |||||
| For The Quarter Ended December 31, 2020 | $ | 21,459 | 0.48 | % | 2.30 | % | |||||
| For The Quarter Ended September 30, 2020 | $ | 18,722 | 0.41 | % | 2.11 | % | |||||
| For The Quarter Ended June 30, 2020 | $ | 21,527 | 0.46 | % | 2.59 | % | |||||
| For The Quarter Ended March 31, 2020 | $ | 23,518 | 0.41 | % | 2.61 | % | |||||
Compensation and benefit costs were $45 million and $49 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The decrease in Compensation and benefit costs were primarily driven by lower bonus and stock based compensation.
G&A expenses were $25 million and $27 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The G&A expenses are primarily comprised of legal, market data and research, auditing, consulting, information technology, and independent investment consulting expenses.
55
We incurred transaction expenses in relation to securitizations of $15 million and $11 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The increase in transaction expenses for the year ended December 31, 2020 is driven by higher securitization activity during the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the same period of 2019.
Servicing Fees
Servicing fees expenses were $37 million and $36 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. These servicing fees are primarily related to the servicing costs of the whole loans held in consolidated securitization vehicles and are paid from interest income earned by the VIEs. The servicing fees generally range from 11 to 50 basis points of unpaid principal balances of our consolidated VIEs.
Core earnings
Core earnings is a non-GAAP measure and is defined as GAAP net income excluding unrealized gains on the aggregate portfolio, provision for credit losses, interest expense on long term debt, impairment losses, realized gains on sales of investments, realized gains or losses on futures, realized gains or losses on swap terminations, gain on deconsolidation, extinguishment of debt and expenses incurred in relation to securitizations. In addition, stock compensation expense charges incurred on awards to retirement eligible employees is reflected as an expense over a vesting period (36 months) rather than reported as an immediate expense.
As defined, core earnings include interest income and expense, as well as periodic cash settlements on interest rate swaps used to hedge interest rate risk and other expenses. Core earnings is inclusive of preferred dividend charges, compensation and benefits (adjusted for awards to retirement eligible employees), general and administrative expenses, servicing fees, as well as income tax expenses incurred during the period. Management believes that the presentation of core earnings provides investors with a useful measure but has important limitations. We believe core earnings as described above helps us evaluate our financial performance period over period without the impact of certain transactions but is of limited usefulness as an analytical tool. Therefore, core earnings should not be viewed in isolation and is not a substitute for net income or net income per basic share computed in accordance with GAAP. In addition, our methodology for calculating core earnings may differ from the methodologies employed by other REITs to calculate the same or similar supplemental performance measures, and accordingly, our reported core earnings may not be comparable to the core earnings reported by other REITs.
The following table provides GAAP measures of net income and net income per diluted share available to common stockholders for the periods presented and details with respect to reconciling the line items to core earnings and related per average diluted common share amounts. The Core earnings is presented on an adjusted dilutive shares basis. Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current period's presentation.
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | |||||||||||
| GAAP Net income available to common stockholders | 15,104 | $ | 340,847 | $ | 368,440 | ||||||
| Adjustments: | |||||||||||
| Interest expense on long term debt | 7,083 | — | — | ||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in provision for credit losses/OTTI | 180 | 4,853 | 21,791 | ||||||||
| Net unrealized (gains) losses on derivatives | (201,000) | 106,209 | 141,162 | ||||||||
| Net unrealized (gains) losses on financial instruments at fair value | 110,664 | (409,634) | (46,632) | ||||||||
| Net realized (gains) losses on sales of investments | (166,946) | (20,360) | 2,743 | ||||||||
| (Gains) losses on extinguishment of debt | 54,418 | (9,318) | (26,376) | ||||||||
| Realized (gains) losses on terminations of interest rate swaps | 463,966 | 359,726 | — | ||||||||
Net realized (gains) losses on derivatives - Futures(1)
|
34,700 | 37,032 | (21,333) | ||||||||
| Transaction Expenses | 15,068 | 10,928 | 9,610 | ||||||||
| Stock Compensation expense for retirement eligible rewards | 414 | 1,199 | 99 | ||||||||
| Core Earnings | 333,651 | $ | 421,482 | $ | 449,504 | ||||||
| GAAP net income per diluted common share | $ | 0.07 | $ | 1.82 | $ | 1.97 | |||||
| Core earnings per adjusted diluted common share (2) | $ | 1.46 | $ | 2.24 | $ | 2.39 | |||||
| (1) Included in net realized gains (losses) on derivatives in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. | |||||||||||
| (2) We note that core and taxable earnings will typically differ, and may materially differ, due to differences on realized gains and losses on investments and related hedges, credit loss recognition, | |||||||||||
| timing differences in premium amortization, accretion of discounts, equity compensation and other items. | |||||||||||
56
The table below summarizes the reconciliation from weighted-average diluted shares under GAAP to the weighted average adjusted diluted shares used for Core Earnings for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
| For the Years Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| Weighted Average diluted shares - GAAP | 226,438,341 | 188,406,444 | 187,748,862 | ||||||||
| Conversions from Convertible Debt | 14,259,495 | — | — | ||||||||
| Non-participating Warrants | (11,415,711) | — | — | ||||||||
| Weighted Average diluted shares - Core earnings | 229,282,125 | 188,406,444 | 187,748,862 | ||||||||
| For the Quarters Ended | |||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | September 30, 2020 | June 30, 2020 | March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | |||||||||||||||||
| GAAP Net income available to common stockholders | $ | 128,797 | $ | 348,891 | $ | (73,393) | $ | (389,193) | $ | 111,881 | |||||||
| Adjustments: | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense on long term debt | 1,197 | 1,495 | 4,391 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in provision for credit losses | 13 | (1,650) | (4,497) | 6,314 | — | ||||||||||||
| Net unrealized (gains) losses on derivatives | — | — | — | (201,000) | (83,656) | ||||||||||||
| Net unrealized (gains) losses on financial instruments at fair value | (61,379) | (260,766) | 171,921 | 260,887 | 112,751 | ||||||||||||
| Net realized (gains) losses on sales of investments | 329 | (65,041) | (26,380) | (75,854) | (17,687) | ||||||||||||
| (Gains) losses on extinguishment of debt | (919) | 55,794 | (459) | — | (9,926) | ||||||||||||
| Realized (gains) losses on terminations of interest rate swaps | — | — | — | 463,966 | 8,353 | ||||||||||||
Net realized (gains) losses on Futures (1)
|
— | — | — | 34,700 | (8,229) | ||||||||||||
| Transaction expenses | 3,827 | 1,624 | 4,710 | 4,906 | 6,639 | ||||||||||||
| Stock Compensation expense for retirement eligible awards | (225) | (275) | (273) | 1,189 | (45) | ||||||||||||
| Core Earnings | $ | 71,640 | $ | 80,072 | $ | 76,020 | $ | 105,915 | $ | 120,081 | |||||||
| GAAP net income per diluted common share | $ | 0.49 | $ | 1.32 | $ | (0.37) | $ | (2.08) | $ | 0.59 | |||||||
Core earnings per adjusted diluted common share (2)
|
$ | 0.29 | $ | 0.33 | $ | 0.32 | $ | 0.56 | $ | 0.64 | |||||||
| (1) Included in net realized gains (losses) on derivatives in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. | |||||||||||||||||
| (2) We note that core and taxable earnings will typically differ, and may materially differ, due to differences on realized gains and losses on investments and related hedges, credit loss recognition, | |||||||||||||||||
| timing differences in premium amortization, accretion of discounts, equity compensation and other items. | |||||||||||||||||
The table below summarizes the reconciliation from weighted-average diluted shares under GAAP to the weighted average adjusted diluted shares used for Core Earnings for the periods reported below.
| For the Quarters Ended | |||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | September 30, 2020 | June 30, 2020 | March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||
| Weighted Average diluted shares - GAAP | 264,882,701 | 265,346,359 | 199,282,790 | 187,018,602 | 188,622,919 | ||||||||||||
| Conversions from Convertible Debt | — | — | 42,910,191 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Non-participating Warrants | (20,278,970) | (20,277,134) | (4,901,962) | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Weighted Average diluted shares - Core earnings | 244,603,731 | 245,069,225 | 237,291,019 | 187,018,602 | 188,622,919 | ||||||||||||
Our core earnings for the year ended December 31, 2020 were $334 million, or $1.46 per average diluted common share and declined by $87 million, or $0.78 per average diluted common share, as compared to $421 million, or $2.24 per average diluted common share, for the year ended December 31, 2019. The decline in core earnings was driven by decline in interest income driven by sale of our Agency RMBS portfolio and higher diluted common shares denominator due to conversions of convertible debt into common shares.
Net Income (Loss) and Return on Total Stockholders' Equity
57
The table below shows our Net Income and Economic Net Interest Income as a percentage of average stockholders' equity and Core Earnings as a percentage of average common stockholders' equity. Return on average equity is defined as our GAAP net income (loss) as a percentage of average equity. Average equity is defined as the average of our beginning and ending stockholders' equity balance for the period reported. Economic Net Interest Income and Core Earnings are non-GAAP measures as defined in previous sections.
| Return on Average Equity | Economic Net Interest Income/Average Equity * | Core Earnings/Average Common Equity | |||||||||
| (Ratios have been annualized) | |||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2020 | 2.46 | % | 14.21 | % | 12.43 | % | |||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2019 | 10.56 | % | 15.26 | % | 13.93 | % | |||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | 11.08 | % | 15.98 | % | 14.31 | % | |||||
| For the Quarter Ended December 31, 2020 | 15.76 | % | 12.53 | % | 10.21 | % | |||||
| For the Quarter Ended September 30, 2020 | 41.43 | % | 14.08 | % | 12.24 | % | |||||
| For the Quarter Ended June 30, 2020 | (6.62) | % | 14.58 | % | 12.72 | % | |||||
| For the Quarter Ended March 31, 2020 | (41.21) | % | 16.73 | % | 15.88 | % | |||||
* Includes effect of realized losses on interest rate swaps and excludes long term debt expense.
Return on average equity decreased by 810 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to the same period of 2019, driven mostly by unrealized mark to market losses on our financial instruments due to COVID-19 related market disruptions. Economic net interest income as a percentage of average equity decreased by 105 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019. Core earnings as a percentage of average common equity decreased by 150 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the same period of 2019. This decrease was primarily driven by decline in interest income due to the sale of our Agency RMBS portfolio.
Financial Condition
Portfolio Review
In a response to current disruptions in financial markets caused by COVID-19, we have taken steps to enhance our liquidity and strengthen our cash position. We have sold our Agency RMBS portfolio to bolster liquidity and de-lever our balance sheet. We used the proceeds from our Agency MBS sales to pay off related secured financing agreements and derivatives. During the year ended December 31, 2020, on an aggregate basis, we purchased $3.0 billion of investments, sold $8.4 billion of investments and received $2.9 billion in principal payments related to our Agency MBS, Non-Agency RMBS and Loans held for investments portfolio.
The following table summarizes certain characteristics of our portfolio at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
58
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
Interest earning assets at period-end (1)
|
$ | 17,093,949 | $ | 26,248,233 | ||||
| Interest bearing liabilities at period-end | $ | 13,513,580 | $ | 21,740,710 | ||||
| GAAP Leverage at period-end | 3.6:1 | 5.5:1 | ||||||
| GAAP Leverage at period-end (recourse) | 1.2:1 | 3.4:1 | ||||||
| Portfolio Composition, at amortized cost | ||||||||
Non-Agency RMBS |
10.2 | % | 7.9 | % | ||||
Senior |
5.0 | % | 4.5 | % | ||||
Subordinated |
3.6 | % | 2.2 | % | ||||
Interest-only |
1.6 | % | 1.2 | % | ||||
Agency RMBS |
0.7 | % | 25.7 | % | ||||
Pass-through |
— | % | 25.1 | % | ||||
Interest-only |
0.7 | % | 0.6 | % | ||||
Agency CMBS |
10.0 | % | 11.0 | % | ||||
Project loans |
9.9 | % | 10.8 | % | ||||
Interest-only |
0.1 | % | 0.2 | % | ||||
| Loans held for investment | 79.1 | % | 55.4 | % | ||||
Fixed-rate percentage of portfolio |
94.9 | % | 95.9 | % | ||||
Adjustable-rate percentage of portfolio |
5.1 | % | 4.1 | % | ||||
(1) Excludes cash and cash equivalents.
GAAP leverage at period-end is calculated as a ratio of our secured financing agreements and securitized debt liabilities over GAAP book value. GAAP recourse leverage is calculated as a ratio of our secured financing agreements over stockholders equity.
The following table presents details of each asset class in our portfolio at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019. The principal or notional value represents the interest income earning balance of each class. The weighted average figures are weighted by each investment’s respective principal/notional value in the asset class.
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Principal or Notional Value at Period-End (dollars in thousands) |
Weighted Average Amortized Cost Basis | Weighted Average Fair Value | Weighted Average Coupon |
Weighted Average Yield at Period-End (1)
|
Weighted Average 3 Month Prepay Rate at Period-End | Weighted Average 12 Month Prepay Rate at Period-End | Weighted Average 3 Month CDR at Period-End | Weighted Average 12 Month CDR at Period-End |
Weighted Average Loss Severity(2)
|
Weighted Average Credit Enhancement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency Mortgage-Backed Securities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior |
$ | 1,560,136 | $ | 50.65 | $ | 81.90 | 4.5 | % | 16.9 | % | 13.4 | % | 11.0 | % | 2.8 | % | 2.9 | % | 47.2 | % | 2.8 | % | |||||||||||||
Subordinated |
$ | 905,674 | $ | 62.46 | $ | 67.43 | 3.8 | % | 6.3 | % | 16.0 | % | 12.5 | % | 0.8 | % | 0.7 | % | 22.1 | % | 3.3 | % | |||||||||||||
Interest-only |
$ | 5,628,240 | $ | 4.43 | $ | 4.66 | 1.5 | % | 16.2 | % | 27.3 | % | 23.0 | % | 2.1 | % | 1.8 | % | 27.8 | % | — | % | |||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pass-through |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
$ | 1,262,963 | $ | 9.41 | $ | 7.18 | 1.7 | % | 1.6 | % | 23.8 | % | 20.6 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Project loans |
$ | 1,527,621 | $ | 101.81 | $ | 112.23 | 4.1 | % | 3.8 | % | — | % | — | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
$ | 1,326,665 | $ | 1.78 | $ | 1.95 | 0.6 | % | 8.4 | % | 10.0 | % | 8.0 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment | $ | 12,640,195 | $ | 98.69 | $ | 103.85 | 5.6 | % | 5.2 | % | 11.9 | % | 9.7 | % | 0.9 | % | 1.2 | % | 39.6 | % | N/A | ||||||||||||||
(1) Bond Equivalent Yield at period end. Weighted Average Yield is calculated using each investment's respective amortized cost.
(2) Calculated based on reported losses to date, utilizing widest data set available (i.e., life-time losses, 12-month loss, etc.)
59
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Principal or Notional Value at Period-End (dollars in thousands) |
Weighted Average Amortized Cost Basis | Weighted Average Fair Value | Weighted Average Coupon |
Weighted Average Yield at Period-End (1)
|
Weighted Average 3 Month Prepay Rate at Period-End | Weighted Average 12 Month Prepay Rate at Period-End | Weighted Average 3 Month CDR at Period-End | Weighted Average 12 Month CDR at Period-End |
Weighted Average Loss Severity(2)
|
Weighted Average Credit Enhancement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency Mortgage-Backed Securities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior |
$ | 2,024,567 | $ | 52.98 | $ | 84.01 | 5.0 | % | 20.8 | % | 9.6 | % | 9.3 | % | 4.5 | % | 4.5 | % | 48.7 | % | 3.8 | % | |||||||||||||
Subordinated |
$ | 876,592 | $ | 63.15 | $ | 71.25 | 3.7 | % | 6.9 | % | 10.1 | % | 11.3 | % | 1.0 | % | 2.8 | % | 42.6 | % | 3.9 | % | |||||||||||||
Interest-only |
$ | 7,458,653 | $ | 4.04 | $ | 3.87 | 1.1 | % | 8.4 | % | 18.3 | % | 11.0 | % | 1.6 | % | 2.4 | % | 56.0 | % | — | % | |||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pass-through |
$ | 6,080,547 | $ | 102.15 | $ | 104.64 | 4.0 | % | 3.4 | % | 37.4 | % | 21.9 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
$ | 1,539,941 | $ | 9.06 | $ | 8.29 | 1.6 | % | 4.0 | % | 14.9 | % | 9.9 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Project loans |
$ | 2,621,938 | $ | 101.82 | $ | 106.86 | 3.7 | % | 3.6 | % | — | % | 0.1 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
$ | 1,817,246 | $ | 2.81 | $ | 2.70 | 0.7 | % | 4.7 | % | 5.3 | % | 2.5 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment | $ | 13,924,291 | $ | 98.61 | $ | 102.83 | 5.7 | % | 5.2 | % | 8.6 | % | 8.5 | % | 1.6 | % | 1.7 | % | 52.0 | % | N/A | ||||||||||||||
(1) Bond Equivalent Yield at period end. Weighted Average Yield is calculated using each investment's respective amortized cost.
(2) Calculated based on reported losses to date, utilizing widest data set available (i.e., life-time losses, 12-month loss, etc.)
Based on the projected cash flows for our Non-Agency RMBS that are not of high credit quality, a portion of the original purchase discount is designated as Accretable Discount, which reflects the purchase discount expected to be accreted into interest income, and a portion is designated as Non-Accretable Difference, which represents the contractual principal on the security that is not expected to be collected. The amount designated as Non-Accretable Difference may be adjusted over time, based on the actual performance of the security, its underlying collateral, actual and projected cash flow from such collateral, economic conditions and other factors. If the performance of a security is more favorable than previously estimated, a portion of the amount designated as Non-Accretable Difference may be transferred to accretable discount and accreted into interest income over time. Conversely, if the performance of a security is less favorable than previously estimated, a provision for credit loss may be recognized resulting in an increase in the amounts designated as Non-Accretable Difference.
The following table presents changes to Accretable Discount (net of premiums) as it pertains to our Non-Agency RMBS portfolio, excluding premiums on IOs, during the previous five quarters.
| For the Quarters Ended | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Accretable Discount (Net of Premiums) | December 31, 2020 | September 30, 2020 | June 30, 2020 | March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of period | $ | 422,981 | $ | 410,447 | $ | 438,232 | $ | 494,255 | $ | 494,780 | |||||||
| Accretion of discount | (21,281) | (20,045) | (22,508) | (24,784) | (44,342) | ||||||||||||
| Purchases | 758 | 2,096 | — | (4,336) | (12,541) | ||||||||||||
| Sales and deconsolidation | 98 | — | (23,425) | 438 | (786) | ||||||||||||
| Transfers from/(to) credit reserve, net | 7,134 | 30,483 | 18,148 | (27,341) | 57,144 | ||||||||||||
| Balance, end of period | $ | 409,690 | $ | 422,981 | $ | 410,447 | $ | 438,232 | $ | 494,255 | |||||||
Liquidity and Capital Resources
General
Liquidity measures our ability to meet cash requirements, including ongoing commitments to repay our borrowings, purchase RMBS, residential mortgage loans and other assets for our portfolio, pay dividends and other general business needs. Our principal sources of capital and funds for additional investments primarily include earnings, principal paydowns and sales from our investments, borrowings under securitizations and re-securitizations, secured financing agreements and other financing facilities including warehouse facilities, and proceeds from equity or other securities offerings.
As discussed throughout this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the COVID-19 pandemic driven disruptions in the real estate and financial markets have negatively affected and could continue to negatively affect our liquidity. During the year ended December 31, 2020, particularly during the first two quarters of 2020, we have observed a mark-down of a portion of our
60
mortgage assets by the counterparties to our financing arrangements, resulting in us having to pay cash or securities to satisfy higher than historical levels of margin calls. Significant margin calls could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, business, liquidity and ability to make distributions to our stockholders, and could cause the value of our common stock to decline. In addition, we have also experienced an increase in haircuts on financings we have rolled. As haircuts are increased, we will be required to post additional collateral. We may also be forced to sell assets at significantly depressed prices to meet such margin calls and to maintain adequate liquidity. As a result of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, we have experienced margins calls above historical norms. These conditions, if they become more pronounced like earlier in the pandemic, will have a negative adverse impact on our liquidity. See the “Market Conditions and our Strategy” section of this “Part II. Item 7 - Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and related “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” for more information on how COVID-19 may impact our liquidity and capital resources. As discussed in greater detail above in “Part II. Item 7 - Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Market Conditions and our Strategy,” we have sought longer-term, more durable financing since the second quarter to reduce our risk to margin calls related to shorter-term repurchase financing.
Our ability to fund our operations, meet financial obligations and finance target asset acquisitions may be impacted by our ability to secure and maintain our master secured financing agreements, warehouse facilities and secured financing agreements facilities with our counterparties. Because secured financing agreements and warehouse facilities are short-term commitments of capital, lenders may respond to market conditions making it more difficult for us to renew or replace on a continuous basis our maturing short-term borrowings and have and may continue to impose more onerous conditions when rolling such financings. If we are not able to renew our existing facilities or arrange for new financing on terms acceptable to us, or if we default on our covenants or are otherwise unable to access funds under our financing facilities or if we are required to post more collateral or face larger haircuts, we may have to curtail our asset acquisition activities and/or dispose of assets.
To meet our short term (one year or less) liquidity needs, we expect to continue to borrow funds in the form of secured financing agreements and, subject to market conditions, other types of financing. The terms of the secured financing transaction borrowings under our master secured financing agreement generally conform to the terms in the standard master secured financing agreement as published by the Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association, or SIFMA, or similar market accepted agreements, as to repayment and margin requirements. In addition, each lender typically requires that we include supplemental terms and conditions to the standard master secured financing agreement. Typical supplemental terms and conditions include changes to the margin maintenance requirements, net asset value, required haircuts or the percentage that is subtracted from the value of MBS that collateralizes the financing, purchase price maintenance requirements, and requirements that all disputes related to the secured financing agreement be litigated or arbitrated in a particular jurisdiction. These provisions may differ for each of our lenders. We expect these terms to be more restrictive and onerous in future as a result of current market disruptions.
Based on our current portfolio, leverage ratio and available borrowing arrangements, we believe our assets will be sufficient to enable us to meet anticipated short-term liquidity requirements. If our cash resources are insufficient to satisfy our liquidity requirements, we may have to sell additional investments, potentially at a loss, issue debt or additional common or preferred equity securities.
To meet our longer-term liquidity needs (greater than one year), we expect our principal sources of capital and funds to continue to be provided by earnings, principal paydowns and sales from our investments, borrowings under securitizations and re-securitizations, secured financing agreements and other financing facilities, as well as proceeds from equity or other securities offerings. If the current market disruptions due to COVID-19 continues for a longer time period it will adversely affect our ability to generate earnings, borrowing under various financing facilities or raise capital by issuing common or preferred equity securities.
In addition to the principal sources of capital described above, we may enter into warehouse facilities and use longer dated structured secured financing agreements. The use of any particular source of capital and funds will depend on market conditions, availability of these facilities, and the investment opportunities available to us.
Current Period
We held cash and cash equivalents of approximately $269 million and $110 million at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively. In our response to COVID-19 pandemic related disruptions we made efforts to increase our liquidity and cash position by $159 million from December 31, 2019 to December 31, 2020.
Our operating activities provided net cash of approximately $258 million and $65 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The cash flows from operations were primarily driven by interest received in excess of interest
61
paid during the period. For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 interest received net of interest paid was $590 million and $592 million, respectively. In addition, during the year ended December 31, 2020 we used cash of $464 million for payments on swap terminations, which was offset by cash received for derivative margin of $326 million.
Our investing activities provided cash of $8.3 billion and $1.2 billion for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2020, we received cash from sale of primarily Agency MBS investments of $7.2 billion, and principal repayments on our Agency MBS, Non-Agency RMBS, and Loans held for investments of $2.9 billion. This cash provided was offset in part by cash used on investment purchases of $3.0 billion, consisting of $2.6 billion in purchases of Loans held for investments, $433 million in Agency CMBS fundings, and $33 million in Non-Agency RMBS purchases. During the year ended December 31, 2019, we received cash for sale of investments of $4.5 billion, and principal repayments on our Agency MBS, Non-Agency RMBS, and Loans held for investments of $4.4 billion. This cash provided was offset in part by cash used on investment purchases of $7.7 billion, consisting of $4.4 billion in purchases of Loans held for investments, $2.9 billion in Agency MBS purchases, and $374 million in Non-Agency RMBS purchases.
Our financing activities used cash of $8.4 billion and $1.2 billion for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2020, our financing efforts were focused on de-levering of our financial position by reducing our secured financing agreements obligations. During the year ended December 31, 2020, we used cash for net payments on our secured financing agreements of $8.8 billion, repayment of principal on our securitized debt of $2.6 billion, and paid common and preferred dividends of $396 million. This cash paid was offset in part by cash received for securitized debt collateralized by loans issuance of $3.0 billion and convertible debt issuance of $361 million. During the year ended December 31, 2019, we used cash for repayment of principal on our securitized debt of $1.9 billion, paid net proceeds on our repurchase agreements of $604 million, and paid common and preferred dividends of $447 million. This cash paid was offset in part by cash received for debt issuance of $1.5 billion and Series D preferred stock offering of $193 million.
Our recourse leverage was 1.2:1 and 3.4:1 at December 31, 2020 and at December 31, 2019, respectively. The reduction in recourse leverage was a result of reduction in our secured financing agreements liability. Our recourse leverage excludes the securitized debt which can only be repaid from the proceeds on the assets securing this debt in their respective VIEs. Our recourse leverage is presented as a ratio of our secured financing agreements, which are recourse to our assets and our equity.
At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the remaining maturities and borrowing rates on our RMBS and loan secured financing agreements were as follows.
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Principal (1) | Weighted Average Borrowing Rates | Range of Borrowing Rates | Principal | Weighted Average Borrowing Rates | Range of Borrowing Rates | ||||||||||||||||||
| Overnight | $ | — | NA | NA | $ | — | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||
| 1 to 29 days | 1,521,134 | 0.38% | 0.20% - 2.72% | 9,709,387 | 2.26% | 1.90% - 3.62% | |||||||||||||||||
| 30 to 59 days | 481,257 | 4.35% | 2.42% - 6.61% | 800,648 | 2.96% | 2.15% - 3.52% | |||||||||||||||||
| 60 to 89 days | 352,684 | 2.78% | 1.34% - 6.30% | 608,520 | 3.00% | 2.59% - 3.35% | |||||||||||||||||
| 90 to 119 days | 301,994 | 7.97% | 7.97% - 7.97% | — | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||||
| 120 to 180 days | 595,900 | 5.29% | 2.40% - 6.26% | 809,077 | 3.38% | 3.06% - 3.46% | |||||||||||||||||
| 180 days to 1 year | 345,204 | 3.60% | 3.25% - 4.50% | 580,886 | 3.42% | 3.26% - 3.51% | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 to 2 years | — | NA | NA | 427,981 | 3.28% | 3.19% - 3.30% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2 to 3 years | 642,696 | 4.91% | 1.65% - 7.00% | — | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||||
| Greater than 3 years | 395,978 | 5.56% | 5.56% - 5.56% | 491,046 | 3.20% | 3.19% - 3.20% | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 4,636,847 | 3.41% | $ | 13,427,545 | 2.52% | |||||||||||||||||
(1) The December 31, 2020 values for secured financing agreements in the table above is net of $8 million of deferred financing cost.
| Average remaining maturity of Secured financing agreements secured by: | ||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Agency RMBS (in thousands) | 12 days | 14 days | ||||||
| Agency CMBS (in thousands) | 11 days | 13 days | ||||||
| Non-agency RMBS and Loans held for investment (in thousands) | 458 days | 255 days | ||||||
62
We collateralize the secured financing agreements we use to finance our operations with our MBS investments. Our counterparties negotiate a ‘haircut’, which is the difference expressed in percentage terms between the fair value of the collateral and the amount the counterparty will lend to us, when we enter into a financing transaction. The size of the haircut reflects the perceived risk and market volatility associated with holding the MBS by the lender. The haircut provides lenders with a cushion for daily market value movements that reduce the need for a margin call to be issued or margin to be returned as normal daily increases or decreases in MBS market values occur. Due to the market disruptions and downward market pricing trends driven by COVID-19, our counterparties have negotiated higher haircuts. At December 31, 2020, the weighted average haircut on our remaining secured financing agreements collateralized by Agency RMBS IOs was 25.0%, Agency CMBS was 5.2% and Non-Agency RMBS and Loans held for investments was 31.8%. At December 31, 2019, the weighted average haircut on secured financing agreements collateralized by Agency RMBS was 5.0%, Agency CMBS was 5.0% and Non-Agency RMBS and Loans held for investments was 22.9%. At December 31, 2020, the weighted average borrowing rates for our secured financing agreements collateralized by Agency RMBS IOs was 0.9%, Agency CMBS was 0.2% and Non-Agency MBS and Loans held for investment was 4.8%. At December 31, 2019, the weighted average borrowing rates for our secured financing agreements collateralized by Agency RMBS was 2.1%, Agency CMBS was 2.1%, and Non-Agency MBS and Loans held for investment was 3.2%, respectively.
As the fair value of the Non-Agency MBS is more difficult to determine in current financial conditions, as well as more volatile period to period than Agency MBS, the Non-Agency MBS typically requires a larger haircut. In addition, when financing assets using standard form of SIFMA Master Repurchase Agreements, the counterparty to the agreement typically nets its exposure to us on all outstanding repurchase agreements and issues margin calls if movement of the fair values of the assets in the aggregate exceeds their allowable exposure to us. A decline in asset fair values could create a margin call or may create no margin call depending on the counterparty’s specific policy. In addition, counterparties consider a number of factors, including their aggregate exposure to us as a whole and the number of days remaining before the repurchase transaction closes prior to issuing a margin call. See Note 5 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion on how we determine the fair values of the RMBS collateralizing our secured financing agreements.
The table below presents our average daily repurchase balance and the repurchase balance at each period end for the periods presented. Our balance at period-end tends to fluctuate from the average daily balances due to the adjusting of the size of our portfolio by using leverage.
| Period | Average Repurchase Balance | Repurchase Balance at Period End | ||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 | $ | 7,316,345 | $ | 4,636,847 | ||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 | $ | 14,492,386 | $ | 13,427,545 | ||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2018 | $ | 9,816,170 | $ | 14,030,465 | ||||
| Quarter End December 31, 2020 | $ | 4,665,324 | $ | 4,636,847 | ||||
| Quarter End September 30, 2020 | $ | 5,269,553 | $ | 4,700,037 | ||||
| Quarter End June 30, 2020 | $ | 6,536,264 | $ | 5,944,201 | ||||
| Quarter End March 31, 2020 | $ | 11,754,793 | $ | 7,146,996 | ||||
We are not required to maintain any specific leverage ratio. We believe the appropriate leverage for the particular assets we are financing depends on the credit quality and risk of those assets. At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the carrying value of our total interest-bearing debt was approximately $13.5 billion and $21.7 billion, respectively, which represented a leverage ratio for both periods of approximately 3.6:1 and 5.5:1. We include our secured financing agreements and securitized debt in the numerator of our leverage ratio and stockholders’ equity as the denominator.
At December 31, 2020, we reduced our exposure to counterparties and had secured financing agreements with 16 counterparties as compared to 31 counterparties at year ended December 31, 2019. All of our secured financing agreements are secured by Agency MBS, Non-Agency RMBS and Loans held for investments and cash. Under these secured financing agreements, we may not be able to reclaim our collateral but will still be obligated to pay our repurchase obligations. We mitigate this risk by ensuring our counterparties are highly rated. As the disruptions due to COVID-19 continues and deteriorate liquidity conditions for our counterparties we believe our risk of loss to our collateral posted increases. As of December 31, 2020, and December 31, 2019, we had $6.7 billion and $15.4 billion, respectively, of securities or cash pledged against our secured financing agreements obligations.
63
We expect to enter into new secured financing agreements at maturity but due to current financial markets disruptions there is a risk that we will not be able to renew them or obtain favorable interest rates and haircuts.
Exposure to Financial Counterparties
We actively manage the number of secured financing agreements counterparties to reduce counterparty risk and manage our liquidity needs. The following table summarizes our exposure to our secured financing agreements counterparties at December 31, 2020:
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||
| Country | Number of Counterparties | Secured Financing Agreement | Interest Rate Swaps at Fair Value |
Exposure (1)
|
||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
| United States | 11 | 3,215,048 | — | 1,458,947 | ||||||||||
| Japan | 1 | 732,764 | — | 420,906 | ||||||||||
| Canada | 1 | 314,253 | — | 124,751 | ||||||||||
| South Korea | 1 | 217,200 | — | 6,993 | ||||||||||
| Switzerland | 1 | 96,115 | — | 63,211 | ||||||||||
| Netherlands | 1 | 61,467 | — | 2,493 | ||||||||||
| Total | 16 | $ | 4,636,847 | $ | — | $ | 2,077,301 | |||||||
(1) Represents the amount of securities and/or cash pledged as collateral to each counterparty less the aggregate of secured financing agreement and unrealized loss on swaps for each counterparty.
At December 31, 2020, we did not use credit default swaps or other forms of credit protection to hedge the exposures summarized in the table above.
Stockholders’ Equity
In March 2020, our Board of Directors reauthorized $150 million under our share repurchase program, or the Repurchase Program. Such authorization does not have an expiration date, and at present, there is no intention to modify or otherwise rescind such authorization. Shares of our common stock may be purchased in the open market, including through block purchases, through privately negotiated transactions, or pursuant to any trading plan that may be adopted in accordance with Rule 10b5-1 of the Exchange Act. The timing, manner, price and amount of any repurchases will be determined at our discretion and the program may be suspended, terminated or modified at any time for any reason. Among other factors, we intend to only consider repurchasing shares of our common stock when the purchase price is less than the last publicly reported book value per common share. In addition, we do not intend to repurchase any shares from directors, officers or other affiliates. The program does not obligate us to acquire any specific number of shares, and all repurchases will be made in accordance with Rule 10b-18, which sets certain restrictions on the method, timing, price and volume of stock repurchases.
Pursuant to our Repurchase Program, during the first quarter of 2020, we repurchased approximately 1.4 million shares of our common stock at an average price of $15.34 per share for a total of $22 million. We did not repurchase any share of common stock during the rest of 2020, and there were no stock repurchases during the year ended December 31, 2019. During the year ended December 31, 2020, we issued approximately 49 million shares of our common stock upon conversion of the $321 million convertible senior notes. Additionally, we issued shares of our common stock as discussed below under “Restricted Stock Grants,” and a de minimis amount under our Dividend Reinvestment Plan.
We declared dividends to common shareholders of $301 million, or $1.40, per share and $377 million, or $2.00, per share during the years ended December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively.
We declared dividends to Series A preferred stockholders of $12 million, or $2.00 per preferred share during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
We declared dividends to Series B preferred stockholders of $26 million, or $2.00 per preferred share during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
We declared dividends to Series C preferred stockholders of $20 million, or $1.94 per preferred share during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
64
We declared dividends to Series D preferred stockholders of $16 million, or $2.00 per preferred share during the years ended December 31, 2020, respectively. We declared dividends to Series D preferred stockholders of $15 million, or $1.87, respectively, per preferred share during the year ended December 31, 2019.
Warrants
On June 8, 2020, we entered into a $400 million senior secured, non-mark-to-market credit agreement with certain lenders. Pursuant to the credit agreement, we pledged approximately $550 million of existing assets, including approximately $482 million of securities from our sponsored mortgage loan securitizations, related risk retention securities, and resecuritizations. In connection with the credit agreement, we issued warrants to each of the lenders, which provides the lenders the right to purchase up to an aggregate of 20,300,000 shares of our common stock, at a price of $0.01 per share, which represented approximately 7.7% of our common stock after giving effect to the issuance of the warrant shares. We are permitted to settle any exercise of the warrants in cash at a price of 90% of the fair market value of our common stock at the time of exercise as discussed in Note 11.
Restricted Stock Unit and Performance Share Unit Grants
Grants of Restricted Stock Units or RSUs
During the year ended of December 31, 2020 and 2019, we granted RSU awards to senior management. These RSU awards are designed to reward our senior management for services provided to us. Generally, the RSU awards vest equally over a three-year period beginning from the grant date and will fully vest after three years. For employees whose years of service to us plus age is equal to or greater than 65, the service period is considered to be fulfilled and all grants are expensed immediately. The RSU awards are valued at the market price of our common stock on the grant date and generally the employees must be employed by us on the vesting dates to receive the RSU awards. We granted 414 thousand RSU awards during the year ended December 31, 2020, with a grant date fair value of $5 million for the 2020 performance year. We granted 487 thousand RSU awards during the year ended December 31, 2019 with a grant date fair value of $9 million, for the 2018 and 2019 performance year.
Grants of Performance Share Units or PSUs
PSU awards are designed to align compensation with our future performance. The PSU awards granted during the first quarter of 2020 and 2019 include a three-year performance period ending on December 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively. The final number of shares awarded will be between 0% and 200% of the PSUs granted based on our Economic Return compared to a peer group. Our three-year Economic Return is equal to our change in book value per common share plus common stock dividends. Compensation expense will be recognized on a straight-line basis over the three-year vesting period based on an estimate of our Economic Return in relation to the entities in the peer group and will be adjusted each period based on our best estimate of the actual number of shares which will vest. During the year ended December 31, 2020, we granted 173 thousand PSU awards to senior management with a grant date fair value of $3 million. During the year ended December 31, 2019, we granted 318 thousand PSU awards to senior management with a grant date fair value of $5 million.
At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, there were approximately 2.1 million and 1.7 million unvested shares of restricted and performance stock units issued to our employees, respectively.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The following tables summarize our contractual obligations at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019. The estimated principal repayment schedule of the securitized debt is based on expected cash flows of the residential mortgage loans or RMBS, as adjusted for expected principal write-downs on the underlying collateral of the debt.
65
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Within One Year | One to Three Years | Three to Five Years | Greater Than or Equal to Five Years | Total | ||||||||||||
| Secured financing agreements | $ | 3,598,173 | $ | 642,696 | $ | 395,978 | $ | — | $ | 4,636,847 | |||||||
| Securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS | 13,552 | 11,229 | 1,589 | 305 | 26,675 | ||||||||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | 1,837,055 | 2,819,646 | 1,774,273 | 2,170,253 | 8,601,227 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense on MBS secured financing agreements (1)
|
19,177 | 2,743 | 2,018 | — | 23,938 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense on securitized debt (1)
|
265,516 | 364,443 | 217,727 | 270,046 | 1,117,732 | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 5,733,473 | $ | 3,840,757 | $ | 2,391,585 | $ | 2,440,604 | $ | 14,406,419 | |||||||
(1) Interest is based on variable rates in effect as of December 31, 2020.
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Within One Year | One to Three Years | Three to Five Years | Greater Than or Equal to Five Years | Total | ||||||||||||
| Secured financing agreements | $ | 12,508,518 | $ | 427,981 | $ | 491,046 | $ | — | $ | 13,427,545 | |||||||
| Securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS | 18,826 | 18,332 | 4,453 | 665 | 42,276 | ||||||||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | 1,582,646 | 2,563,699 | 1,791,756 | 2,129,460 | 8,067,561 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense on MBS secured financing agreements (1)
|
36,789 | 1,249 | 1,340 | — | 39,378 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense on securitized debt (1)
|
311,848 | 435,462 | 259,004 | 361,241 | 1,367,555 | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 14,458,627 | $ | 3,446,723 | $ | 2,547,599 | $ | 2,491,366 | $ | 22,944,315 | |||||||
(1) Interest is based on variable rates in effect as of December 31, 2019.
Not included in the table above are the unfunded construction loan commitments of $106 million and $540 million as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively, which will primarily be paid within one year of reported periods and are reported under Payable for investments purchased in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
We have made a $150 million capital commitment to Hains Point, LLC (Hains Point), a fund which is consolidated by us as the sole investor in the fund. As of December 31, 2020, we have funded $124 million towards that commitment. Capital calls for investments made in Hains Point are subject to our consent and approval.
We have issued Warrants to purchase 20.3 million shares of our common stock. See Note 11 for further discussion. At exercise, we will deliver 20.3 million common shares or cash at a price per share equal to 90% of the fair market value of our common stock at the time of exercise. This commitment is not reflected in our issued and outstanding shares and is not included in the calculation of book value per common share or core earnings per adjusted diluted common shares. We expect a reduction in book value per common share when the warrants are exercised.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as structured finance or special purpose entities, which would have been established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or other contractually narrow or limited purposes. Further, we have not guaranteed any obligations of unconsolidated entities nor do we have any commitment or intent to provide funding to any such entities.
Capital Expenditure Requirements
At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, we had no material commitments for capital expenditures.
66
Dividends
To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must pay annual dividends to our stockholders of at least 90% of our taxable income (subject to certain adjustments). Before we pay any dividend, we must first meet any operating requirements and scheduled debt service on our financing facilities and other debt payable.
Inflation
A significant portion of our assets and liabilities are interest rate sensitive in nature. As a result, interest rates and other factors influence our performance far more so than does inflation. Changes in interest rates do not necessarily correlate with inflation rates or changes in inflation rates. Our consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP and our distributions will be determined by our Board of Directors consistent with our obligation to distribute to our stockholders at least 90% of our REIT taxable income (subject to certain adjustments) on an annual basis in order to maintain our REIT qualification; in each case, our activities and financial condition are measured with reference to historical cost or fair market value without considering inflation.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Accounting policies are integral to understanding our Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations. The preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make certain judgments and assumptions, on the basis of information available at the time of the financial statements, in determining accounting estimates used in the preparation of these statements. Our significant accounting policies and accounting estimates are described in Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. Critical accounting policies are described in this section. An accounting policy is considered critical if it requires management to make assumptions or judgments about matters that are highly uncertain at the time the accounting estimate was made or require significant management judgment in interpreting the accounting literature. If actual results differ from our judgments and assumptions, or other accounting judgments were made, this could have a significant and potentially adverse impact on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. These critical accounting policies were developed by management, and reviewed by our auditors, prior to being presented to and discussed with the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
The accounting policies and estimates which we consider most critical relate to the recognition of revenue on our investments, including recognition of any losses, and the determination of fair value of our financial instruments.
The consolidated financial statements include, on a consolidated basis, our accounts, the accounts of our wholly-owned subsidiaries, and variable interest entities, or VIEs, for which we are the primary beneficiary. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Although our estimates contemplate current conditions and how we expect them to change in the future, it is reasonably possible that actual conditions could be different than anticipated in those estimates, which could materially adversely impact our results of operations and our financial condition. Management has made significant estimates in several areas, including current expected credit losses of Non-Agency RMBS, valuation of Loans held for investments, Agency and Non-Agency MBS and interest rate swaps and income recognition on Loans held for investments and Non-Agency RMBS. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Recognition of Revenue
We primarily invest in pools of mortgage loans. All mortgage loans are carried at fair value with changes in fair value recognized in earnings. Our investments in mortgage loans pay principal and interest which is accrued when due. We also invest in MBS representing interests in obligations backed by pools of mortgage loans. Our investments in MBS includes investments in both Agency MBS and Non-Agency MBS. We delineate between (1) Agency MBS and (2) Non-Agency RMBS as follows: The Agency MBS are mortgage pass-through certificates, collateralized mortgage obligations, or CMOs, and other RMBS representing interests in or obligations backed by pools of residential mortgage loans issued or guaranteed as to principal and/or interest repayment by agencies of the U.S. Government or federally chartered corporations such as Ginnie Mae, Freddie Mac or Fannie Mae. The Non-Agency RMBS are not issued or guaranteed by Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, or Ginnie Mae and are therefore subject to credit risk. We also invests in Interest Only Agency MBS strips and Interest Only Non-Agency
67
RMBS strips, or IO MBS strips. IO MBS strips represent our right to receive a specified proportion of the contractual interest flows of the collateral.
Income on our investments is recognized based on an effective interest rate we expect to earn over the life of the investment. The effective interest rate is determined based on the cost of the investment and the expectation of future cash flows. To determine the future cash flows, we estimate the amount and timing of principal and interest, referred to as the repayment rate, and our expectations of defaults on payments of principal and interest. These estimates require significant judgment which change over time as our expectations change due to changes in market conditions and changes in our investments as principal and interest, other cash flows or losses are experiences. These estimates are compared to actual results of the investment and other similar investments on a regular basis and updated as necessary. These comparisons may result in a favorable or unfavorable change in the effective interest rate expected to be collected. Any favorable or unfavorable changes are reflected as a change in income. Our estimates of the timing and amount of principal and interest, including our expectation of defaults on payments of principal and interest are critical to accurately reporting interest income.
Our accounting policies for recognition of interest income and current expected credit losses related to MBS investments are described in further detail in Note 2 of the consolidated financial statements.
Determination of Fair Value
Substantially all of our investments are carried at fair value. In accordance with current accounting guidance, fair value of our financial instruments represents the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the financial statement reporting date. We use internally developed models to determine fair value of our investments.
We determine the fair value of all of our Non-Agency RMBS investment securities, including Non-Agency represented as securitized debt, based on discounted cash flows utilizing an internal pricing model that incorporates factors such as coupon, repayment speeds, expected losses, expected loss severity, discount rates and other factors. Estimates of repayment speeds, expected losses and expected loss severity, require significant judgment and are based on what we believe a market participant would use to determine the cash flows. To corroborate that the estimates of fair values generated by these internal models are reflective of current market prices, the Company compares the fair values generated by the model to non-binding independent prices provided by an independent third party pricing services.
We estimate the fair value of our Loans held for investment consisting of seasoned subprime residential mortgage loans on a loan by loan basis using an internally developed model which compares the loan held by the Company with a loan currently offered in the market. The loan price is adjusted in the model by considering the loan factors which would impact the value of a loan. These loan factors include loan coupon as compared to coupon currently available in the market, FICO, loan-to-value ratios, delinquency history, owner occupancy, and property type, among other factors. A baseline is developed for each significant loan factor and adjusts the price up or down depending on how that factor for each specific loan compares to the baseline rate. Generally, the most significant impact on loan value is the loan interest rate as compared to interest rates currently available in the market and delinquency history. The determination of the baseline, the market expectation, requires significant judgment. To corroborate that the estimates of fair values generated by these internal models are reflective of current market prices, the Company compares the fair values generated by the model to non-binding independent prices provided by an independent third party pricing services.
To the extent the inputs used to estimate fair value are observable, the values would be categorized in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy; otherwise they would be categorized as Level 3. The Company’s fair value estimation process utilizes inputs other than quoted prices that are observed in the market. The Company’s estimates are deemed to be significant to the fair value measurement process, which renders the resulting Non-Agency fair value estimates Level 3 inputs in the fair value hierarchy. Level 3 assets represent approximately 89% and 64% of total assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. Level 3 liabilities represent approximately 100% and 98% total liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Our accounting policies for the determination of fair value of our investments are described in further detail in Note 2 and Note 5 of the consolidated financial statements.
Variable Interest Entities
VIEs are defined as entities in which equity investors (i) do not have the characteristics of a controlling financial interest, and/or (ii) do not have sufficient equity at risk for the entity to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support from other parties. The entity that consolidates a VIE is known as its primary beneficiary and is generally the entity with (i) the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance, and (ii) the right to receive benefits from the VIE or the obligation to absorb losses of the VIE that could be significant to the VIE. For VIEs’ that do not
68
have substantial on-going activities, the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIEs’ economic performance may be determined by an entity’s involvement with the design of the VIE.
Our Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition contain the assets and liabilities related to thirty-four consolidated variable interest entities or VIEs. Due to the non-recourse nature of these VIEs our net exposure to loss from investments in these entities is limited to our retained beneficial interests.
At December 31, 2020, we consolidated thirty-one residential mortgage loan securitizations and three RMBS re-securitization transactions which are VIEs. The residential mortgage loan securitizations contain jumbo prime and Non-QM residential mortgage loans. The RMBS re-securitization transactions contain Non-Agency RMBS comprised of primarily first lien mortgages of 2005-2007 vintages.
Our determination to consolidate these thirty-four VIEs was significantly influenced by management’s judgment related to the activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of these entities and the identification of the party with the power over such activities. For the residential mortgage loan securitizations, we determined that our ability to remove the servicer without cause resulted in us having the power that most significantly impacts the economic performance of the VIE. For the three consolidated RMBS re-securitization transactions, we determined that no party has power over any ongoing activities of the entities and therefore the determination of the primary beneficiary should be based on involvement with the initial design of the entity. Since we transferred the RMBS to the securitization entities, we determined we had the power over the design of the entity, which resulted in us being considered the primary beneficiary. This determination was influenced by the amount of economic exposure to the financial performance of the entity and required a significant management judgment in determining that we should consolidate these three entities.
Due to the consolidation of these VIEs, our actual ownership interests in the securitization and re-securitizations have been eliminated in consolidation and the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition reflect both the assets held and non-recourse debt issued to third parties by these VIEs. In addition, our operating results and cash flows include the gross amounts related to the assets and liabilities of the VIEs as opposed to the actual economic interests we own in these VIEs. Our interest in these VIEs is restricted to the beneficial interests we retained in these transactions. We are not obligated to provide any financial support to these VIEs.
Our Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition separately present: (i) our direct assets and liabilities, and (ii) the assets and liabilities of our consolidated securitization vehicles net of intercompany eliminations representing securities from the securitization trusts retained by the company. Assets of all consolidated VIEs can only be used to satisfy the obligations of those VIEs, and the liabilities of consolidated VIEs are non-recourse to us.
We have aggregated all the assets and liabilities of the consolidated securitization vehicles due to our determination that these entities are substantively similar and therefore a further disaggregated presentation would not be more meaningful. The notes to our consolidated financial statements describe our direct assets and liabilities and the assets and liabilities of our consolidated securitization vehicles. See Note 9 to our consolidated financial statements for additional information related to our investments in VIEs.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Refer to Note 2 in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of accounting guidance recently adopted by the Company or expected to be adopted by the Company in the future.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
The primary components of our market risk are related to credit risk, interest rate risk, prepayment risk, extension risk, basis risk and market risk. While we do not seek to avoid risk completely, we believe the risk can be quantified from historical experience and we seek to actively manage that risk and to maintain capital levels consistent with the risks we undertake.
Additionally, refer to Item 1A Risk Factors for additional information on effect of COVID-19 pandemic risk.
Credit Risk
Concern about the spread of COVID-19 has caused and is likely to continue to cause business shutdowns, limitations on commercial activity and financial transactions, labor shortages, construction delays, supply chain interruptions, increased unemployment and commercial property vacancy rates, reduced profitability and ability for property owners to make mortgage payments, and overall economic and financial market instability, all of which may cause an increase in credit risk of our
69
underlying MBS investments. If the effects of COVID-19 result in widespread and sustained principal and interest shortfalls on MBS investments in our portfolio, we could incur significant delinquencies, foreclosures and credit losses, particularly if the available collateral is insufficient to cover our exposure. The future effects of COVID-19 on economic activity could negatively affect the collateral values associated with our existing investments, the ability to liquidate the collateral, our ability to obtain additional financing, and the future profitability of our investments. Further, in the event of delinquencies, regulatory changes and policies designed to protect borrowers may slow or prevent us from making our business decisions or may result in a delay in our taking remediation actions. See the “Market Conditions and our Strategy” section of this “Part II. Item 7 - Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and related “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements,” as well as “Part I. Item 1A - Risk Factors” for more information on how COVID-19 may impact the credit quality of our mortgage-related assets.
We are subject to credit risk in connection with our investments in Non-Agency RMBS and residential mortgage loans and face more credit risk on assets we own which are rated below ‘‘AAA’’ or not rated. The credit risk related to these investments pertains to the ability and willingness of the borrowers to pay, which is assessed before credit is granted or renewed and periodically reviewed throughout the loan or security term. We believe that residual loan credit quality, and thus the quality of our assets, is primarily determined by the borrowers’ credit profiles and loan characteristics.
In connection with loan acquisitions, we or a third-party performs an independent review of the mortgage file to assess the origination and servicing of the mortgage loan as well as our ability to enforce the contractual rights in the mortgage. Depending on the size of the loans, we may not review all of the loans in a pool, but rather a sample of loans for diligence review based upon specific risk-based criteria such as property location, loan size, effective loan-to-value ratio, borrower’s characteristics and other criteria we believe to be important indicators of credit risk. Additionally, we obtain representations and warranties from each seller with respect to the residential mortgage loans, including the origination and servicing of the mortgage loan as well as the enforceability of the lien on the mortgaged property. A seller who breaches these representations and warranties in making a loan that we purchase may be obligated to repurchase the loan from us. Our resources include a portfolio management system, as well as third-party software systems. We utilize third-party due diligence firms to perform an independent mortgage loan file review to ensure compliance with existing guidelines. In addition to statistical sampling techniques, we create adverse credit and valuation samples, which we individually review.
Additionally, the Non-Agency RMBS which we acquire for our portfolio are reviewed by us to ensure that they satisfy our risk-based criteria. Our review of Non-Agency RMBS includes utilizing a portfolio management system. Our review of Non-Agency RMBS and other ABS is based on quantitative and qualitative analysis of the risk-adjusted returns on Non-Agency RMBS and other ABS. This analysis includes an evaluation of the collateral characteristics supporting the RMBS such as borrower payment history, credit profiles, geographic concentrations, credit enhancement, seasoning, and other pertinent factors.
Interest Rate Risk
Our net interest income, borrowing activities and profitability could be negatively affected by volatility in interest rates caused by uncertainties stemming from COVID-19. In March 2020, the Federal Reserve lowered the target range for the federal funds rate to a range from 0 to 0.25 percent, citing concerns about the impact of COVID-19 on markets and stress in the energy sector. A prolonged period of extremely volatile and unstable market conditions would likely increase our funding costs and negatively affect market risk mitigation strategies. Higher income volatility from changes in interest rates and spreads to benchmark indices could cause a loss of future net interest income and a decrease in current fair market values of our assets. Fluctuations in interest rates will impact both the level of income and expense recorded on most of our assets and liabilities and the market value of all interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities, which in turn could have a material adverse effect on our net income, operating results, or financial condition.
Interest rate risk is highly sensitive to many factors, including governmental, monetary and tax policies, domestic and international economic and political considerations and other factors beyond our control. We are subject to interest rate risk in connection with our investments and our related debt obligations, which are generally secured financing agreements and securitization/re-securitization trusts. Our secured financing agreements and warehouse facilities may be of limited duration that is periodically refinanced at current market rates. We typically mitigate this risk through utilization of derivative contracts, primarily interest rate swap agreements, swaptions, futures and mortgage options.
We do not currently have any hedges in place to mitigate the risk of rising interest rates.
Interest Rate Effects on Net Interest Income
70
Our operating results depend, in large part, on differences between the income from our investments and our borrowing costs. Most of our warehouse facilities and secured financing agreements provide financing based on a floating rate of interest calculated on a fixed spread over LIBOR. The fixed spread varies depending on the type of underlying asset which collateralizes the financing. During periods of rising interest rates, the borrowing costs associated with our investments tend to increase while the income earned on our investments may remain substantially unchanged or decrease. This will result in a narrowing of the net interest spread between the related assets and borrowings and may even result in losses. Further, defaults could increase and result in credit losses to us, which could adversely affect our liquidity and operating results. Such delinquencies or defaults could also have an adverse effect on the spread between interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities. We generally do not hedge against credit losses. Hedging techniques are partly based on assumed levels of prepayments of our fixed-rate and hybrid adjustable-rate residential mortgage loans and RMBS. If prepayments are slower or faster than assumed, the life of the residential mortgage loans and RMBS will be longer or shorter, which would reduce the effectiveness of any hedging strategies we may use and may cause losses on such transactions.
Economic impacts related to COVID-19 have caused fixed income patterns to move away from their historical trends. We have experienced historically larger spreads to benchmark rates in the repurchase markets and in some cases availability of repurchase financing has been limited or not available.
Interest Rate Effects on Fair Value
Another component of interest rate risk is the effect changes in interest rates will have on the fair value of the assets we acquire. We face the risk that the fair value of our assets will increase or decrease at different rates than that of our liabilities, including our hedging instruments, if any. We primarily assess our interest rate risk by estimating the duration of our assets compared to the duration of our liabilities and hedges. Duration essentially measures the market price volatility of financial instruments as interest rates change. We generally calculate duration using various financial models and empirical data. Different models and methodologies can produce different duration numbers for the same securities.
It is important to note that the impact of changing interest rates on fair value can change significantly when interest rates change beyond 100 basis points from current levels. Therefore, the volatility in the fair value of our assets could increase significantly when interest rates change beyond 100 basis points. In addition, other factors impact the fair value of our interest rate-sensitive investments and hedging instruments, such as the shape of the yield curve, market expectations as to future interest rate changes and other market conditions. Accordingly, in the event of changes in actual interest rates, the change in the fair value of our assets would likely differ from that shown below and such difference might be material and adverse to our stockholders.
Significant government programs, stimulus plans as well as government purchase and finance programs have had and will continue to have an impact on rates and fair values of fixed income assets. It is unclear the impacts of these actions and how long they will continue to drive the interest rate environment.
Effect of U.S. Dollar London Inter Bank Offered Rate or, LIBOR transition
The interest rates on our secured financing agreements, as well as adjustable-rate mortgage loans in our securitizations, are generally based on LIBOR, which is subject to recent national, international, and other regulatory guidance and proposals for reform. Some of these reforms are already effective while others are still to be implemented. These reforms may cause such benchmarks to perform differently than in the past or have other consequences which cannot be predicted.
Currently, it is not possible to predict the effect of any such changes, any establishment of alternative reference rates or any other reforms to LIBOR that may be implemented in the U.K. or elsewhere. Uncertainty as to the nature of such potential changes, alternative reference rates or other reforms may adversely affect the rates on our secured financing facilities, securitizations or residential loans held for longer-term investment. If LIBOR is discontinued or is no longer quoted, the applicable base rate used to calculate interest on our repurchase agreements will be determined using alternative methods. In the U.S., efforts to identify a set of U.S. dollar reference interest rates include proposals by the Alternative Reference Rates Committee of the Federal Reserve Board and the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. The U.S. Federal Reserve, in conjunction with the Alternative Reference Rates Committee, a steering committee comprised of large U.S. financial institutions, is considering replacing U.S. dollar LIBOR with the Secured Overnight Funding Rate, or SOFR.
It is possible that not all of our assets and liabilities will transition away from LIBOR at the same time, and it is possible that not all of our assets and liabilities will transition to the same alternative reference rate, in each case increasing the difficulty of hedging. We and other market participants have less experience understanding and modeling SOFR-based assets and liabilities than LIBOR-based assets and liabilities, increasing the difficulty of investing, hedging, and risk management. The process of transition involves operational risks. It is also possible that no transition will occur for many financial instruments.
71
Any additional changes announced by the regulators or any other successor governance or oversight body, or future changes adopted by such body, in the method pursuant to which reference rates are determined may result in a sudden or prolonged increase or decrease in the reported reference rates. If that were to occur, the level of interest payments we incur may change. Although certain of our LIBOR based obligations provide for alternative methods of calculating the interest rate payable on certain of our obligations if LIBOR is not reported, which include requesting certain rates from major reference banks in London or New York, or alternatively using LIBOR for the immediately preceding interest period or using the initial interest rate, as applicable, uncertainty as to the extent and manner of future changes may result.
Interest Rate Cap Risk
We may also invest in adjustable-rate residential mortgage loans and RMBS. These are mortgages or RMBS in which the underlying mortgages are typically subject to periodic and lifetime interest rate caps and floors, which limit the amount by which the security’s interest yield may change during any given period. However, our borrowing costs pursuant to our financing agreements will not be subject to similar restrictions. Therefore, in a period of increasing interest rates, interest rate costs on our borrowings could increase without limitation by caps, while the interest-rate yields on our adjustable-rate residential mortgage loans and RMBS would effectively be limited. This problem will be magnified to the extent we acquire adjustable-rate RMBS that are not based on mortgages which are fully indexed. In addition, the mortgages or the underlying mortgages in an RMBS may be subject to periodic payment caps that result in some portion of the interest being deferred and added to the principal outstanding. This could result in our receipt of less cash income on our adjustable-rate mortgages or RMBS than we need in order to pay the interest cost on our related borrowings. These factors could lower our net interest income or cause a net loss during periods of rising interest rates, which would harm our financial condition, cash flows and results of operations.
Interest Rate Mismatch Risk
We fund a substantial portion of our acquisitions of RMBS with borrowings that have interest rates based on indices and re-pricing terms similar to, but of somewhat shorter maturities than, the interest rate indices and re-pricing terms of the mortgages and RMBS. In most cases the interest rate indices and re-pricing terms of our mortgage assets and our funding sources will not be identical, thereby creating an interest rate mismatch between assets and liabilities. Our cost of funds would likely rise or fall more quickly than would our earnings rate on assets. During periods of changing interest rates, such interest rate mismatches could negatively impact our financial condition, cash flows and results of operations. To mitigate interest rate mismatches, we may utilize the hedging strategies discussed above. Our analysis of risks is based on our experience, estimates, models and assumptions. These analyses rely on models which utilize estimates of fair value and interest rate sensitivity. Actual economic conditions or implementation of investment decisions by our management may produce results that differ significantly from the estimates and assumptions used in our models and the projected results.
We have entered into agreements for long term, non mark-to-market financing facilities at rates that are higher than short term secured financing agreements. Having non-mark-to-market facilities may be useful in this market to prevent significant margin calls or collateral liquidation in a volatile market. If the market normalizes and repurchase rates fall, we may be locked into long term and higher interest expenses than are otherwise available in the market to finance our portfolio.
Our profitability and the value of our portfolio may be adversely affected during any period as a result of changing interest rates. The following table quantifies the potential changes in net interest income and market value on the assets we retain, if interest rates go up or down 50 and 100 basis points, assuming parallel movements in the yield curves. All changes in income and value are measured as percentage changes from the projected net interest income and the value of the assets we retain at the base interest rate scenario. The base interest rate scenario assumes interest rates at December 31, 2020 and various estimates regarding prepayment and all activities are made at each level of rate change. Actual results could differ significantly from these estimates.
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||
| Change in Interest Rate |
Projected Percentage Change in Net Interest Income (1)
|
Projected Percentage Change in Market Value (2)
|
||||||
| -100 Basis Points | 2.37 | % | 5.80 | % | ||||
| -50 Basis Points | 1.78 | % | 3.28 | % | ||||
| Base Interest Rate | — | — | ||||||
| +50 Basis Points | (4.18) | % | (3.51) | % | ||||
| +100 Basis Points | (8.49) | % | (6.84) | % | ||||
(1) Change in annual economic net interest income. Includes interest expense on interest rate swaps.
(2) Projected Percentage Change in Market Value is based on instantaneous moves in interest rates.
72
Prepayment Risk
As we receive prepayments of principal on these investments, premiums and discounts on such investments will be amortized or accreted into interest income. In general, an increase in actual or expected prepayment rates will accelerate the amortization of purchase premiums, thereby reducing the interest income earned on the investments. Conversely, discounts on such investments are accelerated and accreted into interest income increasing interest income when prepayments increase.
Given the combination of low interest rates, government stimulus and high unemployment, and other disruptions related to COVID-19, it has become more difficult to predict prepayment level for the securities in our portfolio. Actual prepayment results may be materially different than the assumptions we use.
Extension Risk
Management computes the projected weighted-average life of our investments based on assumptions regarding the rate at which the borrowers will prepay the underlying mortgages. In general, when fixed-rate or hybrid adjustable-rate residential mortgage loans or RMBS are acquired via borrowings, we may, but are not required to, enter into an interest rate swap agreement or other hedging instrument that attempts to fix our borrowing costs for a period close to the anticipated average life of the fixed-rate portion of the related assets. This strategy is designed to protect us from rising interest rates as the borrowing costs are managed to maintain a net interest spread for the duration of the fixed-rate portion of the related assets. However, if prepayment rates decrease in a rising interest rate environment, the life of the fixed-rate portion of the related assets could extend beyond the term of the swap agreement or other hedging instrument. This could have a negative impact on our results from operations, as borrowing costs would no longer be fixed after the end of the hedging instrument while the income earned on the fixed and hybrid adjustable-rate assets would remain fixed. In extreme situations, we may be forced to sell assets to maintain adequate liquidity, which could cause us to incur losses.
Basis Risk
We may seek to limit our interest rate risk by hedging portions of our portfolio through interest rate swaps and other types of hedging instruments. Interest rate swaps are generally tied to underlying Treasury benchmark interest rates. Basis risk relates to the risk of the spread between our MBS and underlying hedges widening. Such a widening may cause a decline in the fair value of our MBS that is greater than the increase in fair value of our hedges resulting in a net decline in book value. The widening of mortgage-backed securities yields and Treasury benchmark interest rates may result from a variety of factors such as anticipated or actual monetary policy actions or other market factors.
Given recent market uncertainty, the spread between MBS, hedges and benchmark rates widened significantly. Normal correlations between hedges and portfolio assets did not follow typical patterns and as a result we removed all of the Company’s hedges. It is uncertain when normal market correlations will resume in the fixed income markets.
Market Risk
Market Value Risk
Certain of our available-for-sale securities are reflected at their estimated fair value with unrealized gains and losses excluded from earnings and reported in other comprehensive income. The estimated fair value of these securities fluctuates primarily due to changes in interest rates, prepayment speeds, market liquidity, credit quality, and other factors. Generally, in a rising interest rate environment, the estimated fair value of these securities would be expected to decrease; conversely, in a decreasing interest rate environment, the estimated fair value of these securities would be expected to increase. As market volatility increases or liquidity decreases, the fair value of our investments may be adversely impacted.
The uncertainties stemming from COVID-19 has created unprecedented illiquidity and volatility in the financial markets. Our market value risk has significantly increased. The market value of all interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities have decreased. If this uncertainty continues, we could have a material adverse effect on our net income, operating results, and financial condition.
Real Estate Market Risk
We own assets secured by real property and may own real property directly. Residential property values are subject to volatility and may be affected adversely by a number of factors, including, but not limited to, national, regional and local economic
73
conditions and unemployment (which may be adversely affected by industry slowdowns and other factors); local real estate conditions (such as an oversupply of housing); changes or continued weakness in specific industry segments; construction quality, age and design; demographic factors; natural disasters and other acts of God; and retroactive changes to building or similar codes. In addition, decreases in property values reduce the value of the collateral and the potential proceeds available to a borrower to repay our loans, which could also cause us to incur losses.
Risk Management
Subject to maintaining our REIT status, we seek to manage risk exposure to protect our portfolio of residential mortgage loans, RMBS, and other assets and related debt against the effects of major interest rate changes. We generally seek to manage risk by:
•monitoring and adjusting, if necessary, the reset index and interest rate related to our RMBS and our financings;
•attempting to structure our financing agreements to have a range of different maturities, terms, amortizations and interest rate adjustment periods, rights to post both cash and collateral for margin calls and provisions for non mark-to-market facilities;
•using derivatives, financial futures, swaps, options, caps, floors and forward sales to adjust the interest rate sensitivity of our investments and our borrowings;
•using securitization financing to receive the benefit of attractive financing terms for an extended period of time in contrast to short term financing and maturity dates of the investments not included in the securitization; and
•actively managing, through assets selection, on an aggregate basis, the interest rate indices, interest rate adjustment periods, and gross reset margins of our investments and the interest rate indices and adjustment periods of our financings.
Our efforts to manage our assets and liabilities are focused on the timing and magnitude of the re-pricing of assets and liabilities. We attempt to control risks associated with interest rate movements. Methods for evaluating interest rate risk include an analysis of our interest rate sensitivity “gap,” which is the difference between interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities maturing or re-pricing within a given time period. A gap is considered positive when the amount of interest-rate sensitive assets exceeds the amount of interest-rate sensitive liabilities. A gap is considered negative when the amount of interest-rate sensitive liabilities exceeds interest-rate sensitive assets. During a period of rising interest rates, a negative gap would tend to adversely affect net interest income, while a positive gap would tend to result in an increase in net interest income. During a period of falling interest rates, a negative gap would tend to result in an increase in net interest income, while a positive gap would tend to affect net interest income adversely. Because different types of assets and liabilities with the same or similar maturities may react differently to changes in overall market rates or conditions, changes in interest rates may affect net interest income positively or negatively even if an institution were perfectly matched in each maturity category.
The following table sets forth the estimated maturity or re-pricing of our interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities at December 31, 2020. The amounts of assets and liabilities shown within a particular period were determined in accordance with the contractual terms of the assets and liabilities, except adjustable-rate residential mortgage loans, and securities are included in the period in which their interest rates are first scheduled to adjust and not in the period in which they mature and includes the effect of the interest rate swaps. The interest rate sensitivity of our assets and liabilities in the table could vary substantially based on actual prepayments.
74
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Within 3 Months | 3-12 Months | 1 Year to 3 Years | Greater than 3 Years |
Total | |||||||||||||
| Rate sensitive assets | $ | 125,055 | $ | 732,584 | $ | 89,875 | $ | 16,160,656 | $ | 17,108,170 | |||||||
| Cash equivalents | 269,090 | — | — | — | 269,090 | ||||||||||||
| Total rate sensitive assets | $ | 394,145 | $ | 732,584 | $ | 89,875 | $ | 16,160,656 | $ | 17,377,260 | |||||||
| Rate sensitive liabilities | 6,545,106 | 5,922,659 | 880,752 | — | 13,348,517 | ||||||||||||
| Interest rate sensitivity gap | $ | (6,150,961) | $ | (5,190,075) | $ | (790,877) | $ | 16,160,656 | $ | 4,028,743 | |||||||
| Cumulative rate sensitivity gap | $ | (6,150,961) | $ | (11,341,036) | $ | (12,131,913) | $ | 4,028,743 | |||||||||
| Cumulative interest rate sensitivity gap as a percentage of total rate sensitive assets | (35) | % | (65) | % | (70) | % | 23 | % | |||||||||
Our analysis of risks is based on our management’s experience, estimates, models and assumptions. These analyses rely on models which utilize estimates of fair value and interest rate sensitivity. Actual economic conditions or implementation of investment decisions by our management may produce results that differ significantly from the estimates and assumptions used in our models and the projected results shown in the above tables and in this 2020 Form 10-K. These analyses contain certain forward-looking statements and are subject to the safe harbor statement set forth under the heading, “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
Cybersecurity Risk
We have a suite of controls including technology hardware and software solutions as well as regular training sessions on cybersecurity risks and mitigation strategies. We have established an incident response team to take steps it determines are appropriate to contain, mitigate and remediate a cybersecurity incident and to respond to the associated business, legal and reputational risks. There is no assurance that these efforts will fully mitigate cybersecurity risk and mitigation efforts are not an assurance that no cybersecurity incidents will occur.
The company has been operating remotely since the middle of March 2020. While we feel our remote work environment is secure, cybersecurity attacks may increase to attempt to breach our system and take advantage of employees working from home. The technology in employees’ homes may not be as robust as in our offices and could cause the networks, information systems, applications, and other tools available to employees to be more limited or less reliable than in our offices. We have experienced higher than normal phishing and other attempts to access our systems. We have not had a cybersecurity breach and maintain vigilant about our technology platforms, but there is no assurance that all cybersecurity risks will be mitigated.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
Our consolidated financial statements and the related notes, together with the Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm thereon, are set forth in Part IV of this 2020 Form 10-K.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
a) Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act) are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in reports filed or submitted under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
75
Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, reviewed and evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures covering the preparation and review of this 2020 Form 10-K. Based on such evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the end of such period, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
(b) Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act, as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, our principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by our Board of Directors, management and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and includes those policies and procedures that:
•pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets;
•provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and
•provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect all misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risks that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in the 2013 Internal Control-Integrated Framework.
Based on this assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2020, our internal control over financial reporting was effective.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report under Item 8. "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
(c) Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter and year ended December 31, 2020 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
None.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
We expect to file with the SEC, in April 2021 (and, in any event, not later than 120 days after the close of our last fiscal year), a definitive proxy statement, or the Proxy Statement, pursuant to SEC Regulation 14A in connection with our Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on or about June 10, 2021. The information to be included in the Proxy Statement regarding the Company’s directors, executive officers, and certain other matters required by Item 401 of Regulation S-K is incorporated herein by reference.
76
The information to be included in the Proxy Statement regarding compliance with Section 16(a) of the 1934 Act required by Item 405 of Regulation S-K is incorporated herein by reference.
The information to be included in the Proxy Statement regarding the Company’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics required by Item 406 of Regulation S-K is incorporated herein by reference.
The information to be included in the Proxy Statement regarding certain matters pertaining to the Company’s corporate governance required by Item 407(c)(3), (d)(4) and (d)(5) of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information to be included in the Proxy Statement regarding executive compensation and other compensation related matters required by Items 402 and 407(e)(4) and (e)(5) of Regulation S-K is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
Equity Compensation Plan Information
We have adopted a long term stock incentive plan, or Incentive Plan, to provide incentives to our independent directors and employees to stimulate their efforts towards our continued success, long-term growth and profitability and to attract, reward and retain personnel and other service providers. The Incentive Plan authorizes the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors to grant awards, including incentive stock options as defined under Section 422 of the Code, or ISOs, non-qualified stock options or the NQSOs, restricted shares and other types of incentive awards. The Incentive Plan authorizes the granting of awards for an aggregate of 8,000,000 shares of common stock. For a description of our Incentive Plan, see Note 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
The tables to be included in the Proxy Statement, which will contain information relating to securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans and beneficial ownership of the Company's capital stock required by Items 201(d) and 403 of Regulation S-K, is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence
The information to be included in the Proxy Statement regarding transactions with related persons, promoters and certain control persons and director independence required by Items 404 and 407(a) of Regulation S-K is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information to be included in the Proxy Statement concerning principal accounting fees and services and the Audit Committee’s pre-approval policies and procedures required by Item 9(e) of Schedule 14A is incorporated herein by reference.
Part IV
Item 15. Exhibits
| EXHIBIT INDEX | |||||
| Exhibit Number |
Description | ||||
| 3.1 | |||||
| 3.2 | |||||
| 3.3 | |||||
77
| 3.4 | |||||
| 3.5 | |||||
| 3.6 | |||||
| 3.7 | |||||
| 3.8 | |||||
| 3.9 | |||||
| 3.10 | |||||
| 3.11 | |||||
| 4.1 | |||||
| 4.2 | |||||
| 4.3 | |||||
| 4.4 | |||||
| 4.5 | |||||
| 4.6 | |||||
| 4.7 | |||||
| 4.8 | |||||
| 4.9 | |||||
| 4.1 | |||||
| 4.11 | |||||
| 10.1† | |||||
78
| 10.2† | |||||
| 10.3† | |||||
| 10.4† | |||||
| 10.5† | |||||
| 10.6† | |||||
| 10.7† | |||||
| 10.8† | |||||
| 10.9† | |||||
| 10.10† | |||||
| 10.11† | |||||
| 10.12 | |||||
| 10.13 | |||||
| 21.1 | |||||
| 23.1 | |||||
| 31.1 | |||||
| 31.2 | |||||
| 32.1 | |||||
| 32.2 | |||||
| 101.INS* | XBRL Instance Document - The instance document does not appear in the interactive data file because its XBRL tags are embedded within the inline XBRL document. | ||||
| 101.SCH* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | ||||
| 101.CAL* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | ||||
| 101.LAB* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Linkbase Document | ||||
| 101.PRE* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | ||||
| 101.DEF* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | ||||
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) | ||||
79
| † | Represents a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement | ||||
| * | This exhibit is being furnished rather than filed, and shall not be deemed incorporated by reference into any filing, in accordance with Item 601 of Regulation S-K | ||||
80
CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |||||
| Consolidated Financial Statements | |||||
| Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition as of December 31, 2020 and 2019 | |||||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | |||||
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | |||||
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | |||||
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | |||||
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | |||||
81
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Chimera Investment Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial condition of Chimera Investment Corporation (the Company) as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, changes in stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2020, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2020 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2020, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 18, 2021 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Adoption of ASU No. 2016-13
As discussed in Notes 2(d) and 2(p) to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed its method of accounting for impairment from an incurred loss model to a current expected credit loss model for available-for-sale financial instruments in 2020, and changed its recognition of interest income on certain Non-Agency RMBS due to the adoption of ASU 2016-13, Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
| Valuation of financial instruments using significant unobservable inputs | ||||||||
| Description of the Matter |
As of December 31, 2020, the Company had recognized on its consolidated statement of financial condition the following financial instruments that are categorized as Level 3 in the fair value hierarchy (Level 3 financial instruments): $2.2 billion of Non-Agency RMBS, at fair value; $13.1 billion of Loans held for investment, at fair value; and $8.7 billion of Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment. Management determines the fair value of these Level 3 financial instruments by applying the methodologies described in Note 5 to the financial statements and using significant unobservable inputs. Determining the fair value of each Level 3 financial instrument requires management to make significant judgments about the valuation methodologies (i.e., market approach or income approach), including the unobservable inputs and other assumptions and estimates used in the measurements.
Auditing the fair value of the Company's Level 3 financial instruments involved complex judgment due to the judgment and estimation uncertainty used by the Company in determining the fair value of the financial instruments. In particular, to value its Level 3 financial instruments, the Company used significant unobservable inputs such as discount rates, prepayment speeds, default rates, loss severities, baseline interest rates and delinquency histories, which are significant to the valuation of these Level 3 financial instruments.
|
|||||||
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit |
We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of internal controls over the Company's financial instrument valuation process. This included controls over management's review of the appropriateness of significant assumptions and data inputs and the validation of fair values developed by the Company through comparison to information from third party pricing services, as well as controls over management’s review and approval of the fair value estimates.
Our audit procedures included, among others, evaluating the valuation methodologies used by the Company and testing the mathematical accuracy of the Company's valuation models. With the assistance of our valuation specialists, we independently developed a range of fair value estimates for a sample of financial instruments based on market data and compared them to the Company's estimates. We also evaluated subsequent events and transactions and considered whether they corroborate or contradict the Company's year-end valuations. In addition, we searched for and evaluated information that corroborates or contradicts the Company's fair value estimates.
|
|||||||
| Interest Income on Non-Agency RMBS and Loans held for investment | ||||||||
| Description of the Matter |
As disclosed in Note 5 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company recorded $39.2 million of income related to the net accretion of purchase discounts on the Company’s Non-Agency RMBS portfolio and $85.8 million of expense related to the net amortization of purchase premiums on the Company’s Loans held for investment portfolio, both of which are included in the interest income line item within the consolidated statement of operations for the year ending December 31, 2020. As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company recognizes interest income on these investments using the interest method based on management’s estimates of cash flows, which incorporates significant assumptions regarding the timing and amount of expected future cash flows, prepayment speeds, expected default severities, loss severities, delinquency rates, and other pertinent factors.
Auditing management’s estimate of interest income was complex due to the significant judgment required in determining the appropriateness of the Company’s cash flow estimations used to determine interest income, including the amount and timing of such cash flows. In particular, the estimate was sensitive to significant assumptions with little to no available market data, such as the prepayment speeds and loss assumptions for each investment, which are based on management’s best estimate of future investment and market performance.
|
|||||||
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit |
We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of internal controls over the Company’s processes for determining interest income on Non-Agency RMBS and Loans held for investment. This included the controls over management’s review and approval of significant assumptions utilized for cash flow estimates as well as the Company’s quarterly analysis of yield income.
Our audit procedures included, among others, evaluating the appropriateness of the income recognition model applied to each of the Company’s investments, testing the mathematical accuracy of the models used to calculate and evaluate yields, and testing the Company’s cash flow estimates. With the assistance of our valuation specialists, we independently developed a range of loss projections for a sample of investments based on market data and compared them to the Company’s estimates utilized for income recognition. We also tested the completeness and accuracy of the underlying data used in management’s cash flow projections. In addition, we utilized third-party data to test management’s estimate and identify potential sources of contrary information.
|
|||||||
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2012.
New York, New York
February 18, 2021
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Chimera Investment Corporation
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited Chimera Investment Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Chimera Investment Corporation (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated statements of financial condition of the Company as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, changes in stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2020, and the related notes and our report dated February 18, 2021 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable
assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
New York, New York
February 18, 2021
| CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION | ||||||||
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION | ||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | ||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | $ | ||||||
Non-Agency RMBS, at fair value (net of allowance for credit losses of $ |
||||||||
| Agency RMBS, at fair value | ||||||||
| Agency CMBS, at fair value | ||||||||
| Loans held for investment, at fair value | ||||||||
| Receivable for investments sold | ||||||||
| Accrued interest receivable | ||||||||
| Other assets | ||||||||
| Derivatives, at fair value, net | ||||||||
Total assets (1)
|
$ | $ | ||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||
Secured financing agreements ($ |
$ | $ | ||||||
Securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS ($ |
||||||||
Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment ($ |
||||||||
| Long term debt | ||||||||
| Payable for investments purchased | ||||||||
| Accrued interest payable | ||||||||
| Dividends payable | ||||||||
| Accounts payable and other liabilities | ||||||||
Total liabilities (1)
|
$ | $ | ||||||
| Commitments and Contingencies (See Note 16) | ||||||||
| Stockholders' Equity: | ||||||||
Preferred Stock, par value of $ |
||||||||
| $ | $ | |||||||
Common stock: par value $ |
||||||||
| Additional paid-in-capital | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | ||||||||
| Cumulative earnings | ||||||||
| Cumulative distributions to stockholders | ( |
( |
||||||
| Total stockholders' equity | $ | $ | ||||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | $ | ||||||
(1) The Company's consolidated statements of financial condition include assets of consolidated variable interest entities (“VIEs”) that can only be used to settle obligations and liabilities of the VIE for which creditors do not have recourse to the primary beneficiary (Chimera Investment Corporation). As of December 31, 2020, and December 31, 2019, total assets of consolidated VIEs were $12,165,017 and $12,544,744 , respectively, and total liabilities of consolidated VIEs were $8,063,110 and $8,064,235 , respectively. See Note 9 for further discussion.
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
88
| CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION | |||||||||||
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | |||||||||||
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| Net interest income: | |||||||||||
Interest income (1)
|
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Interest expense (2)
|
|||||||||||
| Net interest income | |||||||||||
| Increase/(decrease) in provision for credit losses | $ | ||||||||||
| Net other-than-temporary credit impairment losses | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Other investment gains (losses): | |||||||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Realized gains (losses) on terminations of interest rate swaps | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Net realized gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Net gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value | ( |
||||||||||
| Net realized gains (losses) on sales of investments | ( |
||||||||||
| Gains (losses) on extinguishment of debt | ( |
||||||||||
| Total other gains (losses) | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Other expenses: | |||||||||||
| Compensation and benefits | |||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | |||||||||||
| Servicing fees | |||||||||||
| Transaction expenses | |||||||||||
| Total other expenses | |||||||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes | |||||||||||
| Income taxes | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Dividends on preferred stock | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common shareholders | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) per share available to common shareholders: | |||||||||||
| Basic | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Diluted | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding: | |||||||||||
| Basic | |||||||||||
| Diluted | |||||||||||
(1) Includes interest income of consolidated VIEs of $683,456 , $780,746 and $904,830 for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. See Note 9 to consolidated financial statements for further discussion.
(2) Includes interest expense of consolidated VIEs of $285,142 , $337,387 and $395,255 for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. See Note 9 to consolidated financial statements for further discussion.
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
89
| CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION | |||||||||||
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | |||||||||||
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss): | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Other comprehensive income: | |||||||||||
| Unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities, net | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for net losses included in net income for other-than-temporary credit impairment losses | |||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for net realized losses (gains) included in net income | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) before preferred stock dividends | $ | ( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||
| Dividends on preferred stock | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) available to common stock shareholders | $ | ( |
$ |
|
$ |
|
|||||
90
| CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Series A Preferred Stock Par Value | Series B Preferred Stock Par Value | Series C Preferred Stock Par Value | Series D Preferred Stock Par Value | Common Stock Par Value |
Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | Cumulative Earnings | Cumulative Distributions to Stockholders | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2019 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | — | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
— | — | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
— | — | — | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Settlement of Convertible Debt | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Settlement of Capped Call | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
— | — | — | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common dividends declared | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred dividends declared | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2020 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Series A Preferred Stock Par Value | Series B Preferred Stock Par Value | Series C Preferred Stock Par Value | Series D Preferred Stock Par Value | Common Stock Par Value |
Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | Cumulative Earnings | Cumulative Distributions to Stockholders | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common dividends declared | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred dividends declared | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of preferred stock | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2019 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Series A Preferred Stock Par Value | Series B Preferred Stock Par Value | Series C Preferred Stock Par Value | Series D Preferred Stock Par Value | Common Stock Par Value |
Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | Cumulative Earnings | Cumulative Distributions to Stockholders | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2017 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | — | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
— | — | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of Common Stock | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
— | — | — | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common dividends declared | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred dividends declared | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of preferred stock | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
91
| CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION | |||||||||||
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | |||||||||||
| (Accretion) amortization of investment discounts/premiums, net | |||||||||||
| Accretion (amortization) of deferred financing costs, debt issuance costs, and securitized debt discounts/premiums, net | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Amortization of swaption premium | |||||||||||
| Net unrealized losses (gains) on derivatives | ( |
||||||||||
| Margin (paid) received on derivatives | ( |
||||||||||
| Net unrealized losses (gains) on financial instruments at fair value | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Net realized losses (gains) on sales of investments | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in provision for credit losses | |||||||||||
| Net other-than-temporary credit impairment losses | |||||||||||
| (Gain) loss on extinguishment of debt | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Equity-based compensation expense | |||||||||||
| Changes in operating assets: | |||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in accrued interest receivable, net | ( |
||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in other assets | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Changes in operating liabilities: | |||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accounts payable and other liabilities | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accrued interest payable, net | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | |||||||||||
| Agency MBS portfolio: | |||||||||||
| Purchases | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
|||||
| Sales | |||||||||||
| Principal payments | |||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS portfolio: | |||||||||||
| Purchases | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Sales | |||||||||||
| Principal payments | |||||||||||
| Loans held for investment: | |||||||||||
| Purchases | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Sales | |||||||||||
| Principal payments | |||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | $ | $ | $ | ( |
|||||||
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | |||||||||||
| Proceeds from secured financing agreements | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Payments on secured financing agreements | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Net proceeds from preferred stock offerings | |||||||||||
| Payments on repurchase of common stock | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Proceeds from securitized debt borrowings, collateralized by loans held for investment | |||||||||||
| Payments on securitized debt borrowings, collateralized by loans held for investment | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Payments on securitized debt borrowings, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Net proceeds from issuance of convertible debt | |||||||||||
92
| Purchase of capped call | ( |
||||||||||
| Common dividends paid | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Preferred dividends paid | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | ( |
||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | |||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | |||||||||||
| Interest received | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Interest paid | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Non-cash investing activities: | |||||||||||
| Payable for investments purchased | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Receivable for investments sold | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Net change in unrealized gain (loss) on available-for sale securities | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
||||||
| Retained beneficial interests | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Non-cash financing activities: | |||||||||||
| Dividends declared, not yet paid | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Conversion of convertible debt | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
93
| CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION | ||||||||||||||
| NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS | ||||||||||||||
1. Organization
Chimera Investment Corporation, or the Company, was organized in Maryland on June 1, 2007. The Company commenced operations on November 21, 2007 when it completed its initial public offering. The Company elected to be taxed as a real estate investment trust, or REIT, under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and regulations promulgated thereunder, or the Code.
The Company conducts its operations through various subsidiaries including subsidiaries it treats as taxable REIT subsidiaries, or TRSs. In general, a TRS may hold assets and engage in activities that the Company cannot hold or engage in directly and generally may engage in any real estate or non-real estate related business. The Company currently has thirteen wholly owned direct subsidiaries: Chimera RMBS Whole Pool LLC and Chimera RMBS LLC formed in June 2009; CIM Trading Company LLC, or CIM Trading, formed in July 2010; Chimera Funding TRS LLC, or CIM Funding TRS, a TRS formed in October 2013, Chimera CMBS Whole Pool LLC and Chimera RMBS Securities LLC formed in March 2015; Chimera Insurance Company, LLC formed in July 2015; Chimera RR Holding LLC formed in April 2016, Anacostia LLC, a TRS formed in June 2018, NYH Funding LLC, a TRS formed in May 2019, Kali 2020 Holdings LLC formed in May 2020, Varuna Capital Partners LLC formed in September 2020 and Aarna Holdings LLC formed in November 2020.
2. Summary of the Significant Accounting Policies
(a) Basis of Presentation and Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements and related notes of the Company have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, or GAAP. In the opinion of the Company, all normal and recurring adjustments considered necessary for a fair presentation of its financial position, results of operations and cash flows have been included. Investment securities transactions are recorded on the trade date. Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current period's presentation.
The consolidated financial statements include the Company’s accounts, the accounts of its wholly-owned subsidiaries, and variable interest entities, or VIEs, in which the Company is the primary beneficiary. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
The Company uses securitization trusts considered to be VIEs in its securitization and re-securitization transactions. VIEs are defined as entities in which equity investors (i) do not have the characteristics of a controlling financial interest, or (ii) do not have sufficient equity at risk for the entity to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support from other parties. The entity that consolidates a VIE is known as its primary beneficiary and is generally the entity with (i) the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIEs’ economic performance, and (ii) the right to receive benefits from the VIE or the obligation to absorb losses of the VIE that could be significant to the VIE. For VIEs that do not have substantial on-going activities, the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIEs’ economic performance may be determined by an entity’s involvement with the design and structure of the VIE.
The trusts are structured as entities that receive principal and interest on the underlying collateral and distribute those payments to the security holders. The assets held by the securitization entities are restricted in that they can only be used to fulfill the obligations of the securitization entity. The Company’s risks associated with its involvement with these VIEs are limited to its risks and rights as a holder of the security it has retained as well as certain risks associated with being the sponsor and depositor of and the seller, directly or indirectly to, the securitizations entities.
Determining the primary beneficiary of a VIE requires judgment. The Company determined that for the securitizations it consolidates, its ownership provides the Company with the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits from the VIE that could be significant to the VIE. In addition, the Company has the power to direct the activities of the VIEs that most significantly impact the VIEs’ economic performance, or power, such as rights to replace the servicer without cause or the Company was determined to have power in connection with its involvement with the structure and design of the VIE.
The Company’s interest in the assets held by these securitization vehicles, which are consolidated on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition, is restricted by the structural provisions of these trusts, and a recovery of the Company’s investment in the vehicles will be limited by each entity’s distribution provisions. The liabilities of the securitization vehicles, which are also consolidated on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition, are non-recourse to the Company, and can only be satisfied using proceeds from each securitization vehicle’s respective asset pool.
94
(b) Statements of Financial Condition Presentation
(c) Cash and Cash Equivalents
(d) Agency and Non-Agency Mortgage-Backed Securities
The Company invests in mortgage backed securities, or MBS, representing interests in obligations backed by pools of mortgage loans. The Company’s investments in MBS includes investments in both Agency MBS and Non-Agency MBS. The Company delineates between Agency MBS and Non-Agency MBS as follows: (1) Agency MBS are mortgage pass-through certificates, collateralized mortgage obligations, or CMOs, and other MBS representing interests in or obligations backed by pools of mortgage loans issued or guaranteed by agencies of the U.S. Government, such as Ginnie Mae, or federally chartered corporations such as Freddie Mac or Fannie Mae where principal and interest repayments are guaranteed by the respective agency of the U.S. Government or federally chartered corporation; and (2) Non-Agency MBS are not issued or guaranteed by a U.S. Government Agency or other institution and are subject to credit risk. Repayment of principal and interest on Non-Agency MBS is not guaranteed and it is subject to the performance of the mortgage loans or MBS collateralizing the obligation. Agency MBS collectively refers to include Agency CMBS and Agency RMBS as defined in Part I of this annual report.
The Company also invests in Interest Only Agency MBS strips and Interest Only Non-Agency RMBS strips, or IO MBS strips. IO MBS strips represent the Company’s right to receive a specified proportion of the contractual interest flows of the collateral.
The Company classifies its MBS as available-for-sale sale (AFS) or in accordance with the fair-value option (FVO). MBS classified as AFS are recorded on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in Other comprehensive income (OCI). MBS classified as FVO are recorded on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings. See Note 5 of these consolidated financial statements for further discussion of MBS carried at FVO and how the Company determines fair value. From time to time, as part of the overall management of its portfolio, the Company may sell any of its investments and recognize a realized gain or loss as a component of earnings in the Consolidated Statements of Operations utilizing the average cost method.
The Company’s accounting policy for interest income and an allowance for credit losses related to its MBS is as follows:
Interest Income Recognition and Allowance for Credit Losses
Investments in Non-agency RMBS securities
The Company considers its investments in Non-Agency RMBS as beneficial interests. Beneficial interests give the Company the right to receive all or portions of specified cash flows received by a trust or other entity. Beneficial interests held by the Company are created in connection with securitization transactions such as those involving mortgage loan obligations. Beneficial interests are accounted for in accordance with guidance Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Accounting Standards Codification (ASC), 325-40, Beneficial Interests in Securitized Financial Assets, (ASC 325-40) as amended by the accounting standards update (ASU) No. 2016-13, Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments (ASU 2016-13).
Interest income on the Company’s beneficial interests is recognized using the interest method based on the Company's estimates of cash flows expected to be collected. The effective interest rate on these securities is based on the Company's estimate for each security of the projected cash flows, which are estimated based on observation of current market information and include assumptions related to fluctuations in prepayment speeds and the timing and amount of credit losses. On a quarterly
95
basis, the Company reviews and, if appropriate, adjusts its cash flow projections based on inputs and analyses received from external sources, internal models, and the Company’s judgments about prepayment rates, the timing and amount of credit losses, and other factors. Changes in the amount or timing of cash flows from those originally projected, or from those estimated at the last evaluation date, are considered to be either favorable changes or adverse changes.
Adverse changes in the timing or amount of cash flows on beneficial interests classified as AFS could result in the Company recording an increase in the allowance for credit losses. The allowance for credit losses are calculated using a discounted cash flow (DCF) approach and is measured as the difference between the beneficial interest’s amortized cost and the estimate of cash flows expected to be collected discounted at the effective interest rate used to accrete the beneficial interest. The allowance for credit losses is recorded as a contra-asset and a reduction in earnings. The allowance for credit losses will be limited to the amount of the unrealized losses on the beneficial interest. Any allowance for credit losses in excess of the unrealized losses on the beneficial interests are accounted for as a prospective reduction of the effective interest rate. No allowance is recorded for beneficial interests in an unrealized gain position. Favorable changes in the DCF will result in a reduction in the allowance for credit losses, if any. Any reduction in allowance for credit losses is recorded in earnings. If there is no allowance for credit losses, or if the allowance for credit losses has been reduced to zero, the remaining favorable changes are reflected as a prospective increase to the effective interest rate.
Beneficial interests for which other than temporary impairment (OTTI) had been recognized prior to the effective date of ASU 2016-13 shall apply the guidance in the update on a prospective basis. In addition, the yield used to accrete the beneficial interest on beneficial interests with prior OTTI will remain unchanged as a result of the adoption of ASU 2016-13. Recoveries of amounts previously written off relating to improvements in cash flows shall be recorded in income in the period received. Therefore, subsequent favorable changes in the DCF of the beneficial interests with prior OTTI will not be reflected as an adjustment to their yield used to accrete the discount. Subsequent adverse changes in the DCF will result in an increase to the allowance for credit losses, limited to the amount of the unrealized losses on the beneficial interest.
Credit losses recognized on beneficial interests will be accreted on a monthly basis at the rate used to recognize interest income, the effective interest rate. The accretion will be recorded as a reduction to interest income in the statement of operations.
The Company presents separately all accrued interest on the statement of financial position. Interest is accrued on all beneficial interests when due. Interest which is not received at the due date is written off when it becomes delinquent. As all interest not received when due is charged off against interest income, no allowance for accrued interest is required.
No allowances for credit losses are recognized on beneficial interests for which the Company has elected the fair value option. All favorable or adverse changes in the Company's estimates of cash flows expected to be collected results in a prospective increase or decrease in the effective interest rate used to recognize interest income.
Investments in agency MBS securities
The Company invests in pass-through mortgage-backed securities guaranteed by Ginnie Mae (GNMA), Fannie Mae (FNMA) and Freddie Mac (FHLMC) (collectively “Agency Securities”).
Interest income for Agency Securities for which changes in fair value are recorded in OCI, including premiums and discounts associated with the acquisition of these securities, is recognized over the life of such securities using the interest method based on the cash flows of the security. In applying the interest method, the Company considers estimates of future principal prepayments in the calculation of the effective yield. Differences that arise between previously anticipated prepayments and actual prepayments received, as well as changes in future prepayment assumptions, result in a recalculation of the effective yield on the security. This recalculation of the effective yield is updated on a monthly basis. Upon a recalculation of the effective yield, the investment in the security is adjusted to the amount that would have existed had the new effective yield been retrospectively applied since acquisition with a corresponding charge or credit to interest income. This adjustment is accounted for as a change in estimate with a cumulative effect adjustment on interest income as a result in the change in the yield. Prepayments are estimated using models generally accepted in the industry.
All securities carried at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in OCI need to be evaluated for expected losses, even if the risk of loss is considered remote. However, the Company is not required to measure expected credit losses on securities in which historical credit loss information adjusted for current conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts results in an expectation that incurring a credit loss is zero. Based on the current facts and circumstances, the Company believes its investments Agency Securities would qualify for zero expected credit losses. The factors considered in reaching this conclusion include the long history of zero credit losses, the explicit guarantee by the US government (although limited for FNMA and FHLMC securities) and yields that, while not risk-free, generally trade based on market views of prepayment and liquidity risk (not credit risk).
96
(e) Loans Held for Investment
The Company's Loans held for investments is primarily comprised of seasoned residential mortgage loans that are not guaranteed as to repayment of principal or interest. These loans are serviced and may be modified by a third-party servicer. Additionally, in certain cases, the Company has the ability to remove the servicer with or without cause upon prior notice. These residential mortgage loans are designated as held for investment. Interest income on loans held for investment is recognized over the expected life of the loans using the interest method with changes in yield reflected in earnings on a prospective basis and are carried at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings.
The Company estimates the fair value of securitized loans as described in Note 5 of these consolidated financial statements.
Interest is accrued on all loans held for investment when due. Interest which is not received at the due date is written off when it becomes delinquent. Nonrefundable fees and costs related to acquiring the Company’s residential mortgage loans are recognized as expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Income recognition is suspended for loans when, based on information from the servicer, a full recovery of interest or principal becomes doubtful.
Real estate owned
(f) Secured Financing Agreements
(g) Securitized Debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS and Securitized Debt, collateralized by Loans held for investment
Certain re-securitization transactions classified as Securitized Debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS, reflect the transfer to a trust of fixed or adjustable rate MBS which are classified as Non-Agency RMBS that pay interest and principal to the debt holders of that re-securitization. Re-securitization transactions completed by the Company that did not qualify as sales are accounted for as secured borrowings. The associated securitized debt is carried at amortized cost, net of any unamortized premiums or discounts.
Certain transactions involving residential mortgage loans are accounted for as secured borrowings and are recorded as Securitized loans held for investment and the corresponding debt as Securitized debt, collateralized by loans held for investment in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. These securitizations are collateralized by residential adjustable or fixed rate mortgage loans that have been placed in a trust and pay interest and principal to the debt holders of that securitization. The Securitized debt, collateralized by loans held for investment, is carried at fair value.
The Company recognizes interest expense on securitized debt over the contractual life of the debt using the interest method with changes in yield reflected in earnings on a retrospective basis. For securitized debt, where the Company has elected fair value option, the interest expense is recognized using the interest method with changes in yield reflected in earnings on a prospective
97
basis. The Company recognizes a gain or loss on extinguishment of debt when it acquires its outstanding debt at discount or premium.
The Company estimates the fair value of its securitized debt as described in Note 5 to these consolidated financial statements.
(h) Long Term Debt
The Company's Long Term Debt currently comprised of Convertible Senior Notes. Convertible notes include unsecured convertible debt that are carried at their unpaid principal balance net of any unamortized deferred issuance costs. Interest on the notes is payable semiannually until such time the notes mature or are converted or exchanged into shares. Any debt discounts or premiums are reported as an adjustment to the carrying amount of the debt liability and amortized into interest expense using the effective interest method. If converted by a holder, the holder of the notes would receive shares of our common stock. Deferred debt issuance costs are expenses associated with the issuance of long-term debt. These expenses typically include underwriting, legal, accounting, and other fees. Deferred debt issuance costs are included in the carrying value of the related long-term debt issued and are amortized as an adjustment to interest expense using the effective interest method, based upon the actual and estimated repayment schedules of the related long-term debt issued.
(i) Fair Value
The Company carries the majority of its financial instruments at fair value. The Company has elected fair value option on certain Non-Agency RMBS, Agency MBS, Loans held for investments and Securitized debt, collateralized by loans held for investment. The Company believes the fair value option election will provide its financial statements user with reduced complexity, greater consistency, understandability and comparability.
Agency MBS:
The Company has elected to account for Agency MBS investments acquired on or after July 1, 2017 under the fair value option. Under the fair value option, these investments will be carried at fair value, with changes in fair value reported in earnings (included as part of “Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value”). Consistent with all other investments for which the Company has elected the fair value option, the Company will recognize revenue on a prospective basis in accordance with guidance in ASC 325-40.
All Agency MBS investments owned prior to July 1, 2017 will continue to be carried at fair value with changes in fair value reported in other comprehensive income (OCI) as available-for-sale investments. All revenue recognition for these Agency MBS investments owned prior to July 1, 2017 will be in accordance with ASC 310-20, per the Company’s accounting practices.
Non-Agency RMBS:
The Company has elected to account for all Non-Agency RMBS investments acquired on or after January 1, 2019 under the fair value option. Under the fair value option, these investments will be carried at fair value, with changes in fair value reported in earnings (included as part of “Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value”). Consistent with all other investments for which the Company has elected the fair value option, the Company will recognize revenue on a prospective basis in accordance with guidance in ASC 325-40.
The Company has elected the fair value option for certain interests in Non-Agency RMBS which it refers to as the overcollateralization classes. The cash flows for these holdings are generally subordinate to all other interests of the trusts and generally only pay out funds when certain ratios are met and excess cash holdings, as determined by the trustee, are available for distribution to the overcollateralization class. Many of the investments in this group have no current cash flows and may not ever pay cash flows, depending on the loss experience of the collateral group supporting the investment. Estimating future cash flows for this group of Non-Agency RMBS investments is highly subjective and uncertain; therefore, the Company records these holdings at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in earnings. Changes in fair value of the overcollateralization classes are presented in Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The fair value of the Non-Agency RMBS carried at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in earnings was $417 million and $423 million as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
98
Interest-Only MBS:
The Company accounts for the IO MBS strips at fair value with changes in fair value reported in earnings. The IO MBS strips are included in MBS, at fair value, on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
Included in Non-Agency RMBS, at fair value on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition are IO MBS strips carried at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in earnings of $262 million and $289 million as of December 31, 2020 and 2019. Included in Agency RMBS, at fair value on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition are IO MBS strips carried at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in earnings of $91 million and $128 million as of December 31, 2020 and 2019. Included in Agency CMBS, at fair value on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition are IO MBS strips carried at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in earnings of $26 million and $49 million as of December 31, 2020 and 2019. Interest income reported on all IO MBS securities was $43 million and $27 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Loans Held for Investment:
The Company’s Loans held for investment are carried at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in earnings. The Company carries Loans held for investment at fair value as it may resecuritize these loans in the future. Additionally, the fair value option allows both the loans and related financing to be consistently reported at fair value and to achieve operational and valuation simplifications.
Changes in fair value of Loans held for investment are presented in Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Securitized Debt, Collateralized by Loans Held for Investment:
The Company’s securitized debt, collateralized by loans held for investment, is carried at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in earnings. The Company has elected the fair value option for these financings as it may call or restructure these debt financings in the future. Additionally, the fair value option allows both the loans and related financing to be consistently reported at fair value and to achieve operational and valuation simplifications. Changes in fair value of securitized debt, collateralized by loans held for investment are presented in Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Fair Value Disclosure
A complete discussion of the methodology utilized by the Company to estimate the fair value of its financial instruments is included in Note 5 to these consolidated financial statements.
(j) Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company’s investment policies permit it to enter into derivative contracts, including interest rate swaps, swaptions, mortgage options, futures, and interest rate caps to manage its interest rate risk and, from time to time, enhance investment returns. The Company’s derivatives are recorded as either assets or liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition and measured at fair value. These derivative financial instrument contracts are not designated as hedges for GAAP; therefore, all changes in fair value are recognized in earnings. The Company estimates the fair value of its derivative instruments as described in Note 5 of these consolidated financial statements. Net payments on derivative instruments are included in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows as a component of net income. Unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives are removed from net income to arrive at cash flows from operating activities.
The Company elects to net the fair value of its derivative contracts by counterparty when appropriate. These contracts contain legally enforceable provisions that allow for netting or setting off of all individual derivative receivables and payables with each counterparty and therefore, the fair values of those derivative contracts are reported net by counterparty. The credit support annex provisions of the Company’s derivative contracts allow the parties to mitigate their credit risk by requiring the party which is in a net payable position to post collateral. As the Company elects to net by counterparty the fair value of derivative contracts, it also nets by counterparty any cash collateral exchanged as part of the derivative. Refer to Note 10 Derivative Instruments for further details.
(k) Sales, Securitizations, and Re-Securitizations
99
(l) Income Taxes
(m) Net Income per Share
(n) Stock-Based Compensation
(o) Use of Estimates
100
(p) Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Financial Instruments - Credit Losses - (Topic 326)
On January 1, 2020 the Company adopted accounting standards update (or ASU) No. 2016-13, Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments. This update replaced the previous model for recognizing credit losses from an incurred credit loss model to a current expected credit loss (or CECL) model for financial instruments measured at amortized cost and required the Company to record an allowance for credit losses on available-for-sale (or AFS) debt securities for all expected (rather than incurred) credit losses of the asset rather than reduce the carrying amount, as the Company did under the OTTI model. This update also revised the accounting model for purchased credit-impaired debt securities. The changes in the allowance for credit losses created in accordance with this update have been recorded in earnings. Expected credit losses are limited to the amount of the unrealized loss on the debt securities impacted by the update.
The update did not have any impact on financial instruments which were carried at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings. As all Loans held for investment are carried at fair value, with changes in fair value recorded in earnings, the update had no impact on the carrying value or revenue recognition of Loans held for investment.
On January 1, 2020, the effective date of the update, the Company was required to record a cumulative-effect adjustment related to financial instruments under the scope of this update to the statement of financial position. As all financial instruments impacted by the update, including all purchased credit impaired debt securities, were in an unrealized gain position as of the effective date, there was no impact on the financial statements at the transition date and no cumulative-effect adjustment was required.
In addition, the update superseded subtopic 310-30, Receivables - Loans and Debt Securities Acquired with Deteriorated Credit Quality. As of January 1, 2020, the Company accounted all investments previously classified as AFS and under subtopic 310-30, using the subtopic 326-30 Financial Instruments - Credit Losses; Available-for-Sale Debt Securities and subtopic 325-40, Investments -Other-Beneficial Interests in Securitized Financial Assets.
Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848)
In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-4, Reference Rate Reform: Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting. The amendments in this update provide optional expedients and exceptions for applying generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) to contracts, hedging relationships, and other transactions affected by reference rate reform if certain criteria are met. The amendments in this update apply only to contracts, hedging relationships, and other transactions that reference London Inter Bank Offering Rate (or LIBOR) or another reference rate expected to be discontinued because of reference rate reform. The amendments in this update are effective for all entities as of March 12, 2020 through December 31, 2022. An entity may elect to apply the amendments for contract modifications by Topic or Industry Subtopic as of any date from the beginning of an interim period that includes or is subsequent to March 12, 2020, or prospectively from a date within an interim period that includes or is subsequent to March 12, 2020, up to the date that the financial statements are available to be issued. The Company has not yet adopted this guidance and is currently evaluating what impact this update will have on the consolidated financial statements.
Debt—Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives and Hedging—Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40)
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-6, Debt—Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives and Hedging—Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40): Accounting for Convertible Instruments and Contracts in an Entity’s Own Equity. The FASB issued this update to simplify the current guidance for convertible instruments and the derivatives scope exception for contracts in an entity’s own equity. Additionally, the amendments affect the diluted EPS calculation for instruments that may be settled in cash or shares and for convertible instruments. The update also provides for expanded disclosure requirements to increase transparency. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021 including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company has not yet adopted this guidance and is currently evaluating what impact this update will have on the consolidated financial statements.
3. Mortgage-Backed Securities
101
first principal repayments in their pro-rata ownership interests at the acquisition date. The tables below present amortized cost, allowance for credit losses, fair value and unrealized gain/losses of Company's MBS investments as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Principal or Notional Value | Total Premium | Total Discount | Amortized Cost | Allowance for credit losses | Fair Value | Gross Unrealized Gains | Gross Unrealized Losses | Net Unrealized Gain/(Loss) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||||||
| Subordinated | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Principal or Notional Value | Total Premium | Total Discount | Amortized Cost | Fair Value | Gross Unrealized Gains | Gross Unrealized Losses | Net Unrealized Gain/(Loss) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||||||
| Subordinated | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||||||
102
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized Loss Position for Less than 12 Months | Unrealized Loss Position for 12 Months or More | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Estimated Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Number of Positions | Estimated Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Number of Positions | Estimated Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Number of Positions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subordinated | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized Loss Position for Less than 12 Months | Unrealized Loss Position for 12 Months or More | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Estimated Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Number of Positions | Estimated Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Number of Positions | Estimated Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Number of Positions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subordinated | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
At December 31, 2020, the Company did not intend to sell any of its Agency and Non-Agency MBS that were in an unrealized loss position, and it was not more likely than not that the Company would be required to sell these MBS investments before recovery of their amortized cost basis, which may be at their maturity. With respect to RMBS held by consolidated VIEs, the ability of any entity to cause the sale by the VIE prior to the maturity of these RMBS is either expressly prohibited, not probable, or is limited to specified events of default, none of which have occurred as of December 31, 2020.
Gross unrealized losses on the Company’s Agency MBS (excluding Agency MBS which are reported at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings) were $69 thousand and $1 million as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively. Given the inherent credit quality of Agency MBS, the Company does not consider any of the current impairments on its Agency MBS to be credit related. In evaluating whether it is more likely than not that it will be required to sell any impaired security before its anticipated recovery, which may be at their maturity, the Company considers the significance of each investment, the amount of impairment, the projected future performance of such impaired securities, as well as the Company’s current and anticipated leverage capacity and liquidity position. Based on these analyses, the Company determined that at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, unrealized losses on its Agency MBS were temporary.
Gross unrealized losses on the Company’s Non-Agency RMBS (excluding Non-Agency RMBS which are reported at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings), net of any allowance for credit losses, was $248 thousand at December 31, 2020. After evaluating the securities and recording the allowance for credit losses, we concluded that the remaining unrealized
103
losses reflected above were non-credit related and would be recovered from the securities' estimated future cash flows. The Company considered a number of factors in reaching this conclusion, including that we did not intend to sell the securities, it was not considered more likely than not that we would be forced to sell the securities prior to recovering the amortized cost, and there were no material credit events that would have caused us to otherwise conclude that we would not recover the amortized cost. The allowance for credit losses are calculated by comparing the estimated future cash flows of each security discounted at the yield determined as of the initial acquisition date or, if since revised, as of the last date previously revised, to the net amortized cost basis. Significant judgment is used in projecting cash flows for Non-Agency RMBS.
Gross unrealized losses on the Company's Non-Agency RMBS (excluding Non-Agency RMBS which are reported at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings), was $348 thousand at December 31, 2019. Based upon the most recent evaluation, the Company does not consider these unrealized losses to be indicative of other-than-temporary and does not believe that these unrealized losses are credit related, but rather are due to other factors.
The Company has reviewed its Non-Agency RMBS that are in an unrealized loss position to identify those securities with losses that are credit related based on an assessment of changes in cash flows expected to be collected for such RMBS, which considers recent bond performance and expected future performance of the underlying collateral. A summary of the credit loss allowance on available-for-sale securities for the year ended December 31, 2020 is presented below.
| For the Year Ended | |||||
| December 31, 2020 | |||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||
| Beginning allowance for credit losses | $ | ||||
| Transition impact from CECL standard | |||||
| Additions to the allowance for credit losses on securities for which credit losses were not previously recorded | |||||
| Allowance on purchased financial assets with credit deterioration | |||||
| Reductions for the securities sold during the period | ( |
||||
| Increase/(decrease) on securities with an allowance in the prior period | ( |
||||
| Write-offs charged against the allowance | ( |
||||
| Recoveries of amounts previously written off | |||||
| Ending allowance for credit losses | $ | ||||
The following table presents significant credit quality indicators used for the credit loss allowance on our Non-Agency RMBS investments as of December 31, 2020.
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
| Prepay Rate | CDR | Loss Severity | ||||||||||||
| Amortized Cost | Weighted Average | Weighted Average | Weighted Average | |||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||
| Senior | ||||||||||||||
The increase in the allowance for credit losses for the year ended December 31, 2020 is primarily due to increased expected losses and delinquencies as compared to the beginning of the year. In addition, certain Non-Agency RMBS positions, which had previously been in an unrealized gain position as of the prior year-end, are now in an unrealized loss position as of the end of the current period due to the decline in fair value. These Non-Agency RMBS positions now in an unrealized loss have resulted in the recognition of an allowance for credit losses which was previously limited by unrealized gains on these investments.
104
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Unrealized Gain Included in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | Gross Unrealized Gain Included in Cumulative Earnings | Total Gross Unrealized Gain | Gross Unrealized Loss Included in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | Gross Unrealized Loss Included in Cumulative Earnings | Total Gross Unrealized Loss | |||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
||||||||||||
| Subordinated | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
|||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Unrealized Gain Included in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | Gross Unrealized Gain Included in Cumulative Earnings | Total Gross Unrealized Gain | Gross Unrealized Loss Included in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | Gross Unrealized Loss Included in Cumulative Earnings | Total Gross Unrealized Loss | |||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
||||||||||||
| Subordinated | ( |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | ( |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
|||||||||||
Changes in prepayments, actual cash flows, and cash flows expected to be collected, among other items, are affected by the collateral characteristics of each asset class. The Company chooses assets for the portfolio after carefully evaluating each investment’s risk profile.
The following tables provide a summary of the Company’s MBS portfolio at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| Principal or Notional Value at Period-End (dollars in thousands) |
Weighted Average Amortized Cost Basis |
Weighted Average Fair Value | Weighted Average Coupon |
Weighted Average Yield at Period-End (1)
|
|||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
Senior |
$ | $ | % | % | |||||||||||||
Subordinated |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | % | % | |||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||
Project loans |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
105
(1) Bond Equivalent Yield at period end.
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||
| Principal or Notional Value at Period-End (dollars in thousands) |
Weighted Average Amortized Cost Basis |
Weighted Average Fair Value | Weighted Average Coupon |
Weighted Average Yield at Period-End (1)
|
|||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
Senior |
$ | $ | $ | % | % | ||||||||||||
Subordinated |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
Pass-through |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||
Project loans |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
Interest-only |
% | % | |||||||||||||||
(1) Bond Equivalent Yield at period end.
The following table presents the weighted average credit rating of the Company’s Non-Agency RMBS portfolio at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| AAA | % | % | ||||||
| AA | % | % | ||||||
| A | % | % | ||||||
| BBB | % | % | ||||||
| BB | % | % | ||||||
| B | % | % | ||||||
| Below B | % | % | ||||||
| Not Rated | % | % | ||||||
| Total | % | % | ||||||
Actual maturities of MBS are generally shorter than the stated contractual maturities. Actual maturities of the Company’s MBS are affected by the contractual lives of the underlying mortgages, periodic payments of principal and prepayments of principal. The following tables provide a summary of the fair value and amortized cost of the Company’s MBS at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 according to their estimated weighted-average life classifications. The weighted-average lives of the MBS in the tables below are based on lifetime expected prepayment rates using the Company's prepayment assumptions for the Agency MBS and Non-Agency RMBS. The prepayment model considers current yield, forward yield, steepness of the interest rate curve, current mortgage rates, mortgage rates of the outstanding loan, loan age, margin, and volatility.
106
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Weighted Average Life | |||||||||||||||||
| Less than one year | Greater than one year and less than five years |
Greater than five years and less than ten years |
Greater than ten years | Total | |||||||||||||
| Fair value | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Subordinated | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Total fair value | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Amortized cost | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Subordinated | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Total amortized cost | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Weighted Average Life | |||||||||||||||||
| Less than one year | Greater than one year and less than five years |
Greater than five years and less than ten years |
Greater than ten years | Total | |||||||||||||
| Fair value | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Subordinated | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Total fair value | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Amortized cost | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Senior | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Subordinated | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Total amortized cost | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
107
The Non-Agency RMBS investments are secured by pools of mortgage loans which are subject to credit risk. The following table summarizes the delinquency, bankruptcy, foreclosure and REO total of the pools of mortgage loans securing the Company’s investments in Non-Agency RMBS at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019. When delinquency rates increase, it is expected that the Company will incur additional credit losses.
| December 31, 2020 | 30 Days Delinquent | 60 Days Delinquent | 90+ Days Delinquent | Bankruptcy | Foreclosure | REO | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| % of Unpaid Principal Balance | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | ||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | 30 Days Delinquent | 60 Days Delinquent | 90+ Days Delinquent | Bankruptcy | Foreclosure | REO | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| % of Unpaid Principal Balance | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | ||||||||||||||||
The Non-Agency RMBS in the Portfolio have the following collateral characteristics at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||
| Weighted average maturity (years) | ||||||||||||||
Weighted average amortized loan to value (1)
|
% | % | ||||||||||||
Weighted average FICO (2)
|
||||||||||||||
| Weighted average loan balance (in thousands) | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average percentage owner occupied | % | % | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average percentage single family residence | % | % | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average current credit enhancement | % | % | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average geographic concentration of top four states | CA | % | CA | % | ||||||||||
| NY | % | FL | % | |||||||||||
| FL | % | NY | % | |||||||||||
| NJ | % | TX | % | |||||||||||
(1) Value represents appraised value of the collateral at the time of loan origination.
(2) FICO as determined at the time of loan origination.
The table below presents the origination year of the underlying loans related to the Company’s portfolio of Non-Agency RMBS at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| Origination Year | December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||
| 2003 and prior | % | % | ||||||
| 2004 | % | % | ||||||
| 2005 | % | % | ||||||
| 2006 | % | % | ||||||
| 2007 | % | % | ||||||
| 2008 and later | % | % | ||||||
| Total | % | % | ||||||
Gross realized gains and losses are recorded in “Net realized gains (losses) on sales of investments” on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Operations. The proceeds and gross realized gains and gross realized losses from sales of investments for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 are as follows:
108
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Proceeds from sales: | |||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||
| Gross realized gains: | |||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | |||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||
| Gross realized losses: | |||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Agency RMBS | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Agency CMBS | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Net realized gain (loss) | $ | $ | $ | ( |
|||||||
Included in the gross realized gains for the year ended December 31, 2018 in the table above are exchanges of securities with a fair value of $81 million. The Company exchanged its investment in a re-REMIC security for the underlying collateral supporting the group related to the exchanged asset. These exchanges were treated as non-cash sales and purchases and resulted in a net realized gain of $3 million, reflected in earnings for the year ended December 31, 2018. There were no such exchanges during the year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
During the first quarter of 2020, the Company transferred Non-Agency RMBS investments with a market value of $135 million to a third party. As part of the transfer, the Company purchased an option to re-acquire these assets for a fixed price at a future date. This transfer was accounted for as a secured borrowing within the Secured financing agreements on the Statement of Financial Condition. During the third quarter of 2020, the Company exercised its option and repurchased the transferred investments with an amortized cost of $196 million for $251 million, which extinguished the secured borrowing. This transaction resulted in a loss on extinguishment of debt of $55 million.
4. Loans Held for Investment
The Loans held for investment are comprised primarily of loans collateralized by seasoned reperforming residential mortgages. Additionally, it includes non-conforming, single family, owner occupied, jumbo, prime residential mortgages.
At December 31, 2020, all Loans held for investment are carried at fair value. See Note 5 for a discussion on how the Company determines the fair values of the Loans held for investment. As changes in the fair value of these loans are reflected in earnings, the Company does not estimate or record a loan loss provision. The total amortized cost of our Loans held for investment was $12.5 billion and $13.7 billion as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively.
109
| For the Year Ended | For the Year Ended | |||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||
| Balance, beginning of period | $ | $ | ||||||
| Purchases | ||||||||
| Principal paydowns | ( |
( |
||||||
| Sales and settlements | ( |
( |
||||||
| Net periodic accretion (amortization) | ( |
( |
||||||
| Realized gains (losses) on sales and settlements | ||||||||
| Change in fair value | ||||||||
| Balance, end of period | $ | $ | ||||||
The primary cause of the change in fair value is due to market demand and changes in credit risk of mortgage loans. During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company sold $1.1 billion of loans, with the Company retaining $22 million of beneficial interests. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company sold $1.8 billion of loans, with the Company retaining $124 million of beneficial interests.
During the year ended December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the Company transferred loans with unpaid principal balances of $653 million and $343 million, respectively, to a third party. The Company evaluated the sales under ASC 860 and determined that the sales did not effectively transfer control of the loans from the Company, the transferor, to the third party, the transferee, due to a right by the Company to call the loans at a fixed price at a future date. As such, these transfers have been accounted for by the Company as secured borrowings and no gain or loss was recorded upon the transfer of the loans. The proceeds received, net of any collateral received in the transfer, has been recorded as a Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. The secured borrowings related to the unpaid principal amount of these loans are non-recourse to the Company and these loans can only be used to satisfy the obligations of the transferee and the obligations of the transferee are non-recourse to the Company. See footnote 7 for more details regarding Securitized debt.
Residential mortgage loans
The loan portfolio for all residential mortgages were originated during the following periods:
| Origination Year | December 31, 2020 |
December 31, 2019 (1)
|
||||||
| 2002 and prior | % | % | ||||||
| 2003 | % | % | ||||||
| 2004 | % | % | ||||||
| 2005 | % | % | ||||||
| 2006 | % | % | ||||||
| 2007 | % | % | ||||||
| 2008 | % | % | ||||||
| 2009 | % | % | ||||||
| 2010 and later | % | % | ||||||
| Total | % | % | ||||||
(1) The table above excludes approximately $754 million of Loans held for investments for December 31, 2019, which was purchased prior to the reporting date and settled subsequent to the reporting period.
110
| December 31, 2020 |
December 31, 2019 (1)
|
|||||||||||||
| Number of loans | ||||||||||||||
| Weighted average maturity (years) | ||||||||||||||
| Weighted average loan to value | % | % | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average FICO | ||||||||||||||
| Weighted average loan balance (in thousands) | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average percentage owner occupied | % | % | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average percentage single family residence | % | % | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average geographic concentration of top five states | CA | % | CA | % | ||||||||||
| FL | % | FL | % | |||||||||||
| NY | % | NY | % | |||||||||||
| PA | % | OH | % | |||||||||||
| VA | % | PA | % | |||||||||||
The following tables show various characteristics of our residential loan portfolio and outstanding principal balance of the loans that are 30 days delinquent and greater for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Loan Balance | Number of Loans | Interest Rate | Maturity Date | Total Principal | 30-89 Days Delinquent | 90+ Days Delinquent | ||||||||||||||
| Held-for-Investment at fair value: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustable rate loans: | ||||||||||||||||||||
$ |
6/1/1983 - 2/1/2059 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
12/1/2027 - 2/1/2057 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
1/1/2034 - 10/1/2056 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
7/1/2036 - 2/1/2052 | |||||||||||||||||||
Over $ |
10/1/2034 - 6/1/2049 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed loans: | ||||||||||||||||||||
$ |
6/1/1989 - 5/1/2062 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
12/1/2005 - 3/1/2065 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
6/1/2020 - 10/1/2059 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
3/1/2013 - 11/1/2058 | |||||||||||||||||||
Over $ |
12/1/2019 - 6/1/2059 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
The foreclosure, bankruptcy, and REO principal balances on our loans were $298 million, $277 million and $30 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2020, which are included in the table above.
111
December 31, 2019 (1)
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Loan Balance | Number of Loans | Interest Rate | Maturity Date | Total Principal | 30-89 Days Delinquent | 90+ Days Delinquent | ||||||||||||||
| Held-for-Investment at fair value: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustable rate loans: | ||||||||||||||||||||
$ |
6/1/1983 - 3/13/2057 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
3/1/2023 - 7/1/2057 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
1/1/2034 - 10/1/2056 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
10/1/2036 - 11/1/2048 | |||||||||||||||||||
Over $ |
5/1/2036 - 10/1/2048 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed loans: | ||||||||||||||||||||
$ |
6/1/1989 - 5/1/2062 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
12/1/2019 - 3/1/2065 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
8/1/2019 - 9/1/2059 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ |
3/1/2013 - 1/1/2058 | |||||||||||||||||||
Over $ |
9/1/2019 - 12/1/2057 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
(1) The table above excludes approximately $754 million of Loans held for investments for December 31, 2019, which was purchased prior to the reporting date and settled subsequent to the reporting period.
The foreclosure, bankruptcy, and REO principal balances on our loans were $299 million, $322 million and $59 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2019, which are included in the table above.
The fair value of residential mortgage loans 90 days or more past due was $910 million and $597 million as of December 31,
2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively.
5. Fair Value Measurements
The Company applies fair value guidance in accordance with GAAP to account for its financial instruments. The Company categorizes its financial instruments, based on the priority of the inputs to the valuation technique, into a three-level fair value hierarchy. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3). If the inputs used to measure the financial instruments fall within different levels of the hierarchy, the categorization is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement of the instrument. Financial assets and liabilities recorded at fair value on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition or disclosed in the related notes are categorized based on the inputs to the valuation techniques as follows:
Level 1 – inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets and liabilities in active markets.
Level 2 – inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
Level 3 – inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to fair value.
Fair value measurements categorized within Level 3 are sensitive to changes in the assumptions or methodology used to determine fair value and such changes could result in a significant increase or decrease in the fair value. Any changes to the
112
valuation methodology are reviewed by the Company to ensure the changes are appropriate. As markets and products evolve and the pricing for certain products becomes more transparent, the Company will continue to refine its valuation methodologies. The methodology utilized by the Company for the periods presented is unchanged. The methods used to produce a fair value calculation may not be indicative of net realizable value or reflective of future fair values. Furthermore, the Company believes its valuation methods are appropriate and consistent with other market participants. Using different methodologies, or assumptions, to determine the fair value of certain financial instruments could result in a different estimate of fair value at the reporting date. The Company uses inputs that are current as of the measurement date, which may include periods of market dislocation, during which price transparency may be reduced.
The Company determines the fair values of its investments using internally developed processes and validates them using a third-party pricing service. During times of market dislocation, the observability of prices and inputs can be difficult for certain investments. If third-party pricing service is unable to provide a price for an asset, or if the price provided by them is deemed unreliable by the Company, then the asset will be valued at its fair value as determined by the Company without validation to third-party pricing. Illiquid investments typically experience greater price volatility as an active market does not exist. Observability of prices and inputs can vary significantly from period to period and may cause instruments to change classifications within the three level hierarchy.
A description of the methodologies utilized by the Company to estimate the fair value of its financial instruments by instrument class follows:
Agency MBS and Non-Agency RMBS
The Company determines the fair value of all of its investment securities based on discounted cash flows utilizing an internal pricing model that incorporates factors such as coupon, prepayment speeds, loan size, collateral composition, borrower characteristics, expected interest rates, life caps, periodic caps, reset dates, collateral seasoning, delinquency, expected losses, expected default severity, credit enhancement, and other pertinent factors. To corroborate that the estimates of fair values generated by these internal models are reflective of current market prices, the Company compares the fair values generated by the model to non-binding independent prices provided by an independent third-party pricing service. For certain highly liquid asset classes, such as Agency fixed-rate pass-through bonds, the Company’s valuations are also compared to quoted prices for To-Be-Announced, or TBA, securities.
Each quarter the Company develops thresholds generally using market factors or other assumptions as appropriate. If internally developed model prices differ from the independent prices provided by greater than a market derived predetermined threshold for the period, the Company highlights these differences for further review, both internally and with the third-party pricing service. The Company obtains the inputs used by the third-party pricing service and compares them to the Company’s inputs. The Company updates its own inputs if the Company determines the third-party pricing inputs more accurately reflect the current market environment. If the Company believes that its internally developed inputs more accurately reflect the current market environment, it will request that the third-party pricing service review market factors that may not have been considered by the third-party pricing service and provide updated prices. The Company reconciles and resolves all pricing differences in excess of the predetermined thresholds before a final price is established. After the review for the period ended December 31, 2020, 23 investment holdings with an internally developed fair value of $389 million had a difference between the model generated prices and third-party prices provided in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period. The internally developed prices were $3 million lower than the third-party prices provided of $392 million. After review and discussion, the Company affirmed and valued the investments at the lower internally developed prices. No other differences were noted at December 31, 2020 in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period. At December 31, 2019 six investment holdings with an internally developed fair value of $22 million had a difference between the model generated prices and third-party prices provided in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period. The internally developed prices were $3 million higher than the third-party prices provided of $19 million. After review and discussion, the Company affirmed and valued the investments at the lower internally developed prices. No other differences were noted at December 31, 2019 in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period.
The Company’s estimate of prepayment, default and severity curves all involve judgment and assumptions that are deemed to be significant to the fair value measurement process. This subjective estimation process renders the majority of the Non-Agency RMBS fair value estimates as Level 3 in the fair value hierarchy. As the fair values of Agency MBS are more observable, these investments are classified as level 2 in the fair value hierarchy.
Loans Held for Investment
Loans consisting of seasoned reperforming residential mortgage loans:
113
The Company estimates the fair value of its Loans held for investment consisting of seasoned reperforming residential mortgage loans on a loan by loan basis using an internally developed model which compares the loan held by the Company with a loan currently offered in the market. The loan price is adjusted in the model by considering the loan factors which would impact the value of a loan. These loan factors include loan coupon as compared to coupon currently available in the market, FICO, loan-to-value ratios, delinquency history, owner occupancy, and property type, among other factors. A baseline is developed for each significant loan factor and adjusts the price up or down depending on how that factor for each specific loan compares to the baseline rate. Generally, the most significant impact on loan value is the loan interest rate as compared to interest rates currently available in the market and delinquency history.
The Company also monitors market activity to identify trades which may be used to compare internally developed prices; however, as the portfolio of loans held at fair value is a seasoned subprime pool of mortgage loans, comparable loan pools are not common or directly comparable. There are limited transactions in the marketplace to develop a comprehensive direct range of values.
The Company reviews the fair values generated by the model to determine whether prices are reflective of the current market by corroborating its estimates of fair value by comparing the results to non-binding independent prices provided by an independent third-party pricing service for the loan portfolio. Each quarter the Company develops thresholds generally using market factors or other assumptions as appropriate.
If the internally developed fair values of the loan pools differ from the independent prices provided by greater than a predetermined threshold for the period, the Company highlights these differences for further review, both internally and with the third-party pricing service. The Company obtains certain inputs used by the third-party pricing service and evaluates them for reasonableness. The Company updates its own model if the Company determines the third-party pricing inputs more accurately reflect the current market environment or observed information from the third-party vendor. If the Company believes that its internally developed inputs more accurately reflect the current market environment, it will request that the third-party pricing service review market factors that may not have been considered by the third-party pricing service. The Company reconciles and resolves all pricing differences in excess of the predetermined thresholds before a final price is established.
After the review for the period ended December 31, 2020, 3 investment holdings with an internally developed fair value of $503 million had a difference between the model generated prices and third-party prices provided in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period. The internally developed prices were $55 million higher than the third-party prices provided of $448 million. After review and discussion, the Company affirmed and valued the investments at the higher internally developed prices. No other differences were noted at December 31, 2020 in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period. At December 31, 2019, the internally developed fair value of one loan pool of $147 million had a difference between the model generated prices and third-party prices provided in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period. The internally developed price was $20 million higher than the third-party price provided of $127 million. After review and discussion, the Company affirmed and valued the investment at the higher internally developed price.
The Company’s estimates of fair value of Loans held for investment involve judgment and assumptions that are deemed to be significant to the fair value measurement process, which renders the resulting fair value estimates level 3 inputs in the fair value hierarchy.
Loans collateralized by jumbo, prime residential mortgages:
The loans collateralized by jumbo, prime residential mortgages are carried at fair value. The loans are held as part of a consolidated Collateralized Financing Entity, or a CFE. A CFE is a variable interest entity that holds financial assets, issues beneficial interests in those assets and has no more than nominal equity and the beneficial interests have contractual recourse only to the related assets of the CFE. Accounting guidance for CFEs allow the Company to elect to measure the CFE’s financial assets using the fair value of the CFE’s financial liabilities as the fair values of the financial liabilities of the CFE are more observable. Therefore, the fair value of the loans collateralized by jumbo, prime residential mortgages is based on the fair value of the financial liabilities. See discussion of the fair value of Securitized Debt, collateralized by Loans Held for Investment at fair value below.
As the more observable financial liabilities are considered level 3 in the fair value hierarchy, the Loans collateralized by jumbo, prime residential mortgages are also level 3 in the fair value hierarchy.
Securitized Debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS
The Company carries securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS at the principal balance outstanding plus unamortized premiums, less unaccreted discounts recorded in connection with the financing of the loans or RMBS with third
114
parties. For disclosure purposes, the Company estimates the fair value of securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS by estimating the future cash flows associated with the underlying assets collateralizing the secured debt outstanding. The Company models the fair value of each underlying asset by considering, among other items, the structure of the underlying security, coupon, servicer, delinquency, actual and expected defaults, actual and expected default severities, reset indices, and prepayment speeds in conjunction with market research for similar collateral performance and the Company's expectations of general economic conditions in the sector and other economic factors. This process, including the review process, is consistent with the process used for Agency MBS and Non-Agency RMBS using internal models. For further discussion of the valuation process and benchmarking process, see Agency MBS and Non-Agency RMBS discussion herein.
The Company’s estimates of fair value of securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS involve judgment and assumptions that are deemed to be significant to the fair value measurement process, which renders the resulting fair value estimates level 3 inputs in the fair value hierarchy.
Securitized Debt, collateralized by Loans Held for Investment
The process for determining the fair value of securitized debt, collateralized by loans held for investment is based on discounted cash flows utilizing an internal pricing model that incorporates factors such as coupon, prepayment speeds, loan size, collateral composition, borrower characteristics, expected interest rates, life caps, periodic caps, reset dates, collateral seasoning, expected losses, expected default severity, credit enhancement, and other pertinent factors. This process, including the review process, is consistent with the process used for Agency MBS and Non-Agency RMBS using internal models. For further discussion of the valuation process and benchmarking process, see Agency MBS and Non-Agency RMBS discussion herein. The primary cause of the change in fair value is due to market demand and changes in credit risk of mortgage loans.
After the review for the period ended December 31, 2020, 2 investment holdings with an internally developed fair value of $209 million had a difference between the model generated prices and third-party prices provided in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period. The internally developed prices were $17 million higher than the third-party prices provided of $192 million. After review and discussion, the Company affirmed and valued the investments at the higher internally developed prices. No other differences were noted at December 31, 2020 in excess of the derived predetermined threshold for the period. At December 31, 2019, there were no pricing differences in excess of the predetermined thresholds between the model generated prices and third party prices.
The Company’s estimates of fair value of securitized debt, collateralized by loans held for investment involve judgment and assumptions that are deemed to be significant to the fair value measurement process, which renders the resulting fair value estimates level 3 inputs in the fair value hierarchy.
Fair value option
115
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Unpaid Principal/ Notional |
Fair Value | Unpaid Principal/ Notional |
Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Subordinated | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Pass-through | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS | |||||||||||||||||
| Project loans | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | |||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment, at fair value | |||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | |||||||||||||||||
The table below shows the impact of change in fair value on each of the financial instruments carried with fair value option in statement of operations as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively:
| For the Year Ended | ||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||
| Gain/(Loss) on Change in Fair Value | ||||||||
| Assets: | ||||||||
| Non-agency RMBS | ||||||||
| Senior | ||||||||
| Subordinated | ( |
|||||||
| Interest-only | ||||||||
| Agency RMBS | ||||||||
| Pass-through | ( |
|||||||
| Interest-only | ( |
( |
||||||
| Agency CMBS | ||||||||
| Project loans | ||||||||
| Interest-only | ||||||||
| Loans held for investment, at fair value | ||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | ( |
( |
||||||
Derivatives
Interest Rate Swaps and Swaptions
The Company uses clearing exchange market prices to determine the fair value of its exchange cleared interest rate swaps. For bi-lateral swaps, the Company determines the fair value based on the net present value of expected future cash flows on the swap. The Company uses option pricing model to determine the fair value of its swaptions. For bi-lateral swaps and swaptions,
116
the Company compares its own estimate of fair value with counterparty prices to evaluate for reasonableness. Both the clearing exchange and counter-party pricing quotes, incorporate common market pricing methods, including a spread measurement to the Treasury yield curve or interest rate swap curve as well as underlying characteristics of the particular contract. Interest rate swaps and swaptions are modeled by the Company by incorporating such factors as the term to maturity, swap curve, overnight index swap rates, and the payment rates on the fixed portion of the interest rate swaps. The Company has classified the characteristics used to determine the fair value of interest rate swaps and swaptions as Level 2 inputs in the fair value hierarchy.
Treasury Futures
The fair value of Treasury futures is determined by quoted market prices in an active market. The Company has classified the characteristics used to determine the fair value of Treasury futures as Level 1 inputs in the fair value hierarchy.
Secured Financing Agreements
Secured financing agreements are collateralized financing transactions utilized by the Company to acquire investment securities. For short term secured financing agreements and longer term floating rate secured financing agreements, the Company estimates fair value using the contractual obligation plus accrued interest payable. The fair value of longer term fixed rate secured financing agreements is determined using present value of discounted cash flows based on the imputed market rates. The Company has classified the characteristics used to determine the fair value of Secured Financing Agreements as Level 2 inputs in the fair value hierarchy.
Long Term Debt
Convertible Senior Notes
Convertible notes include unsecured convertible senior notes that are carried at their unpaid principal balance net of any unamortized deferred issuance costs. The fair value of the convertible notes is determined using quoted prices in generally active markets and classified as Level 2.
Short-term Financial Instruments
The carrying value of cash and cash equivalents, accrued interest receivable, dividends payable, payable for investments purchased, receivable for investments sold and accrued interest payable are considered to be a reasonable estimate of fair value due to the short term nature and low credit risk of these short-term financial instruments.
The Company’s financial assets and liabilities carried at fair value on a recurring basis, including the level in the fair value hierarchy, at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 are presented below.
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Counterparty and Cash Collateral, netting | Total | |||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS, at fair value | $ | $ | $ | $ | — | $ | |||||||||||
| Agency RMBS, at fair value | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS, at fair value | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment, at fair value | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | |||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | |||||||||||||||||
117
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Counterparty and Cash Collateral, netting | Total | |||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS, at fair value | $ | $ | $ | — | $ | ||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS, at fair value | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Agency CMBS, at fair value | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for investment, at fair value | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | ( |
||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | ( |
||||||||||||||||
The table below provides a summary of the changes in the fair value of financial instruments classified as Level 3 at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| Fair Value Reconciliation, Level 3 | |||||||||||
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | Loans held for investment | Securitized Debt | |||||||||
| Beginning balance Level 3 | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Transfers into Level 3 | |||||||||||
| Transfers out of Level 3 | ( |
||||||||||
| Purchases of assets/ issuance of debt | |||||||||||
| Principal payments | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Sales and Settlements | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Net accretion (amortization) | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Gains (losses) included in net income | |||||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in provision for credit losses | ( |
||||||||||
| Realized gains (losses) on sales and settlements | ( |
||||||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) included in income | ( |
||||||||||
| Gains (losses) included in other comprehensive income | |||||||||||
| Total unrealized gains (losses) for the period | ( |
||||||||||
| Ending balance Level 3 | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
118
| Fair Value Reconciliation, Level 3 | |||||||||||
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | Loans held for investment | Securitized Debt | |||||||||
| Beginning balance Level 3 | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Transfers into Level 3 | |||||||||||
| Transfers out of Level 3 | |||||||||||
| Purchases of assets/ issuance of debt | |||||||||||
| Principal payments | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Sales and Settlements | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||
| Net accretion (amortization) | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Gains (losses) included in net income | |||||||||||
| Other than temporary credit impairment losses | ( |
||||||||||
| Realized gains (losses) on sales and settlements | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) included in income | |||||||||||
| Gains (losses) included in other comprehensive income | |||||||||||
| Total unrealized gains (losses) for the period | ( |
||||||||||
| Ending balance Level 3 | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
During the first quarter of 2020 there were transfers out of Level 3 of $135 million, as prices were based on unadjusted quoted prices on these assets. These investments were transferred into Level 3 during the second quarter of 2020 as unadjusted quoted prices were unavailable and the Company used internal pricing model to value them. There were no transfers in or out from Level 3 during the year ended December 31, 2019. The Company determines when transfers have occurred between levels of the fair value hierarchy based on the date of the event or change in circumstances that caused the transfer.
The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Company’s Non-Agency RMBS and securitized debt are the weighted average discount rates, prepayment rate, constant default rate, and the loss severity.
Discount Rate
The discount rate refers to the interest rate used in the discounted cash flow analysis to determine the present value of future cash flows. The discount rate takes into account not just the time value of money, but also the risk or uncertainty of future cash flows. An increased uncertainty of future cash flows results in a higher discount rate. The discount rate used to calculate the present value of the expected future cash flows is based on the discount rate implicit in the security as of the last measurement date. As discount rates move up, the values of the discounted cash flows are reduced.
The discount rates applied to the expected cash flows to determine fair value are derived from a range of observable prices on securities backed by similar collateral. As the market becomes more or less liquid, the availability of these observable inputs will change.
Prepayment Rate
The prepayment rate specifies the percentage of the collateral balance that is expected to prepay at each point in the future. The prepayment rate is based on factors such as interest rates, loan-to-value ratio, debt-to-income ratio, and is scaled up or down to reflect recent collateral-specific prepayment experience as obtained from remittance reports and market data services.
Constant Default Rate
Constant default rate represents an annualized rate of default on a group of mortgages. The constant default rate, or CDR, represents the percentage of outstanding principal balances in the pool that are in default, which typically equates to the home being past 60-day and 90-day notices and in the foreclosure process. When default rates increase, expected cash flows on the underlying collateral decreases. When default rates decrease, expected cash flows on the underlying collateral increases.
119
Default vectors are determined from the current “pipeline” of loans that are more than 30 days delinquent, in foreclosure, bankruptcy, or are REO. These delinquent loans determine the first 30 months of the default curve. Beyond month 30, the default curve transitions to a value that is reflective of a portion of the current delinquency pipeline.
Loss Severity
Loss severity rates reflect the amount of loss expected from a foreclosure and liquidation of the underlying collateral in the mortgage loan pool. When a mortgage loan is foreclosed the collateral is sold and the resulting proceeds are used to settle the outstanding obligation. In many circumstances, the proceeds from the sale do not fully repay the outstanding obligation. In these cases, a loss is incurred by the lender. Loss severity is used to predict how costly future losses are likely to be. An increase in loss severity results in a decrease in expected future cash flows. A decrease in loss severity results in an increase in expected future cash flows.
The curve generated to reflect the Company’s expected loss severity is based on collateral-specific experience with consideration given to other mitigating collateral characteristics. Collateral characteristics such as loan size, loan-to-value, seasoning or loan age and geographic location of collateral also effect loss severity.
Sensitivity of Significant Inputs – Non-Agency RMBS and securitized debt, collateralized by loans held for investment
Prepayment rates vary according to interest rates, the type of financial instrument, conditions in financial markets, and other factors, none of which can be predicted with any certainty. In general, when interest rates rise, it is relatively less attractive for borrowers to refinance their mortgage loans, and as a result, prepayment speeds tend to decrease. When interest rates fall, prepayment speeds tend to increase. For RMBS investments purchased at a premium, as prepayment rates increase, the amount of income the Company earns decreases as the purchase premium on the bonds amortizes faster than expected. Conversely, decreases in prepayment rates result in increased income and can extend the period over which the Company amortizes the purchase premium. For RMBS investments purchased at a discount, as prepayment rates increase, the amount of income the Company earns increases from the acceleration of the accretion of the discount into interest income. Conversely, decreases in prepayment rates result in decreased income as the accretion of the purchase discount into interest income occurs over a longer period.
For securitized debt carried at fair value issued at a premium, as prepayment rates increase, the amount of interest expense the Company recognizes decreases as the issued premium on the debt amortizes faster than expected. Conversely, decreases in prepayment rates result in increased expense and can extend the period over which the Company amortizes the premium.
For debt issued at a discount, as prepayment rates increase, the amount of interest the Company expenses increases from the acceleration of the accretion of the discount into interest expense. Conversely, decreases in prepayment rates result in decreased expense as the accretion of the discount into interest expense occurs over a longer period.
A summary of the significant inputs used to estimate the fair value of Level 3 Non-Agency RMBS held for investment at fair value as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 follows. The weighted average discount rates were based on fair value. Previously issued financial statement filings were based on amortized cost. We believe fair value provides an improved presentation of weighted average discount rates.
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Significant Inputs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount Rate | Prepay Rate | CDR | Loss Severity | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subordinated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
120
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Significant Inputs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount Rate | Prepay Rate | CDR | Loss Severity | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Agency RMBS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subordinated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-only | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A summary of the significant inputs used to estimate the fair value of securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment, as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 follows:
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Significant Inputs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount Rate | Prepay Rate | CDR | Loss Severity | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | |||||||||||||||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Significant Inputs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount Rate | Prepay Rate | CDR | Loss Severity | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | Range | Weighted Average | |||||||||||||||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All of the significant inputs listed have some degree of market observability based on the Company’s knowledge of the market, information available to market participants, and use of common market data sources. Collateral default and loss severity projections are in the form of “curves” that are updated quarterly to reflect the Company’s collateral cash flow projections. Methods used to develop these projections conform to industry conventions. The Company uses assumptions it considers its best estimate of future cash flows for each security.
Sensitivity of Significant Inputs – Loans held for investment
The Loans held for investment are comprised primarily of loans collateralized by seasoned reperforming residential mortgages. Additionally, it includes non-conforming, single family, owner occupied, jumbo, prime residential mortgages. The significant unobservable inputs used to estimate the fair value of the Loans held for investment collateralized by seasoned reperforming residential mortgage loans, as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 include coupon, FICO score at origination, loan-to-value ratios (LTV), owner occupancy status, and property type. A summary of the significant inputs used to estimate the fair value of Loans held for investment collateralized primarily by seasoned reperforming mortgages at fair value as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 follows:
121
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||
| Factor: | |||||||||||
| Coupon | |||||||||||
Base Rate |
|||||||||||
Actual |
|||||||||||
| FICO | |||||||||||
Base Rate |
|||||||||||
Actual |
|||||||||||
| Loan-to-value (LTV) | |||||||||||
Base Rate |
|||||||||||
Actual |
|||||||||||
| Loan Characteristics: | |||||||||||
| Occupancy | |||||||||||
| Owner Occupied | |||||||||||
| Investor | |||||||||||
| Secondary | |||||||||||
| Property Type | |||||||||||
| Single family | |||||||||||
| Manufactured housing | |||||||||||
| Multi-family/mixed use/other | |||||||||||
The loan factors are generally not observable for the individual loans and the base rates developed by the Company’s internal model are subjective and change as market conditions change. The impact of the loan coupon on the value of the loan is dependent on whether the loan is clean or reperforming. A clean loan, with no history of delinquent payments and a relatively high loan interest rate would result in a higher overall value than a reperforming loan which has a history of delinquency. Similarly, a higher FICO score and a lower LTV ratio results in increases in the fair market value of the loan and a lower FICO score and a higher LTV ratio results in a lower value.
Property types also affect the overall loan values. Property types include single family, manufactured housing and multi-family/mixed use and other types of properties. Single family homes represent properties which house one to four family units. Manufactured homes include mobile homes and modular homes. Loan value for properties that are investor or secondary homes have a reduced value as compared to the baseline loan value. Additionally, single family homes will result in an increase to the loan value where manufactured and multi-family/mixed use and other properties will result in a decrease to the loan value, as compared to the baseline.
Financial instruments not carried at fair value
The following table presents the carrying value and fair value, as described above, of the Company’s financial instruments not carried at fair value on a recurring basis at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Level in Fair Value Hierarchy | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | |||||||||
Secured financing agreements (1)
|
2 | ||||||||||
| Securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS | 3 | ||||||||||
| Long Term Debt | 2 | ||||||||||
(1) The fair value of secured financing agreements includes one secured financing agreement with a non-detachable Warrant.
122
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Level in Fair Value Hierarchy | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | |||||||||
| Secured financing agreements | 2 | ||||||||||
| Securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS | 3 | ||||||||||
6. Secured Financing Agreements
Secured financing agreements include short term repurchase agreements with original maturity dates of less than one-year, long-term financing agreements with original maturity dates of more than one year and loan warehouse credit facilities collateralized by loans acquired by the Company.
The repurchase agreements are collateralized by Agency and non-agency mortgage backed securities with interest rates generally indexed to the one-month and three-month LIBOR rates and re-price accordingly. The maturity dates on the repurchase agreements are all less than one year and generally are less than 180 days. The collateral pledged as security on the repurchase agreements may include the Company’s investments in consolidated VIEs, which are eliminated in consolidation.
The long-term financing agreements include long-term repurchase agreements and secured financing arrangements with an original term of one year or greater which are secured by non-agency RMBS pledged as collateral. Maturity dates on these long-term financing agreements range from April 2021 through April 2025. The collateral pledged as security on the long-term financing agreements may include the Company’s investments in consolidated VIEs, which are eliminated in consolidation. $400 million of the long-term financing agreements has a fixed interest rate of 7 % and include an attached equity warrant. See Note 11 for details of the equity warrants issued. The interest rates on the remaining long-term financing agreements are generally indexed to one-month and three-month LIBOR rates. During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company has significantly increased its long-term financing agreements.
The warehouse credit facilities collateralized by loans are repurchase agreements intended to hold loans acquired by the Company. These loans are generally held in the warehouse credit facilities until they can be sold into a longer-term securitization structure. The maturity dates on the warehouse credit facilities range from 30 days to one year with interest rates indexed to the one-month and three-month LIBOR rates.
The Secured financing agreements require the Company to post collateral at a specific rate in excess of the unpaid principal balance of the Agreement. For certain Secured financing agreements, this may require the Company to post additional margin if the fair value of the assets were to drop. To mitigate this risk, during the first half of 2020, the Company has negotiated several long-term financing agreements which are not subject to additional margin requirements upon a drop in the fair value of the collateral pledged. At December 31, 2020, the Company has $1.2 billion of Secured financing agreements which are not subject to additional margin requirements upon a change in the fair value of the collateral pledged. Repurchase agreements may allow the credit counterparty to avoid the automatic stay provisions of the Bankruptcy Code, in the event of a bankruptcy of the Company, and take possession of, and liquidate, the collateral under such repurchase agreements without delay. $796 million of the long-term financing agreements are secured borrowing arrangements which are subject to the automatic stay provisions of the Bankruptcy Code.
123
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Secured financing agreements outstanding secured by: | ||||||||
| Agency RMBS (in thousands) | $ | $ | ||||||
| Agency CMBS (in thousands) | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS and Loans held for investment (in thousands) (1)
|
||||||||
| Total: | $ | $ | ||||||
| MBS pledged as collateral at fair value on Secured financing agreements: | ||||||||
| Agency RMBS (in thousands) | $ | $ | ||||||
| Agency CMBS (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Non-agency RMBS and Loans held for investment (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Total: | $ | $ | ||||||
| Average balance of Secured financing agreements secured by: | ||||||||
| Agency RMBS (in thousands) | $ | $ | ||||||
| Agency CMBS (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Non-agency RMBS and Loans held for investment (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Total: | $ | $ | ||||||
| Average borrowing rate of Secured financing agreements secured by: | ||||||||
| Agency RMBS (in thousands) | % | % | ||||||
| Agency CMBS (in thousands) | % | % | ||||||
| Non-agency RMBS and Loans held for investment (in thousands) | % | % | ||||||
| Average remaining maturity of Secured financing agreements secured by: | ||||||||
| Agency RMBS (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Agency CMBS (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Non-agency RMBS and Loans held for investment (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Average original maturity of Secured financing agreements secured by: | ||||||||
| Agency RMBS (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Agency CMBS (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Non-agency RMBS and Loans held for investment (in thousands) | ||||||||
(1) The December 31, 2020 values for secured financing agreements in the table above is net of $8 million of deferred financing cost.
At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, we pledged $42 million and $20 million, respectively, of margin cash collateral to our secured financing agreement counterparties. At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the secured financing agreements collateralized by MBS and Loans held for investment had the following remaining maturities and borrowing rates.
124
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Principal (1)
|
Weighted Average Borrowing Rates | Range of Borrowing Rates | Principal | Weighted Average Borrowing Rates | Range of Borrowing Rates | ||||||||||||||||||
| Overnight | $ | NA | NA | $ | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 to 29 days | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 to 59 days | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60 to 89 days | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90 to 119 days | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 120 to 180 days | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 180 days to 1 year | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 to 2 years | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 to 3 years | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Greater than 3 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||
(1) The December 31, 2020 values for secured financing agreements in the table above is net of $8 million of deferred financing cost.
Certain of the long-term financing agreements and warehouse credit facilities are subject to certain covenants. These covenants include that the Company maintain its REIT status as well as maintain a net asset value or GAAP equity greater than a certain level. If the Company fails to comply with these covenants at any time, the financing may become immediately due in full. Additionally, certain financing agreements become immediately due if the total stockholders' equity of the Company drops by 50 % from the most recent year end. Currently, the Company is in compliance with all covenants and does not expect to fail to comply with any of these covenants within the next twelve months. The Company has a total of $1.1 billion unused uncommitted warehouse credit facilities as of December 31, 2020.
7. Securitized Debt
All of the Company’s securitized debt is collateralized by residential mortgage loans or Non-Agency RMBS. For financial reporting purposes, the Company’s securitized debt is accounted for as secured borrowings. Thus, the residential mortgage loans or RMBS held as collateral are recorded in the assets of the Company as Loans held for investment or Non-Agency RMBS and the securitized debt is recorded as a non-recourse liability in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
Securitized Debt Collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS
At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the Company’s securitized debt collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS is carried at amortized cost and had a principal balance of $135 million and $152 million, respectively. At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the debt carried a weighted average coupon of 6.5 %. As of December 31, 2020, the maturities of the debt range between the years 2035 and 2037. None of the Company’s securitized debt collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS is callable.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company did no t acquire any securitized debt collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company acquired securitized debt collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS with an amortized cost balance of $2.9 million for $3.5 million. This transaction resulted in net loss on extinguishment of debt of $608 thousand.
125
RMBS, as adjusted for projected losses on the underlying collateral of the debt. All of the securitized debt recorded in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition is non-recourse to the Company.
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||
| Within One Year | $ | $ | ||||||
| One to Three Years | ||||||||
| Three to Five Years | ||||||||
| Greater Than Five Years | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
Maturities of the Company’s securitized debt collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS are dependent upon cash flows received from the underlying collateral. The estimate of their repayment is based on scheduled principal payments on the underlying collateral. This estimate will differ from actual amounts to the extent prepayments or losses are experienced. See Note 3 for a more detailed discussion of the securities collateralizing the securitized debt.
Securitized Debt Collateralized by Loans Held for Investment
At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the Company’s securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investment had a principal balance of $8.7 billion and $8.2 billion, respectively. At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the total securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investment carried a weighted average coupon equal to 3.4 % and 4.2 %, respectively. As of December 31, 2020, the maturities of the debt range between the years 2023 and 2067.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company acquired securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investment with an amortized cost balance of $785 million for $784 million. This transaction resulted in net gain on extinguishment of debt of $1 million. The Company did no t acquire any securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investments during the year ended December 31, 2019.
The following table presents the estimated principal repayment schedule of the securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investment at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, based on expected cash flows of the residential mortgage loans or RMBS, as adjusted for projected losses on the underlying collateral of the debt. All of the securitized debt recorded in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition is non-recourse to the Company.
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||
| Within One Year | $ | $ | ||||||
| One to Three Years | ||||||||
| Three to Five Years | ||||||||
| Greater Than Five Years | ||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
Maturities of the Company’s securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investment are dependent upon cash flows received from the underlying loans. The estimate of their repayment is based on scheduled principal payments on the underlying loans. This estimate will differ from actual amounts to the extent prepayments or loan losses are experienced. See Note 4 for a more detailed discussion of the loans collateralizing the securitized debt.
Certain of the securitized debt collateralized by loans held for investment contain call provisions at the option of the Company. The following table presents the par value of the callable debt by year at December 31, 2020.
126
| December 31, 2020 | |||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||
| Year | Principal | ||||
| Currently callable | |||||
| 2021 | |||||
| 2022 | |||||
| 2023 | |||||
| Total | $ | ||||
8. Long Term Debt
Convertible Senior Notes
In April 2020, the Company completed its registered underwritten public offering of $374 million (including exercise of the underwriters' overallotment option) aggregate principal amount of 7.0 % convertible senior notes due 2023 (the “Notes” or “Note Offering”). These Notes require semi-annual interest payments at a fixed coupon rate of 7.0 % until maturity or conversion, which will be no later than April 1, 2023. After deducting the underwriting discount and offering costs, the Company received $362 million. At completion of the offering, these notes were convertible at the option of the holder at a conversion rate of 153.8461 common shares per $1,000 principal amount of convertible senior notes (equivalent to a conversion price of $6.50 per common share). Upon conversion of these notes by a holder, the holder will receive shares of our common stock.
As of December 31, 2020, approximately $321 million of senior notes were converted into approximately 49 million common stock of the Company. At December 31, 2020, the outstanding principal amount of these notes was $53 million and the accrued interest payable on the debt was $1 million. At December 31, 2020, the unamortized deferred debt issuance cost was $1 million and the net interest expense was $7 million. The unamortized deferred debt issuance costs will be amortized until maturity or conversion, which will be no later than April 1, 2023.
In April 2020, concurrently with the pricing of the Notes, the Company entered into call option transactions with respect to the Common Stock (the “Capped Call Transactions”) with affiliates of Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC (the “Counterparty”). The Capped Call Transactions have an initial strike price of approximately $6.50 per share and cover approximately $250 million of the offering. The Capped Call Transactions will expire upon the maturity of the Notes, if not earlier exercised or terminated. The Capped Call Transactions are expected generally to reduce the potential dilution to the Company’s common stock upon any conversion of the Notes and/or offset any cash payments the Company is required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted Notes, as the case may be, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap initially equal to approximately $8.45 (which represents a premium of approximately 30 % over the last reported sale price of the common stock on April 7, 2020). The Capped Call Transactions are separate transactions, entered into by the Company with the Counterparty, and are not part of the terms of the Notes. The Company used approximately $33.75 million of the net proceeds from the offering of the Notes to pay the cost of the Capped Call Transactions which is recorded within additional paid in capital on the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity. The Company exercised its capped call options during the fourth quarter of 2020 and received a settlement of 4.7 million shares, which were retired and removed from issued and outstanding shares.
9. Consolidated Securitization Vehicles and Other Variable Interest Entities
Since its inception, the Company has utilized VIEs for the purpose of securitizing whole mortgage loans or re-securitizing RMBS and obtaining long-term, non-recourse financing. The Company evaluated its interest in each VIE to determine if it is the primary beneficiary.
As of December 31, 2020, the Company’s Consolidated Statement of Financial Condition includes assets of consolidated VIEs with a carrying value of $12.2 billion and liabilities with a carrying value of $8.1 billion. As of December 31, 2019, the Company’s Consolidated Statement of Financial Condition includes assets of consolidated VIEs with a carrying value of $12.5 billion and liabilities with a carrying value of $8.1 billion.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company securitized and consolidated approximately $2.5 billion unpaid principal balance of seasoned residential subprime mortgage loans. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company securitized and consolidated approximately $1.5 billion unpaid principal balance of seasoned residential subprime mortgage loans.
127
VIEs for Which the Company is the Primary Beneficiary
The retained beneficial interests in VIEs for which the Company is the primary beneficiary are typically the subordinated tranches of these securitizations and in some cases the Company may hold interests in additional tranches. The table below reflects the assets and liabilities recorded in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition related to the consolidated VIEs as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||
| Assets: | ||||||||
Non-Agency RMBS, at fair value (1)
|
$ | $ | ||||||
| Loans held for investment, at fair value | ||||||||
| Accrued interest receivable | ||||||||
| Other assets | ||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Securitized debt, collateralized by Non-Agency RMBS | $ | $ | ||||||
| Securitized debt at fair value, collateralized by loans held for investment | ||||||||
| Accrued interest payable | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | ||||||||
(1) December 31, 2020 balance includes allowance for credit losses of $117 thousand..
Income and expense amounts related to consolidated VIEs recorded in the Consolidated Statements of Operations is presented in the tables below.
| For the Year ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Interest income, Assets of consolidated VIEs | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Interest expense, Non-recourse liabilities of VIEs | |||||||||||
| Net interest income | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in provision for credit losses | $ | ( |
$ | $ | |||||||
| Net other-than-temporary credit impairment losses | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
||||||
| Servicing fees | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
VIEs for Which the Company is Not the Primary Beneficiary
10. Derivative Instruments
128
In connection with the Company’s interest rate risk strategy, the Company economically hedges a portion of its interest rate risk by entering into derivative financial instrument contracts in the form of interest rate swaps, swaptions, and Treasury futures. The Company’s swaps are used to lock in a fixed rate related to a portion of its current and anticipated payments on its secured financing agreements. The Company typically agrees to pay a fixed rate of interest, or pay rate, in exchange for the right to receive a floating rate of interest, or receive rate, over a specified period of time. Treasury futures are derivatives which track the prices of generic benchmark Treasury securities with identical maturity and are traded on an active exchange. It is generally the Company’s policy to close out any Treasury futures positions prior to delivering the underlying security. The Company uses Treasury futures to lock in a fixed rate related to a portion of its current and anticipated payments on its secured financing agreements.
The use of derivatives creates exposure to credit risk relating to potential losses that could be recognized if the counterparties to these instruments fail to perform their obligations under the contracts. In the event of a default by the counterparty, the Company could have difficulty obtaining its RMBS or cash pledged as collateral for these derivative instruments. The Company periodically monitors the credit profiles of its counterparties to determine if it is exposed to counterparty credit risk. See Note 14 for further discussion of counterparty credit risk.
The table below summarizes the location and fair value of the derivatives reported in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition after counterparty netting and posting of cash collateral as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019. The Company did not have any derivative instruments as of December 31, 2020.
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative Assets | Derivative Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative Instruments | Notional Amount Outstanding | Location on Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition |
Net Estimated Fair Value/Carrying Value | Location on Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition |
Net Estimated Fair Value/Carrying Value | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps | $ | Derivatives, at fair value, net | $ | Derivatives, at fair value, net | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury Futures | Derivatives, at fair value, net | Derivatives, at fair value, net | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative Assets | Derivative Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative Instruments | Notional Amount Outstanding | Location on Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition |
Net Estimated Fair Value/Carrying Value | Location on Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition |
Net Estimated Fair Value/Carrying Value | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps | $ | Derivatives, at fair value, net | $ | Derivatives, at fair value, net | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury Futures | Derivatives, at fair value, net | Derivatives, at fair value, net | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
129
| Net gains (losses) on derivatives for the year ended |
||||||||||||||
| Derivative Instruments | Location on Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income |
December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps | Net unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps |
Net realized gains (losses) on derivatives (1)
|
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||
| Treasury Futures | Net unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
( |
|||||||||||
| Treasury Futures | Net realized gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
( |
|||||||||||
| Swaptions | Net unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
||||||||||||
| Swaptions | Net realized gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
( |
|||||||||||
| Total | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
||||||||
(1) Includes loss on termination of interest rate swaps of $464 million and $360 million during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. There were no swap terminations during the year ended December 31, 2018.
The Company paid $464 million to terminate interest rate swaps with a notional value of $4.1 billion during the year ended December 31, 2020. The terminated swaps had original maturities from 2023 to 2048. The company paid $360 million to terminate interest rate swaps with a notional value of $6.4 billion during the year ended December 31, 2019.
The Company did not have any interest rate swaps as of December 31, 2020. The weighted average pay rate on the Company’s interest rate swaps at December 31, 2019 was 2.62 % and the weighted average receive rate was 1.94 %. The weighted average maturity on the Company’s interest rate swaps at December 31, 2019 was 6 years.
When the Company enters into derivative contracts, they are typically subject to International Swaps and Derivatives Association Master Agreements or other similar agreements which may contain provisions that grant counterparties certain rights with respect to the applicable agreement upon the occurrence of certain events such as (i) a decline in stockholders’ equity in excess of specified thresholds or dollar amounts over set periods of time, (ii) the Company’s failure to maintain its REIT status, (iii) the Company’s failure to comply with limits on the amount of leverage, and (iv) the Company’s stock being delisted from the New York Stock Exchange, or NYSE. Upon the occurrence of any one of items (i) through (iv), or another default under the agreement, the counterparty to the applicable agreement has a right to terminate the agreement in accordance with its provisions. Certain of the Company’s interest rate swaps are cleared through a registered commodities exchange. Each of the Company’s International Swaps and Derivative Association, or ISDA, and clearing exchange agreements contains provisions under which the Company is required to fully collateralize its obligations under the interest rate swap agreements if at any point the fair value of the swap represents a liability greater than the minimum transfer amount contained within the agreements. The Company is also required to post initial collateral upon execution of certain of its swap transactions. If the Company breaches any of these provisions, it will be required to settle its obligations under the agreements at their termination values, which approximates fair value. The Company uses clearing exchange market prices to determine the fair value of its interest rate swaps.
11. Capital Stock
Preferred Stock
The Company declared dividends to Series A preferred stockholders of $12 2.00
The Company declared dividends to Series B preferred stockholders of $26 2.00
The Company declared dividends to Series C preferred stockholders of $20 1.94
The Company declared dividends to Series D preferred stockholders of $16 million, or $2.00 per preferred share during the years ended December 31, 2020, respectively. The Company declared dividends to Series D preferred stockholders of $15 million, or $1.87 , respectively, per preferred share during the year ended December 31, 2019.
Common Stock
130
In March 2020, our Board of Directors reauthorized $150 million under our share repurchase program, or the Repurchase Program. Such authorization does not have an expiration date, and at present, there is no intention to modify or otherwise rescind such authorization. Shares of our common stock may be purchased in the open market, including through block purchases, through privately negotiated transactions, or pursuant to any trading plan that may be adopted in accordance with Rule 10b5-1 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act. The timing, manner, price and amount of any repurchases will be determined at our discretion and the program may be suspended, terminated or modified at any time for any reason. Among other factors, the Company intends to only consider repurchasing shares of our common stock when the purchase price is less than the last publicly reported book value per common share. In addition, the Company does not intend to repurchase any shares from directors, officers or other affiliates. The program does not obligate the Company to acquire any specific number of shares, and all repurchases will be made in accordance with Rule 10b-18, which sets certain restrictions on the method, timing, price and volume of stock repurchases.
The Company repurchased approximately 1.4 million shares of its common stock at an average price of $15.34 per share for a total of $22 million during the year ended December 31, 2020. The Company did not repurchase any of its common stock during the year ended December 31, 2019. The approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the Repurchase Program is $128 million as of December 31, 2020.
The Company declared dividends to common shareholders of $301 million, or $1.40 , per share and $377 million, or $2.00 , per share during the years ended December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively.
Warrants
On June 8, 2020, the Company and certain lenders entered into a $400 million senior secured, non-mark-to-market Credit Agreement. In connection with the Credit Agreement, on June 8, 2020, the Company issued non-detachable Warrants to affiliates of each of the Lenders, which provides the Lenders the right to purchase up to an aggregate of 20,300,000 shares (the “Warrant Shares”) of the Company’s common stock, at a price of $0.01 per share, which represented approximately 7.7 % of the Company’s common stock after giving effect to the issuance of the Warrant Shares. The number of Warrant Shares may be proportionally adjusted for stock distributions, stock splits, cash distributions above specified threshold amounts, mergers, reorganizations, spin-offs and other customary events, as well as issuances by the Company of common stock below specified levels (subject to certain exceptions). The Warrants have an exercise price of $0.01 per share and are exercisable generally on the earlier of (i) June 8, 2023; (ii) the date on which the amounts financed under the Credit Agreement are discharged in full, and (iii) an event of default is declared under the Credit Agreement and all amounts are then due, and are exercisable for one year. The Company is permitted to settle any exercise of the Warrants in cash at a price of 90 % of the fair market value of the Company’s common stock at the time of exercise.
Earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 respectively, are computed as follows:
| For the Year Ended | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Numerator: | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common shareholders - Basic | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Effect of dilutive securities: | |||||||||||
| Interest expense attributable to convertible notes | $ | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common shareholders - Diluted | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Denominator: | |||||||||||
| Weighted average basic shares | |||||||||||
| Effect of dilutive securities | |||||||||||
| Weighted average dilutive shares | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) per average share attributable to common stockholders - Basic | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) per average share attributable to common stockholders - Diluted | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
131
12. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income
The following table presents the changes in the components of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, or the AOCI, for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019:
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||
| Unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities, net | Total Accumulated OCI Balance | |||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | $ | $ | ||||||
| OCI before reclassifications | ( |
( |
||||||
| Amounts reclassified from AOCI | ( |
( |
||||||
| Net current period OCI | ( |
( |
||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | $ | $ | ||||||
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||
| Unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities, net | Total Accumulated OCI Balance | |||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | $ | $ | ||||||
| OCI before reclassifications | ||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from AOCI | ||||||||
| Net current period OCI | ||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | $ | $ | ||||||
The following table presents the details of the reclassifications from AOCI for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019:
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||
| Details about Accumulated OCI Components | Amounts Reclassified from Accumulated OCI |
Amounts Reclassified from Accumulated OCI |
Affected Line on the Consolidated Statements Of Operations | ||||||||
| Unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities | |||||||||||
| $ | $ | ( |
Net realized gains (losses) on sales of investments | ||||||||
| ( |
Net other-than-temporary credit impairment losses | ||||||||||
| $ | $ | ( |
Income before income taxes | ||||||||
| Income taxes | |||||||||||
| $ | $ | ( |
Net of tax | ||||||||
13. Equity Compensation, Employment Agreements and other Benefit Plans
In accordance with the terms of the Company’s 2007 Equity Incentive Plan (as amended and restated on December 10, 2015), or the Incentive Plan, directors, officers and employees of the Company are eligible to receive restricted stock grants. These awards generally have a vesting period lasting three years . During the vesting period, these shares may not be sold. There were approximately 3 million shares available for future grants under the Incentive Plan as of December 31, 2020.
The Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company has approved a Stock Award Deferral Program, or the Deferral Program. Under the Deferral Program, non-employee directors and certain executive officers can elect to defer
132
payment of certain stock awards made pursuant to the Equity Plan. Deferred awards are treated as deferred stock units and paid at the earlier of separation from service or a date elected by the participant who is separating. Payments are generally made in a lump sum or, if elected by the participant, in five annual installments. Deferred awards receive dividend equivalents during the deferral period in the form of additional deferred stock units. Amounts are paid at the end of the deferral period by delivery of shares from the Incentive Plan (plus cash for any fractional deferred stock units), less any applicable tax withholdings. Deferral elections do not alter any vesting requirements applicable to the underlying stock award.
Grants of Restricted Stock Units or, RSUs
During years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, the Company granted RSU awards to senior management. These RSU awards are designed to reward senior management of the Company for services provided to the Company. Generally, the RSU awards vest equally over a three-year period beginning from the grant date and will fully vest after three years . For employees whose years of service to the Company plus age is equal to or greater than 65, the service period is considered to be fulfilled and all grants are expensed immediately. The RSU awards are valued at the market price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date and generally the employees must be employed by the Company on the vesting dates to receive the RSU awards. The Company granted 414 thousand RSU awards during the year ended December 31, 2020, with a grant date fair value of $5 million for the 2020 performance year. The Company granted 487 thousand RSU awards during the year ended December 31, 2019 with a grant date fair value of $9 million, for the 2018 and 2019 performance years.
Grants of Performance Share Units or, PSUs
PSU awards are designed to align compensation with the Company’s future performance. The PSU awards granted during the year of 2020 and 2019 include a three-year performance period ending on December 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively. The final number of shares awarded will be between 0 % and 200 % of the PSUs granted based on the Company Economic Return compared to a peer group. The Company’s three-year Company Economic Return is equal to the Company’s change in book value per common share plus common stock dividends. Compensation expense will be recognized on a straight-line basis over the three-year vesting period based on an estimate of the Company Economic Return in relation to the entities in the peer group and will be adjusted each period based on the Company’s best estimate of the actual number of shares which will vest. During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company granted 173 thousand PSU awards to senior management with a grant date fair value of $3 million. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company granted 318 thousand PSU awards to senior management with a grant date fair value of $5 million.
The following table presents information with respect to the Company's stock awards during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
| For the Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||
| Number of Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | Number of Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||||||||
| Unvested shares outstanding - beginning of period | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Granted | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Vested | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||
| Forfeited | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||
| Unvested shares outstanding - end of period | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
The Company recognized stock based compensation expenses of $9 million and $13 million, respectively, for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
The Company also maintains a qualified 401(k) plan. The plan is a retirement savings plan that allows eligible employees to contribute a portion of their wages on a tax-deferred basis under Section 401(k) of the Code. For the year ended December 31, 2020, employees may contribute, through payroll deductions, up to $19,500 if under the age of 50 years and an additional $6,500 “catch-up” contribution for employees 50 years or older. The Company matches 100 % of the first 6 % of the eligible compensation deferred by employee contributions. The employer funds the 401(k) matching contributions in the form of cash, and participants may direct the Company match to an investment of their choice. The benefit of the Company’s contributions vests immediately. Generally, a participating employee is entitled to distributions from the plans upon termination of employment, retirement, death or disability. The 401(k) expenses related to the Company’s qualified plan for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, were $446 thousand and $434 thousand, respectively.
133
14. Income Taxes
For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, the Company qualified to be taxed as a REIT under Code Sections 856 through 860. As a REIT, the Company is not subject to U.S. federal income tax to the extent that it makes qualifying distributions of taxable income to its stockholders. To maintain qualification as a REIT, the Company must distribute at least 90% of its annual REIT taxable income (subject to certain adjustments) to its shareholders and meet certain other requirements such as assets it may hold, income it may generate and its shareholder composition. It is generally the Company’s policy to distribute to its shareholders all of the Company’s taxable income.
The state and local tax jurisdictions in which the Company is subject to tax-filing obligations recognize the Company’s status as a REIT and therefore the Company generally does not pay income tax in such jurisdictions. The Company may, however, be subject to certain minimum state and local tax filing fees and its TRSs are subject to U.S. federal, state and local taxes. There were no significant income tax expenses for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019. The Company recorded a gross deferred tax asset of $30 million and $5 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, relating to the activities of its TRSs. Of these amounts, the amount related to cumulative net operating losses was $25 million and $22 thousand as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and the amount related to losses which were disallowed under Code Section 267(a) was $4 1 30 million and $5 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
The Company’s effective tax rate differs from its combined U.S. federal, state and city corporate statutory tax rate primarily due to the deduction of dividend distributions required to be paid under Code Section 857(a).
The Company’s U.S. federal, state and local tax returns for the tax years ending on or after December 31, 2017 remain open for examination.
15. Credit Risk and Interest Rate Risk
The Company’s primary components of market risk are credit risk and interest rate risk. The Company is subject to interest rate risk in connection with its investments in Agency MBS and Non-Agency RMBS, residential mortgage loans, borrowings under secured financing agreements and securitized debt. When the Company assumes interest rate risk, it attempts to minimize interest rate risk through asset selection, hedging and matching the income earned on mortgage assets with the cost of related financing.
The Company attempts to minimize credit risk through due diligence, asset selection and portfolio monitoring. The Company has established a whole loan target market including qualified mortgages, non-qualified mortgages and reperforming loans, compliance with regulatory requirements, geographic diversification, owner-occupied property, and moderate loan-to-value ratios. These factors are considered to be important indicators of credit risk.
By using derivative instruments and secured financing agreements, the Company is exposed to counterparty credit risk if counterparties to the contracts do not perform as expected. If a counterparty fails to perform on a derivative hedging instrument, the Company’s counterparty credit risk is equal to the amount reported as a derivative asset on its balance sheet to the extent that amount exceeds collateral obtained from the counterparty or, if in a net liability position, the extent to which collateral posted exceeds the liability to the counterparty. The amounts reported as a derivative asset/(liability) are derivative contracts in a gain/(loss) position, and to the extent subject to master netting arrangements, net of derivatives in a loss/(gain) position with the same counterparty and collateral received/(pledged). If the counterparty fails to perform on a secured financing agreement, the Company is exposed to a loss to the extent that the fair value of collateral pledged exceeds the liability to the counterparty. The Company attempts to minimize counterparty credit risk by evaluating and monitoring the counterparty’s credit, executing master netting arrangements and obtaining collateral, and executing contracts and agreements with multiple counterparties to reduce exposure to a single counterparty.
Our secured financing agreements and derivative transactions are governed by underlying agreements that provide for a right of setoff under master netting arrangements, including in the event of default or in the event of bankruptcy of either party to the transactions. The Company presents its assets and liabilities subject to such arrangements on a net basis in our consolidated statements of financial condition. As of December 31, 2020, the Company is not a party to any derivative instrument and not subject to this risk.
134
The following table presents information about our liabilities that are subject to such arrangements and can potentially be offset on our consolidated statements of financial condition as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
| December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Amounts of Recognized Assets (Liabilities) | Gross Amounts Offset in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position | Net Amounts Offset in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position | Gross Amounts Not Offset with Financial Assets (Liabilities) in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position | |||||||||||||||||
| Financial Instruments |
Cash Collateral (Received) Pledged (1)
|
Net Amount | ||||||||||||||||||
| Secured Financing Agreements | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
(1) Included in other assets
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Amounts of Recognized Assets (Liabilities) | Gross Amounts Offset in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position | Net Amounts Offset in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position | Gross Amounts Not Offset with Financial Assets (Liabilities) in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position | |||||||||||||||||
| Financial Instruments |
Cash Collateral (Received) Pledged (1)
|
Net Amount | ||||||||||||||||||
| Secured Financing Agreements | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps - Gross Assets | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps - Gross Liabilities | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury Futures - Gross Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury Futures - Gross Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
(1) Included in other assets
16. Commitments and Contingencies
From time to time, the Company may become involved in various claims and legal actions arising in the ordinary course of business. In connection with certain securitization transactions engaged in by the Company, it has the obligation under certain circumstances to repurchase assets from the VIE upon breach of certain representations and warranties.
The Company has made a $150 million capital commitment to Hains Point, LLC (Hains Point), a fund which is consolidated by the Company as the sole investor in the fund. As of December 31, 2020, the Company has funded $124 million towards that commitment. Capital calls for investments made in Hains Point are subject to our consent and approval.
The Company issued Warrants to purchase 20.3 million shares of the Company’s common stock. See Note 11 for further discussion. At exercise, the Company will deliver 20.3 million common shares or cash at a price per share equal to 90 % of the fair market value of the Company’s common stock at the time of exercise. This commitment is not reflected in the Company’s issued and outstanding shares.
17. Subsequent Events
18. Summarized Quarterly Results (Unaudited)
135
| For the Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | September 30, 2020 | June 30, 2020 | March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||
| Net Interest Income: | ||||||||||||||
| Interest income | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | ||||||||||||||
| Net interest income | ||||||||||||||
| Increase/(decrease) in provision for credit losses | ( |
( |
||||||||||||
| Net gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
|||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value | ( |
( |
||||||||||||
| Net realized gains (losses) on sales of investments | ( |
|||||||||||||
| Gain (loss) on Extinguishment of Debt | ( |
|||||||||||||
| Total other expenses | ||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
||||||||
| Dividend on preferred stock | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common shareholders | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
||||||||
| Net income per common share-basic | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
||||||||
The following is a presentation of the results of operations for the quarters ended December 31, 2019, September 30, 2019, June 30, 2019 and March 31, 2019.
| For the Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | September 30, 2019 | June 30, 2019 | March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||
| Net Interest Income: | ||||||||||||||
| Interest income | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | ||||||||||||||
| Net interest income | ||||||||||||||
| Net other-than-temporary credit impairment losses | ( |
|||||||||||||
| Net gains (losses) on derivatives | ( |
( |
( |
|||||||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments at fair value | ( |
|||||||||||||
| Net realized gains (losses) on sales of investments | ( |
|||||||||||||
| Gain (loss) on Extinguishment of Debt | ( |
|||||||||||||
| Total other expenses | ||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Dividend on preferred stock | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common shareholders | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Net income per common share-basic | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
136
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the city of New York, State of New York.
| CHIMERA INVESTMENT CORPORATION | |||||||||||
| Date: February 18, 2021 | By: | /s/ Mohit Marria | |||||||||
| Mohit Marria Chief Executive Officer |
|||||||||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the date indicated.
137
| Signatures | Title | Date | |||||||||
| /s/ Mohit Marria | Chief Executive Officer, Chief Investment Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) |
February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Mohit Marria | |||||||||||
| /s/ Rob Colligan | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Rob Colligan | |||||||||||
| /s/ Choudhary Yarlagadda | President, Chief Operating Officer and Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Choudhary Yarlagadda | |||||||||||
| /s/ Mark Abrams | Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Mark Abrams | |||||||||||
| /s/ Paul Donlin | Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Paul Donlin | |||||||||||
| /s/ Gerard Creagh | Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Gerard Creagh | |||||||||||
| /s/ Dennis Mahoney | Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Dennis Mahoney | |||||||||||
| /s/ John P. Reilly | Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| John P. Reilly | |||||||||||
| /s/ Teresa Bryce Bazemore | Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Teresa Bryce Bazemore | |||||||||||
| /s/ Debra Still | Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Debra Still | |||||||||||
| /s/ Brian Patrick Reilly | Director | February 18, 2021 | |||||||||
| Brian Patrick Reilly | |||||||||||
138